IT Resilience: Ensuring Business Continuity during Disruptions

Resiliency and continuous availability are crucial for businesses to maintain uninterrupted operations in the face of disruptions. IT resilience ensures data protection and governance.
With businesses heavily reliant on IT systems for critical functions, ensuring business and tech resilience is crucial to minimize the impact of unplanned disruptions. Any downtime or data loss can have severe consequences on continuous availability.
By ensuring continuous availability and IT resilience, businesses can minimize downtime and protect against unplanned disruptions while maintaining productivity and protecting workloads. This includes the ability to quickly and seamlessly move workloads as needed.
Below, we delve into the key components of resilient IT infrastructure and discuss strategies for building a resilient IT environment.
On this page:
- What is IT Resilience?
- Importance of IT resilience in the digital age
- Defining IT resilience
- Key components of an effective IT resilience strategy
- Strategies for achieving IT resilience
- Real-world examples of successful IT resilience implementation
- Comparing IT resilience with high availability and disaster recovery
- The significance of prioritizing IT resilience
- IT Resilience: Frequently Asked Questions
What is IT Resilience?
IT resilience is the ability to handle any disruption to mitigate the risk of downtime and focus on more critical tasks. IT resilience is built through a set of tools and applications that automatically protect data from issues.
Disruptions can manifest in the form of natural disasters, planned attacks, and misconfiguration. IT resilience makes the organization prepared for planned and unplanned disruptions to ensure the business keeps moving forward. It also accelerates transformation within the business by allowing you to adapt to changes to prevent disasters.
An organization can maintain acceptable service levels beyond disruptions to its IT systems and processes with a solid IT resilience strategy.
The organization can focus on recovery, awareness, review, protection, and improvement to minimize disruptions to IT services, which can be highly expensive to the entity in this competitive business environment.

Importance of IT resilience in the digital age
In today’s digital age, businesses rely on technology to drive operations and stay competitive.
This digital transformation brings numerous benefits, such as increased efficiency, improved customer experience, enhanced productivity, and technology implementation.
However, it also introduces new challenges and risks that organizations must navigate.
Digital Transformation Increases Reliance on Technology
Digital transformation has revolutionized how businesses operate by leveraging technologies to streamline processes, automate tasks, and enhance communication.
Organizations are embracing these advancements, from cloud computing and mobility solutions to data analytics and artificial intelligence, to gain a competitive edge.
However, this heavy reliance on technology also means that any disruption or failure in IT systems can have severe consequences for businesses.
Whether it’s a cyber attack, hardware failure, or software glitch, companies must be prepared for potential disruptions that could halt their operations.
With the increasing threat of cyber attacks and the possibility of hardware failure or software glitches, companies must have a robust system to mitigate these risks.
RELATED: Navigating DX: Examples of Digital Transformation Successes
Cyber Threats Pose Significant Risks to Businesses
The rise of cyber threats in recent years has made IT resilience even more crucial for organizations.
Hackers are constantly evolving their tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in networks and systems.
A successful cyber attack can lead to data breaches, financial losses due to ransomware attacks, or theft of sensitive information.
To mitigate these risks, businesses must implement robust cybersecurity measures while also having mechanisms to recover from an attack quickly. IT resilience is critical in ensuring organizations can detect breaches promptly, respond effectively, and restore operations swiftly.
Unplanned Outages Can Result in Financial Losses and Reputational Damage
Unplanned outages can occur for various reasons, such as power failures, network disruptions, or natural disasters.
These outages disrupt business continuity and result in financial losses due to downtime and reputational damage.
For example:
-
A retail website experiencing an outage during peak shopping season may lose significant revenue.
-
An online banking platform facing prolonged downtime may erode customer trust and loyalty.
IT resilience enables organizations to minimize the impact of these outages by implementing strategies such as backup systems, disaster recovery plans, and redundant infrastructure.
These measures ensure businesses can quickly recover from disruptions, minimizing financial losses and preserving their reputation.
IT Resilience Enables Organizations to Adapt and Thrive
In a rapidly changing technological landscape, IT resilience is essential for organizations to adapt and thrive.
It allows businesses to embrace new technologies, such as cloud computing and agile development methodologies, without compromising their operations or security.
By building resilient IT systems, organizations can leverage the benefits of digital transformation while mitigating its associated risks.
This resilience empowers companies to innovate, scale their operations, and meet evolving customer demands effectively.
Defining IT resilience
IT resilience is a crucial aspect of modern technology systems. It refers to the ability of these systems to withstand disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted service delivery during adverse events.
Let’s delve into IT resilience and why it is so important.
Ability to Withstand Disruptions
At its core, IT resilience involves the capacity of systems to endure and recover from incidents that could disrupt normal operations.
This includes proactive measures taken to prevent such disruptions and reactive strategies for responding and recovering when they occur.
Proactive Measures
To achieve IT resilience, organizations must take proactive steps to minimize the impact of potential disruptions.
This can involve implementing redundancy measures, such as backup systems or data replication, to ensure critical information is always available, even if one component fails.
Regular system maintenance and updates are also essential in preventing vulnerabilities that cyber threats could exploit.
Response and Recovery
Despite preventive measures, incidents may still occur. In such cases, organizations need well-defined response plans in place.
These plans outline clear steps for identifying and mitigating the impact of disruptions on the system. They also include procedures for restoring normal operations as quickly as possible.
Technical and Organizational Aspects
IT resilience encompasses both technical and organizational aspects. On the technical side, it involves designing systems with built-in redundancy, failover mechanisms, and robust security measures.
Organizations must also consider network infrastructure, hardware reliability, and software compatibility factors.
However, it’s not just about technology; organizational aspects are equally important. This includes having skilled personnel who can effectively respond to incidents and manage recovery processes.
It also involves establishing communication channels within the organization so all stakeholders know their roles during an incident.
Importance of Uninterrupted Service Delivery
The ultimate goal of IT resilience is to ensure uninterrupted service delivery, even in the face of disruptions or incidents. Any downtime or service interruption can result in significant financial losses, damage to reputation, and customer dissatisfaction.
By investing in IT resilience, organizations can minimize the impact of disruptions and maintain business continuity.
This helps protect revenue streams and safeguards customer trust and loyalty. In a highly competitive market, businesses that can quickly recover from incidents and continue providing reliable services gain a distinct advantage over their competitors.
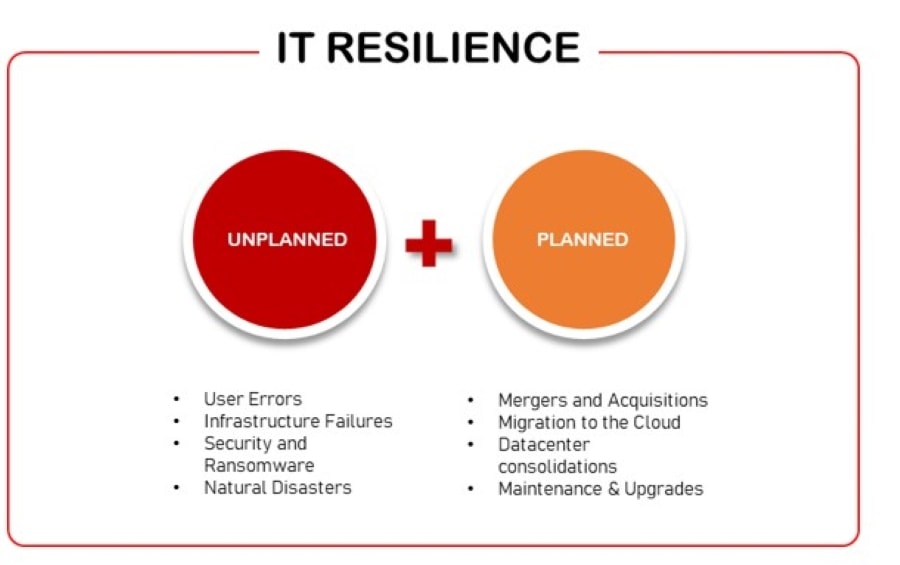
Key components of an effective IT resilience strategy
Robust backup and recovery mechanisms for data protection
One crucial component of an effective IT resilience strategy is the implementation of robust backup and recovery mechanisms.
These mechanisms protect valuable data in case of unexpected incidents or system failures.
By regularly backing up data and having a well-defined recovery process, organizations can minimize the risk of data loss and maintain business continuity.
Pros:
-
Provides a safety net against accidental deletion, hardware failures, or cyberattacks.
-
Enables quick restoration of critical data, minimizing downtime.
-
Offers peace of mind, knowing that important information is safeguarded.
Cons:
-
Requires additional storage space and resources to store backups.
-
Backup processes may impact system performance during peak usage times.
-
Inadequate backup strategies may result in incomplete or corrupted backups.
RELATED: Creating an Effective Data Backup Strategy
Redundancy in hardware, software, and network infrastructure for enhanced reliability
To build resilience in IT operations, redundancy plays a vital role. Redundancy involves duplicating critical components such as hardware, software, and network infrastructure to ensure reliable functioning even if one component fails.
By implementing redundancy measures, organizations can reduce single points of failure and mitigate the impact of potential disruptions.
Pros:
-
Enhances system availability by providing backup options when primary components fail.
-
Minimizes service interruptions by switching seamlessly to redundant components.
-
Increases overall system reliability by distributing workloads across multiple resources.
Cons:
-
Requires additional investment in duplicate equipment or infrastructure.
-
May increase complexity in managing multiple redundant systems.
-
Inefficient redundancy implementations can lead to increased maintenance efforts.
RELATED: Uptime vs. Availability: What they measure, and how they differ
Continuous monitoring to identify vulnerabilities and potential failures
Continuous monitoring is an essential aspect of an effective IT resilience strategy.
It involves actively monitoring systems, networks, applications, and security measures to identify vulnerabilities or potential failures before they escalate into significant issues.
By proactively identifying and addressing these weaknesses, organizations can prevent or minimize the impact of disruptions.
Pros:
-
Enables early detection of potential threats or vulnerabilities.
-
Facilitates prompt response and mitigation actions to prevent system failures.
-
Provides insights for ongoing improvement and optimization of IT infrastructure.
Cons:
-
Requires dedicated resources and tools for continuous monitoring.
-
Monitoring processes may generate a significant amount of data that needs analysis.
-
Inadequate monitoring strategies may result in missed alerts or false positives.
RELATED: Continuous Security Monitoring (CSM): What is it, & How does it help improve my Cyber Defenses?
Regular testing and updating of disaster recovery plans for readiness
Regular testing and updating disaster recovery plans are crucial to an effective IT resilience strategy.
Organizations need to periodically assess the effectiveness of their plans by conducting simulated scenarios to ensure readiness in the event of a disaster.
By identifying gaps or weaknesses through testing, organizations can refine their plans and improve their ability to recover quickly.
Pros:
-
Validates the effectiveness of existing disaster recovery plans.
-
Identifies areas for improvement and allows for plan updates.
-
Builds confidence among stakeholders that systems can be restored successfully.
Cons:
-
Testing procedures may disrupt normal operations temporarily.
-
Requires coordination among various teams involved in the testing process.
-
Ineffective testing methods may not accurately reflect real-world scenarios.
RELATED: Disaster Recovery and Cybersecurity: Integrating Cyber Security and Business Continuity
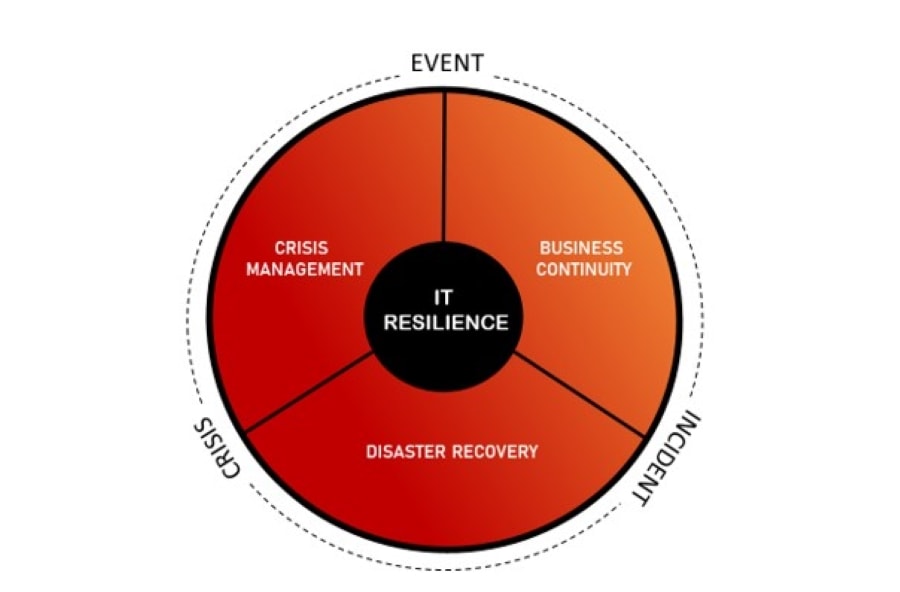
Strategies for achieving IT resilience
Implementing Cloud-Based Solutions
One effective strategy for achieving IT resilience is by implementing cloud-based solutions. Organizations can reduce their dependency on physical infrastructure by moving critical systems and data to the cloud.
This minimizes the risk of hardware failures and provides greater flexibility and scalability.
With cloud solutions, organizations can quickly scale up or down based on their needs, ensuring that they are well-prepared to handle any unexpected surges in demand or sudden changes in business requirements.
RELATED: Using Cloud Computing to achieve Business Continuity
Embracing Virtualization
Another key strategy for IT resilience is embracing virtualization. Virtualization allows organizations to create virtual versions of their physical infrastructure, including servers, storage devices, and networks.
This enables them to quickly recover from system failures by restoring operations on alternate virtual machines.
Virtualization improves flexibility by enabling organizations to easily migrate workloads between physical servers without disrupting services. It also enhances scalability by allowing resources to be dynamically allocated based on demand.
RELATED: What is Virtual Infrastructure?
Automation for Streamlined Processes
Automation plays a crucial role in achieving IT resilience by streamlining processes and reducing the risk of human error.
By automating routine tasks and workflows, organizations can ensure consistent execution while minimizing the chances of manual mistakes that could lead to system failures or downtime.
Automation also enables faster response times during incidents, eliminating the need for manual intervention in remediation efforts. Organizations can improve operational efficiency and enhance overall resiliency by implementing automation practices.
RELATED: IT Operations Automation: What are the Benefits of automation in information technology?
Establishing Strong Partnerships with Reliable Vendors
Establishing strong partnerships with reliable vendors is another essential aspect of building IT resilience.
Working closely with trusted vendors ensures access to robust support services and products designed specifically for maintaining high levels of resilience.
These vendors often provide comprehensive playbooks and guidelines that help organizations develop effective strategies for mitigating potential risks and responding swiftly in case of failure events.
By leveraging the expertise of these vendors, organizations can strengthen their IT resilience and effectively navigate challenging situations.
RELATED: Supplier Management Best Practices
Real-world examples of successful IT resilience implementation
Netflix utilizes a distributed architecture that allows seamless streaming even during server failures
Netflix is a prime example of a company successfully implementing IT resilience. With millions of users streaming content simultaneously, Netflix must maintain uninterrupted service delivery. To achieve this, Netflix has adopted a distributed architecture approach.
By distributing its servers across various locations, Netflix ensures that redundant servers can handle user requests seamlessly, even if one server fails.
This means minimal disruption during server failures and uninterrupted streaming for its customers.
Key Takeaways Netflix’s IT resilience implementation:
-
Continuous service availability: By leveraging a distributed architecture, Netflix minimizes the impact of any single point of failure. Users can enjoy uninterrupted streaming regardless of any localized server issues.
-
Improved user experience: Maintaining seamless streaming despite server failures enhances the user experience. Customers do not face buffering or downtime issues, which leads to higher customer satisfaction and retention rates.
-
Global scalability: The distributed nature of Netflix’s infrastructure allows them to scale their services globally without compromising performance or availability.
-
Increased reliability: By leveraging multiple data centers across different regions, Netflix ensures customers have uninterrupted access to their platform. This enhances reliability and minimizes downtime risks.
Delta Airlines implemented a comprehensive backup system after a major outage caused flight cancellations
Delta Airlines experienced a major IT outage in 2016, resulting in widespread flight cancellations and delays.
This incident highlighted the importance of IT resilience for critical operations in the airline industry. In response, Delta Airlines implemented a comprehensive backup system to prevent similar disruptions in the future.
The backup system employed by Delta Airlines includes redundant servers, data replication, and failover mechanisms. These measures ensure that critical systems remain operational despite an issue with the primary infrastructure.
As a result, Delta Airlines can quickly recover from any IT failures and continue providing reliable services to its passengers.
Key Takeaways from Delta Airlines’ IT resilience implementation:
-
Minimized service disruptions: With a robust backup system, Delta Airlines can swiftly recover from any IT failures and minimize the impact on flight schedules. This leads to fewer flight cancellations and delays, improving customer satisfaction.
-
Enhanced operational efficiency: The comprehensive backup system enables Delta Airlines to maintain smooth operations even during unexpected events. This allows them to manage their resources and provide consistent service quality efficiently.
Comparing IT resilience with high availability and disaster recovery
High availability, disaster recovery, and IT resilience are all critical components of ensuring the smooth operation of an organization’s IT infrastructure.
While they share similarities, each concept has its unique focus and purpose. Let’s take a closer look at how these three concepts compare.
High Availability: Minimizing Downtime through Redundancy and Fault-Tolerant Systems
High availability is all about minimizing downtime and ensuring that systems remain accessible to users. It focuses on redundancy and fault-tolerant systems to achieve this goal.
By implementing failover clustering, organizations can seamlessly switch from one system or server to another in the event of a failure, thereby reducing user impact.
Pros:
-
Provides continuous availability for critical applications.
-
Minimizes disruption to business operations.
-
Ensures acceptable service levels for users.
Cons:
-
May require additional hardware or infrastructure investment.
-
Can be complex to set up and maintain.
-
Does not address data loss or catastrophic events.
Disaster Recovery: Recovering from Catastrophic Events and Restoring Operations
On the other hand, disaster recovery is focused on recovering from catastrophic events such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or hardware failures.
Its primary objective is to restore operations as quickly as possible after a disruption occurs. This typically involves having backup systems in place along with well-defined recovery plans.
Pros:
-
Enables organizations to recover from major disruptions.
-
Protects against data loss by regularly backing up critical information.
-
Provides peace of mind knowing that there is a plan for worst-case scenarios.
Cons:
-
Recovery time may vary depending on the scale of the disaster.
-
Requires regular testing and updating of recovery plans.
-
May involve significant costs for maintaining backup systems and offsite storage facilities.
IT Resilience: Ensuring Continuity in the Face of Disruptions
IT resilience encompasses both high availability and disaster recovery strategies. However, it goes beyond mere uptime and data recovery.
IT resilience ensures continuity in various disruptions, whether small-scale incidents or large-scale disasters.
It involves a comprehensive approach that includes technical solutions, processes, people, and communication.
Pros:
-
Provides a holistic approach to business continuity.
-
Reduces the impact of disruptions on operations.
-
Enables organizations to adapt and recover quickly from unexpected events.
Cons:
-
Requires careful planning and coordination across different teams.
-
Can be resource-intensive to implement and maintain.
-
Relies on effective communication and collaboration between IT and other departments.
The significance of prioritizing IT resilience
With the increasing reliance on technology for business operations, organizations must ensure their IT systems can withstand disruptions and quickly recover from potential failures.
IT resilience refers to the ability of an organization’s IT infrastructure to adapt, respond, and recover from unexpected events or disasters while maintaining its critical functions.
With an effective IT resilience strategy organizations can minimize downtime, mitigate financial losses, protect sensitive data, maintain customer trust, and safeguard their overall business continuity by implementing these components.
Organizations can position themselves at the forefront of technological advancements and ensure their long-term success by adopting a detail-oriented approach to building a resilient IT infrastructure and staying informed about emerging trends.
IT Resilience: Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common challenges in achieving IT resilience?
Achieving IT resilience can come with its fair share of challenges.
Some common obstacles include insufficient budget allocation for necessary technologies or resources, lack of executive buy-in or support for implementing resilient strategies, difficulty identifying critical applications or systems that require immediate attention during disruptions, and limited expertise or knowledge regarding best practices in building resilient architectures.
How does IT resilience differ from high availability?
While both concepts aim to minimize downtime and ensure business continuity during disruptions or failures, they differ.
High availability minimizes planned downtime by providing redundant systems to take over if one fails immediately. On the other hand, IT resilience encompasses high availability. It emphasizes rapid recovery after unplanned events such as natural disasters or cyberattacks.
IT resilience takes a holistic approach to ensure that the entire IT infrastructure can adapt and recover from various disruptions.
What role does data backup play in IT resilience?
Data backup is a crucial component of IT resilience. Regularly backing up critical data ensures that organizations can restore their systems and resume operations swiftly, even if an unexpected event occurs.
Backups should be performed regularly, ideally with multiple copies stored in different locations, to protect against physical damage or loss. Testing the backup process is also essential to verify its effectiveness and identify any potential issues before they become problematic.
Can cloud computing enhance IT resilience?
Yes, cloud computing can enhance IT resilience by providing scalable and flexible infrastructure that can quickly adapt to changing demands or recover from failures.
Cloud-based solutions often include built-in redundancy, automated backups, and disaster recovery capabilities, making them an attractive option for organizations aiming to improve their resilience.
By leveraging the cloud’s resources, organizations can reduce the burden on their infrastructure and take advantage of the advanced technologies cloud service providers offer.
How often should an organization test its IT resilience strategy?
Regular testing is vital to ensure the effectiveness of an organization’s IT resilience strategy. The testing frequency may vary depending on factors such as industry regulations, business requirements, and the systems’ complexity.
However, conducting tests at least annually or whenever significant changes occur within the IT environment (e.g., system upgrades or architectural modifications) is generally recommended. Testing helps identify vulnerabilities or gaps in the strategy.
It allows organizations to refine their processes for optimal performance during real-world disruptions.

