IP Telephony: A Guide for Business Users

You may be considering replacing your existing office phones with a modern phone system more suited to your business needs. When researching for a phone system for your business, you are likely to find the market dominated by IP telephony systems.
But what is IP telephony? How does it work? And what benefits does it provide to your business? Below, we answer these and other frequently asked questions, making this article an indispensable guide for business users seeking to understand IP telephony better.
On this page:
What is IP Telephony?
IP telephony, also referred to as VoIP and Internet Telephony, uses Voice over IP (VoIP) technologies to transmit and receive telephone calls via the internet instead of the traditional PSTN (public switched telephone network).
IP telephony systems comprise of three crucial components which allow voice signal to be sent and received:
-
IP phones – Convert analog voice signals to digital data
-
Local Area Network (LAN) – Which acts as the connector and transport mechanism for the entire IP phone system
-
IP-PBX – Manages your IP phones call control and connection to voice services.
Related: What is a PBX?
An IP telephony installation can include any combination of IP enabled physical phones (such as desk, cordless, and conference phones), softphones, mobile applications, and browser-based call management software.
Chances are you already have used IP telephony when making phone calls on popular applications such as Skype or Whatsapp. These applications connect through your local internet connection, Wi-Fi or 4G (or LTE), instead of a traditional phone line, to enable VoIP calls.
Key Features of IP Telephony Systems
You need to consider the features given below:
-
Voicemail – When an employee can take a call, call forwarding and voicemails become handy. Ensure that the IP telephony provider allows callers to leave voice messages. Moreover, check that they offer a voicemail to email services. In this way, you can follow up on the missed calls.
-
Call Recordings – If your industry is heavily regulated, you’ll need call recording. This feature can help train sales representatives and improve customer experience. Moreover, you can use these recorded calls as real-life examples.
-
Auto Attendant – Another essential feature of IP telephony. It welcomes every caller with a greeting message and routes them to the concerned person. It provides a pleasant and fast customer experience.
-
Caller ID – You can change your caller ID and add a phone number and business name before making an outgoing call.
-
Audio and Video Conferencing – Do you need multiple people on the same call? IP telephony provides you with a robust feature of audio and video conferencing.
-
Security – When you opt for an IP telephony system, you prefer the lowest cost IP telephony provider. While doing this, you often ignore safety. It would be great if your vendor offers end-to-end encryption. Moreover, don’t forget to ask about the accreditations of vendors. How they handle security protocols internally and identify and mitigate potential threats.
IP telephony is feature-rich and allows your business to decrease costs. But what makes IP telephony different from traditional business telephone systems?
How do IP Telephony differ from traditional PSTN?
PSTNs (Public Switched Telephone Network) use circuit switching technology, a concept used by telephone networks for more than 100 years.
In circuit switching, the connection is maintained in both directions for the duration of the call between two parties, thereby creating a circuit.
IP telephony use packet switching technology, the same method used to transfer all other information over the internet.
Rather than sending information in one large chunk, packet switching enables data to be separated into many small “packets”. Each of these packets travels independently over the internet and theoretically on a different route from other packets. These packets are reassembled into the original information as they arrive at the destination.
By using packet switching rather than circuit switching, IP telephony can utilize existing internet connections. By doing so, IP telephony is revolutionary and is likely to rework global phone systems completely.
How does IP Telephony work?
IP telephony works by converting analogue voice signals into digital data and then transmitting that data using packet-switching technology. In simple terms, your voice is converted into digital data and sent via the internet to make phone calls.
To enable this ability, IP telephony addresses three fundamental problems:
-
Call Signalling – Alerting the recipient that you want to call them
-
Call Transmission – Converting your voice into digital data to be sent over the internet (and receiving in the opposite direction)
-
Interfacing with the ordinary telephone network (PSTN) – If your call is going to a traditional landline phone or cellphone (mobile phone)
Call Signalling
Internet telephony allows individuals to have unique telephone numbers not permanently linked to a single physical location. Consequently, the recipient could be anywhere on the planet and may not be in the same place two days consecutively.
To make a VoIP call, your phone system must locate the receiver on the internet and signal the receiving phone system to accept a call. Once that’s done, the two computers agree on how they will exchange the data.
For VoIP to work effectively, the above process is governed by protocols. These protocols set up a communication route between two IP addresses (the sender’s and the receiver’s) to allow telephone call data to be sent and received.
The two protocols that cover signalling are SIP (Session Initiation Protocol, sometimes also known as RFC 4168) and H.323.

Call Transmission
A person’s voice has to be converted from analog to digital to allow the transmission and receiving of telephone calls over the internet. The technology to achieve this has been around for many years, such as CDs or MP3s.
The software that converts analog audio into digital data and back again is known as a CODEC (Coder-Decoder).
Once the voice has to be converted from analog to digital, it can be transmitted like any other data packet over the internet.
For VoIP, the data-sending protocol used is RTP (real-time protocol), typically used with SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), which establishes connections across the network.

Interfacing with PSTNs
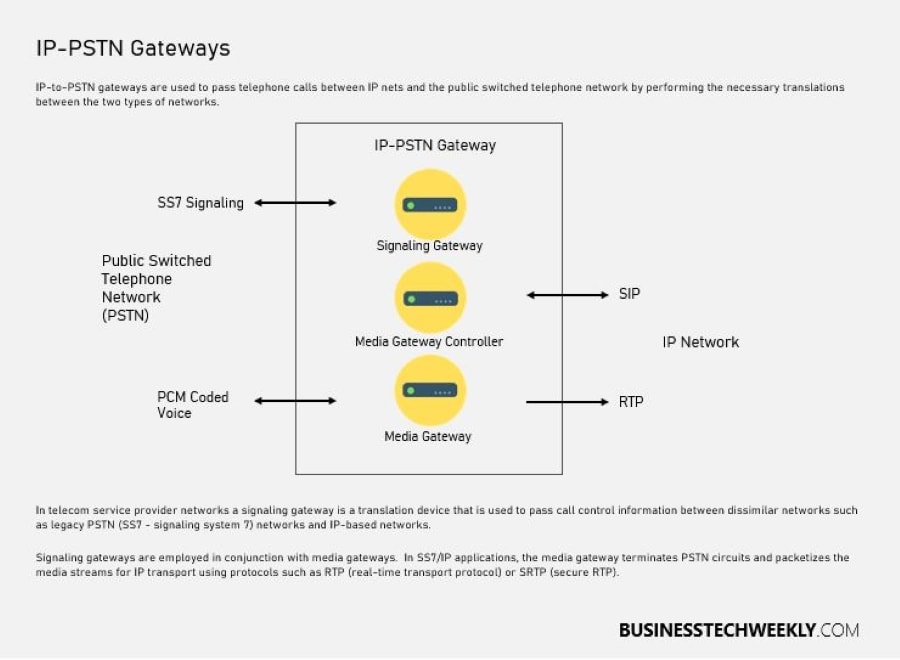
Making a telephone call from an IP telephony system to a Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) is a complex process since voice data needs to be translated from one network to another.
What enables this is an extra piece of equipment called an IP-to-PSTN gateway, often part of the telecoms provider’s infrastructure, which creates a bridge between the internet and the PSTN networks.
IP-to-PSTN gateways are used to pass telephone calls between IP networks and the public switched telephone network, by performing the necessary translations between the two types of networks.
Installing IP Telephony for your Business
When installing a Voice over IP (VoIP) telephone system for your business, you will need to engage with a VoIP service provider.
The level of engagement will be dependent on several factors depending on your business needs but are primarily driven by the type of deployment you choose. Generally, there are two options from which you can select – Hosted or On-Premise:
-
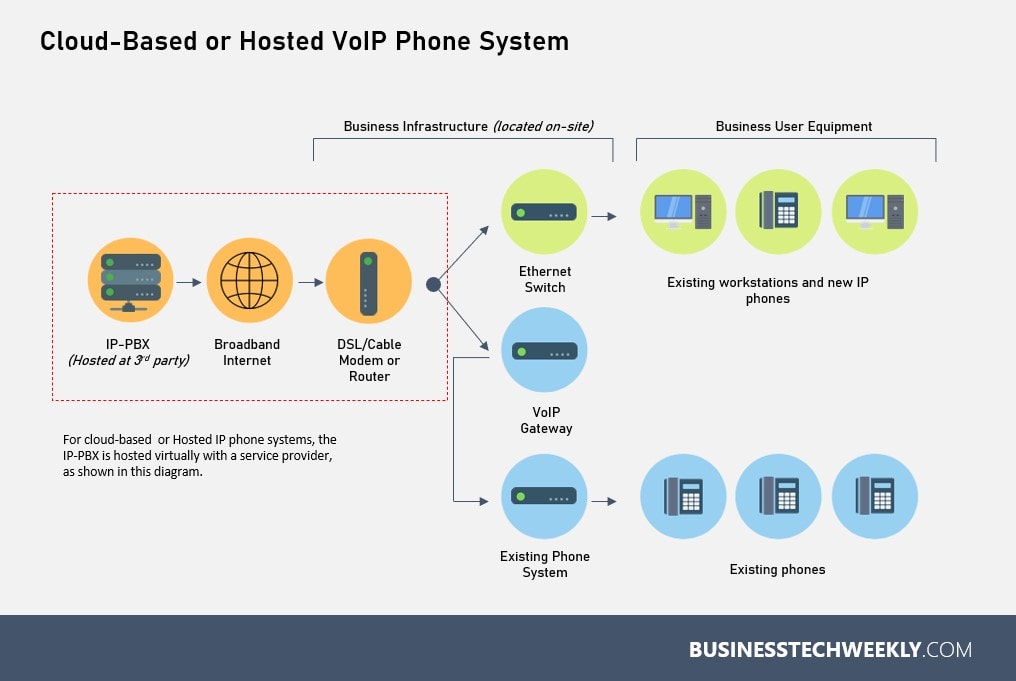
Hosted – Either as a Cloud service, managed and operated by a VoIP service provider and typically offered as subscription-based service. Only IP handsets are located in the business office(s). These connect to your VoIP provider via your internet connection.
-
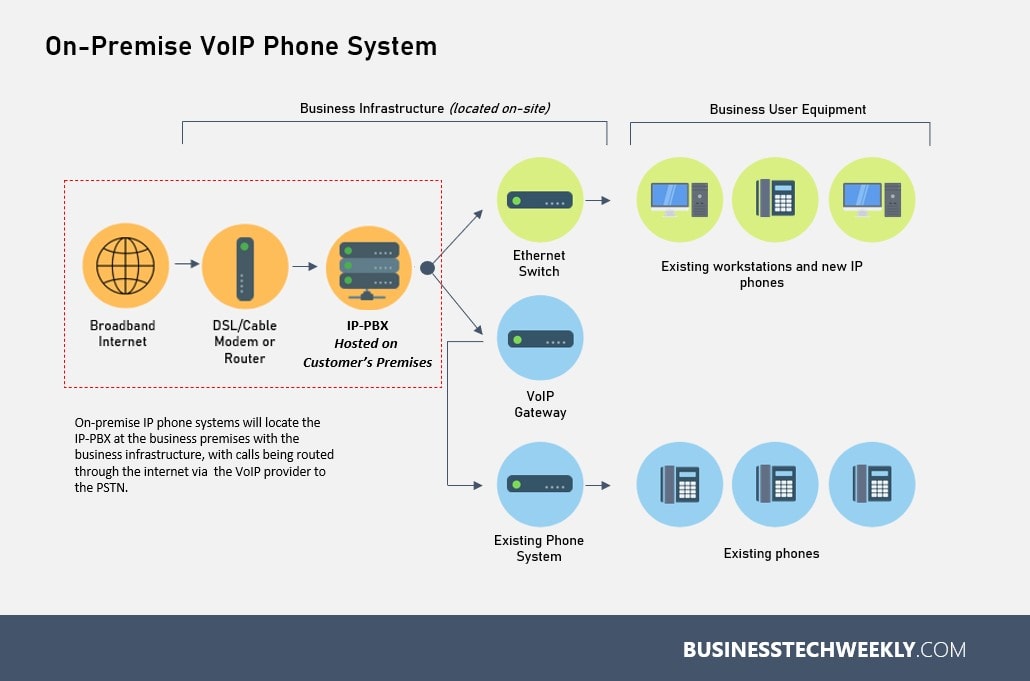
On-Premise – Often shortened to “on-prem”, this is a dedicated telephone system, with the hardware and components that power and manage your phone system kept on-site in your office. The system is connected to your VoIP provider via the internet.
To install your VoIP system, you’ll need to have the right equipment. Explained below are some of the components that make up a typical IP telephony system.
IP Telephony Components
A typical Voice of IP (VoIP) phone system will comprise of several components:
-
IP-PBX – Also known as a virtual PBX (Private Branch Exchange). It’s a cloud-based server that virtually manages incoming calls and transmits the audio file. You only need to have a cloud-hosted server to receive and make calls by using the internet.
-
Analog Telephone Adaptor (ATA) – A device that converts analog signals to digital data to be transferred over the internet. ATA adaptors are used to connect your existing traditional analog phones to your network (LAN).
-
SIP Trunks – SIP trunking is a dedicated internet connection to carry your voice data. It prevents your existing internet connection from being over-burdened. SIP trunks connect your IP-PBX to your VoIP service provider and are typically used in an On-Premise IP deployment model.
-
IP Phones – Available in either software and hardware form. Also known as VoIP or SIP phones, these devices enable business users to make and receive calls. Physical IP phones resemble traditional phones and come with all the hardware and software needed to connect to your IP phone system.
Types of IP phones
It’s worth looking at the different types of phones available. IP phones are available in four primary forms, desk, wireless, software and conferencing:
-
IP Desk Phones– VoIP desk phones look like traditional desk phones with a handset/receiver wired to a base with a keypad. Most modern VoIP desk phones are Powered over Ethernet (PoE). They can be used with either an optional headset or the built-in wired receiver.
-
Wireless VoIP Phones – Wireless IP phones can be either Wi-Fi or DECT and connect to a wireless access point (Wi-Fi) or ethernet connected base station (DECT). Wireless phones enable users to move around their office space while on a call.
-
Softphones – Softphones are a software application installed on a desktop computer, laptop or mobile device. These enable the device to make and receive calls. Softphones are typically used with a headset and are cost-effective for remote workers.
-
Conferencing VoIP Phones – A IP conference phone will usually function in the same way as an analog conferencing phone. These are typically be used where multiple participants are attending a call.
IP telephony offers a workable and practical solution for many businesses, which require a fast, reliable and high-quality communications system.
With an understanding of the components, the next step is to compare IP telephony deployment models.
IP Telephony Deployment Models: Hosted vs On-Premise
IP Telephony is usually deployed in one of two ways, either on-premises or hosted (cloud-based).
While both operate a Private Branch Exchange (PBX), each approach has its advantages and disadvantages depending on your business needs.
Hosted & Cloud IP Phone Systems
A hosted IP PBX, also referred to as a virtual PBX or internet telephony, is an IP telephony system where the phone system’s actual hardware resides at an off-site location. The users access the systems via the internet.
Usually, a third-party company VoIP service provider is responsible for the setup and maintenance of the IP-PBX system.
Hosted VoIP Systems – Pros and Cons
Some of the advantages and disadvantages of Hosted IP telephony systems are:
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
On-Premise IP Telephony Systems
In an On-premise IP PBX, all the hardware and component required to make VoIP calls is located in the same location as it is being used. If available, most businesses have a designated server room in which they locate their telecommunications equipment. Calls are made from IP phones connected to a PBX (or IP-PBX server) using a LAN connection.
On-Premise VoIP Systems – Pros and Cons
The advantages and disadvantages offered by On-Premise IP telephony systems include:
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IP Telephony: Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between VoIP vs Internet Telephony vs IP Telephony vs Hosted PBX phones vs Hybrid PBX vs Cloud telephony?
Essentially, they all generally refer to the provision of telephony services over an internet connection.
“VoIP” (Voice service over an IP network) and “Internet Telephony” are the general terms used to describe making phone calls over the internet instead of the traditional copper wire-based telephone network. IP (internet protocol) is one of the foundational protocols of data networks such as local business networks (local area networks – LAN) and the internet.
The other terms describe the manner that internet telephony can be deployed.
Cloud-based or hosted business telephone systems are hosted off-site at a VoIP service provider’s data center. In most cases, businesses pay a monthly subscription, usually per employee, to use the service.
Some organizations may already have an on-site PBX, in which case they may choose, with some integration, a hybrid solution, allowing them to use some components of cloud telephony via the existing PBX system.
How much does an IP Telephony cost?
Your business size and the deployment model you opt for will be some of the many considerations that will dictate your IP Telephony costs.
For small and medium businesses, hosted or cloud-based systems tend to be more cost-effective. These are typically offered as a monthly subscription service. Depending on the provider, this could be as low as $20 per employee per month. Costs for On-Premise IP telephony are considerably more.
Many service providers offer a range of packages according to your business needs. Typically, IP telephony system packages are divided into three tiers: Entry-Level, Mid-Range, and Enterprise Grade.
A basic system can start from as little as $20 per user per month. While features may vary between service providers, an entry-level IP telephony systems is likely to include the core features of a business telephony system, such as on-hold music and auto-attendant.
At the other end of the scale, an Enterprise level IP Telephony Systems will have several advanced features such as voicemail-to-text, recording, and voice analytics. Pricing models vary too and may depend on the organization’s exact needs and size.
You can choose any of the IP telephony system packages according to your business size and needs.
Are IP Phones Systems secure?
From a security perspective, the internet is a vulnerable place for several reasons. Any service or system which uses the internet is potentially exposed to the vulnerability posed by the internet.
Businesses considering moving to IP Telephony should take steps to ensure that their networks are adequately secured. Key areas to address are user authentication, VLAN configuration, encryption and signaling methods.
You can learn more about VoIP Security in our article, Is VoIP Secure? VoIP Security Risks, Issues & Threats.
What happens if my internet service is disrupted?
As an IP based service, internet telephony systems are dependent on an internet connection being available. If your internet service is disrupted, your IP telephony system will be too.
Larger organizations may opt for implementing redundancy and capacity in the internet telephony system by procuring SIP trunks.
On the other hand, smaller organizations may, as part of their business continuity planning (BCP), rely on accessing their VoIP lines via a mobile device such as a smartphone or laptop.
How fast does my company’s broadband connection need to be?
Wired broadband will offer you ‘real-time,’ which you will need for a IP Telephony service. You should avoid any wireless or satellite services in this case.
ADSL is regular broadband, and it offers you a contention ratio. The higher the rato, the more trouble you may have. 10:1 means you and nine others are using the service. While the ratio usually does not affect the quality of the internet, if lots of people are using the service, such as watching videos, it can affect your VoIP call quality.
On the other hand, SDSL, cable, and fiber connections do not pose such troubles but are more expensive and not available everywhere.
If ADSL is your only option, you can ask the provider if they offer the ‘Traffic Prioritization” feature. It means that when they detect a VoIP call, the call gets priority above everything else.
You can do fine with 1MB a second line for all businesses when using IP Telephony. You do not have to go for 500 MB per second offers as those can allow 50,000 IP calls simultaneously- they could not be very cost-effective for you.
If you do not throttle it with general data traffic, you do not have to upgrade your existing broadband connection.
Are IP phones systems scalable?
When selecting a commercial VoIP service provider, you should consider the price and features and determine how scalable the service is.
One of the unique selling points of VoIP is that it allows you to quickly and cheaply expand your phone system as your business evolves.
Due to the flexibility offered by IP communications, businesses can make scalable adjustments to their phone systems whenever required.
Since IP telephony systems are completely modular, you can add more phones to your system without the need for expensive engineers. In most cases, it’s as simple as buying the IP phones and plugging them into the internet.
Can I use my existing phones with VoIP?
Most likely – depending on the telephone system you currently have.
For analog phones, you may need to purchase ATAs (Analog Telephone Adaptor), which converts analog signals to digital data to be transferred over the internet.
If you already have VoIP phones, you can use these with a new IP telephone system. However, depending on the age and model of your IP phones, you may not be able to utilize all the latest VoIP features.
In case your existing phones are not ideal, there are plenty of dedicated VoIP telephones available.
One of the unique selling points of VoIP is that you don’t even need a physical phone handset. Through a softphone app, you can make and receive calls from a cell phone or even through your computer.
Top 12 tips for choosing a VoIP supplier for your business
Presented below are 12 factors for you to consider when selecting a IP Telephony supplier.
1. Price
Many VOIP providers are competing for market share, and they focus on different things. Some focus exclusively on business customers, others on consumers.
They provide deals differently. For example, you may find great monthly packages for yourself, or you could choose the Pay-As-You-Go option.
What you have to do is determine your calling patterns and times. What offers will be more beneficial for you without wasting any money? Just a few minutes of this research will save a lot of money for you.
2. Quality
When considering the VoIP providers, make sure you check the reviews of their other business customers.
VoIP providers need to make continuous capital investments, and they can offer lower prices by cutting back on such important investments. This will cause a drop in quality in dropped calls, poor sound quality, latency problems, etc.
Beware of the providers who supply the most at the lowest price. However, there are a few that buy in bulk, which helps them keep the cost low.
3. Do you get a free trial?
Having the chance to try the service for free for a while creates a good impression. Some providers offer you 30-day free trials, and others want you to commit for longer. Try to find free trials, and during the trial, figure out if the service is offering what it initially promised to offer. Is it working out for you?
4. Is it easy to use?
Some VoIP providers will make their service a bit complex to use with cryptic instructions. If your company does not have a dedicated IT department, this might be hard to deal with. But, if you have the experts or if you like tinkering with an API- it is not half as bad.
On the other hand, a few providers just need you to download and install programs, and you are set to go. The ease of use is subjective here, but one thing is for sure- the more complex the program, it will be harder to deal with future problems.
5. Choose a VoIP provider for the features you’ll use
VoIP systems offer far greater flexibility and functions than you’d expect from a standard PBX system.
Many of these extra services are included in the monthly subscription fee, and some attract additional charges. Only select the services you need to make efficient use of money.
6. Can you scale services?
VOIP provides the opportunity to connect staff members from different departments quicker, easier, and more cheaply than ever before.
If you think your business will change in size or the VoIP service requirements will vary, ask the provider how flexible they are in allowing such changes. Consider how many features they will be willing to change within financial penalty and commitment.
7. Are your calls private?
Poor tech security will leak your company’s valuable information to eavesdroppers. Therefore, VoIP may become a vulnerability rather than a strength. So, ask your VoIP provider if they support secure communications.
8. Emergency services support
VoIP providers support 999 services now, but you will have to follow their procedure to enable it. It’s best to choose a provider that includes such a service, or else you will need a traditional phone for it.
9. Clear billing information
If you are following the pay-as-you-go method, then make sure your provider has a customer portal to keep track of your expenditure- transparency is essential here.
10. Customer support
You may run into trouble anytime, so check what kind of support the VOIP provider will provide if its control panel or your phone is not working.
Many providers offer 24/7 service through telephone or online webchat, so make sure it fits your business requirements.
11. Choice of the phone number
VoIP works over the internet, allowing you to choose a phone number that does not have to be your actual location.
12. Number porting
Many small overseas operators do not have fully automated porting processes, making the switch over long and proving human error.
Another question you have to ask is whether you can keep your existing dial-in numbers. If you wish to port your number, then find a provider that supports it. Otherwise, you have to keep it the same.
Choosing the best IP Telephony System for your Business
When choosing the best IP telephony system for your business, you also need to ensure your provider is the right fit for your organization. Whether you already have a relationship with a VoIP provider, or if you’re new to internet telephony, getting the best deal for your business will be one of your priorities.
For new VoIP customers
If your planning to migrate to IP telephony from an analog phone system, your existing phone supplier should be able to recommend a suitable solution that meet your business requirements.
For startups and small businesses, cloud telephony offers the opportunity to minimize capital investment while gaining advanced features.
For larger organizations VoIP provides the chance to integrate their telephony service with other systems, such as CRM. Such integrations offer advanced features such as “one-click” dialing, call recording and follow me numbering for your employees.
If you’re looking to get started with VoIP today, your first port of call should be checking what VoIP systems a range of providers can offer you.
For existing VoIP customers
If you are considering upgrading your existing IP telephony system, you may want to contemplate switching to a new VoIP provider.
There are several reasons for switch VoIP providers, but pricing and features are the most prominent ones. In most cases, a new provider should be able to work with your existing hardware so that any upheaval will be minimal.

