Antimalware Service Executable High CPU Usage: SOLVED for Windows 11/10

Antimalware Service Executable, a vital component of Windows Security and antivirus, operates discreetly in the background, without excessive file activity.
However, there are instances when this service, like malicious malware, can adversely affect the performance of Windows 10 computers by consuming excessive CPU resources.
In this guide, we provide insights into the purpose of antimalware service executable, explain the reasons behind its high CPU usage, offer practical tips to optimize your Windows 10 computer and prevent excessive CPU consumption, and detail how the task works to scan and process.
On this page:
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
The Antimalware Service Executable, or msmpeng.exe, is a process within Windows Security that actively defends against malware and can cause high CPU usage.
Windows Defender scans files and programs for potential threats silently in the background, periodically using the Windows Security process and the Antimalware Service Executable process as part of the Windows Defender Antimalware Suite.
Upon detecting a virus or other malicious attacks, the Windows Defender antivirus program’s Antimalware Service Executable takes action by deleting or isolating them.
Why does Antimalware Service Executable use a lot of CPU?
Antimalware Service Executable works continuously in the background, scanning and utilizing excessive CPU resources.
While functioning in the background, it actively scans various programs and files, taking appropriate action when it detects potential threats.
Moreover, the excessive CPU usage can be attributed to the scanning of its own folder, namely C:\\Program Files\\Windows Defender, for malware.
To reduce CPU consumption, one effective approach is to prevent Antimalware Service Executable from scanning its own folder.
How to Stop Antimalware Service Executable from Using Too Much CPU
There are two primary methods to reduce the excessive CPU usage caused by Antimalware Service Executable.
The other method involves preventing the executable from scanning its own folder, which will disable the real-time protection feature against malware.
One way to reduce the frequency of Windows Security scans is to reschedule them.
The steps for both fixes are explained below:
FIX 1: Stop Antimalware Service Executable from Scanning its Own Folder
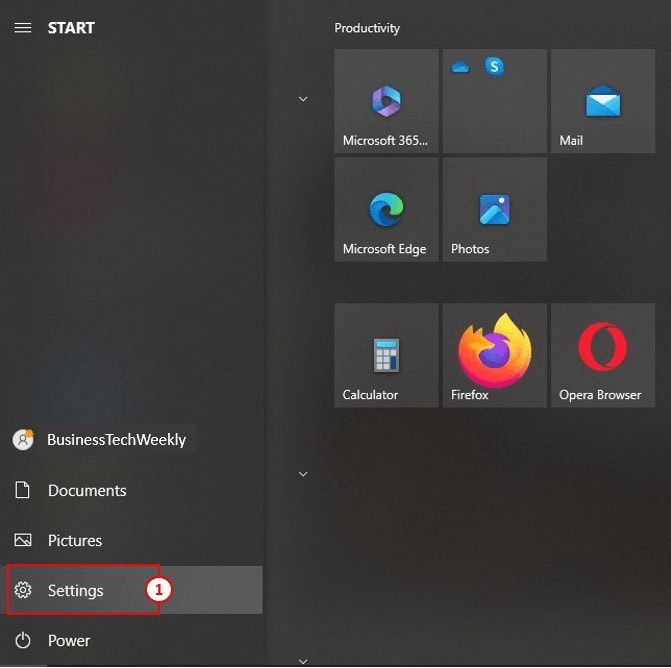
1: To get started, open the Settings app by pressing the WIN key on your keyboard and selecting the gear icon.
2: Click on Update & Security 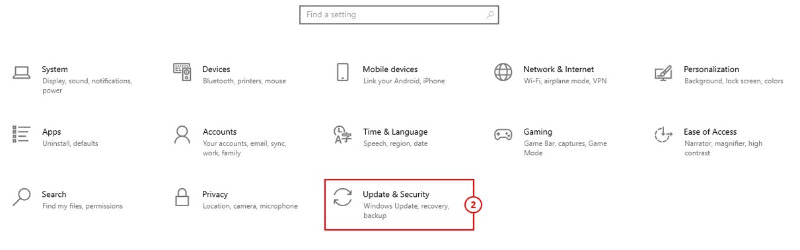
3: To open the Windows Security app, select Windows Security and click Virus & Threat Protection to protect against malware. 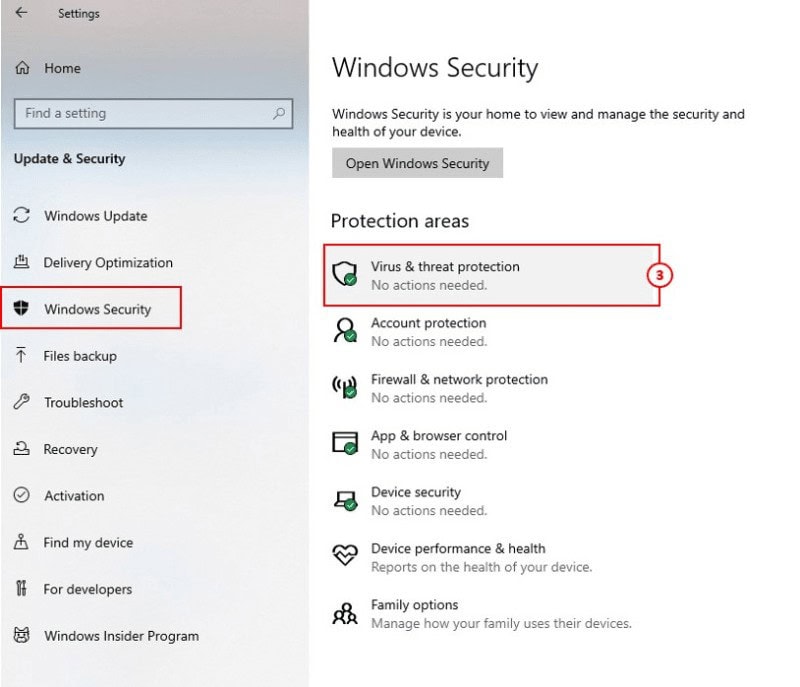
4: The Windows Security app will open. Scroll down to Virus & threat protection settings. Under this heading, click on the link that says Manage Settings. 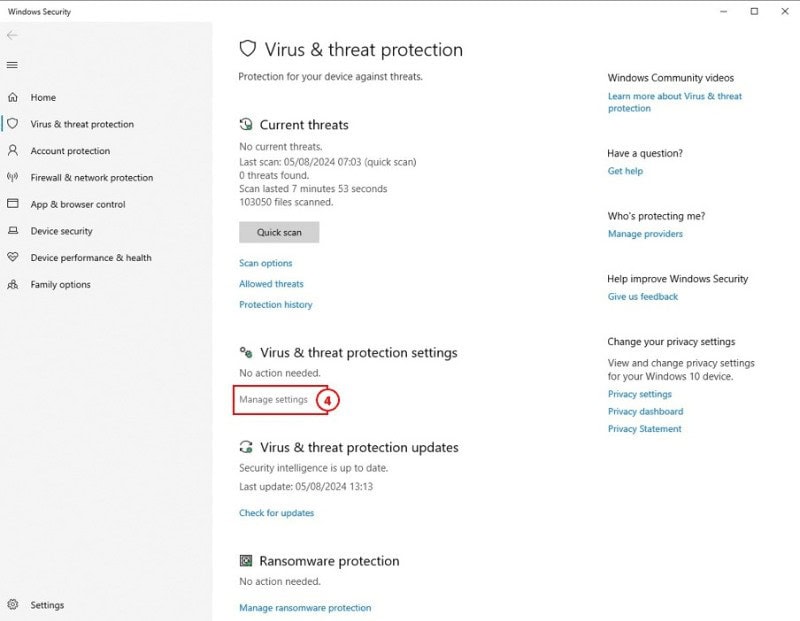
5: Select the Add or remove exclusions link under Exclusions to exclude the folder. 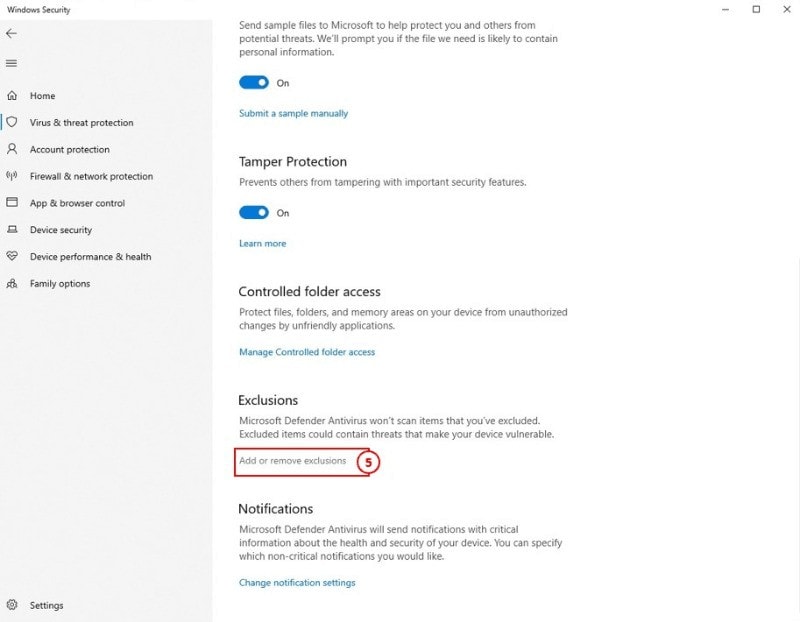
6: Next, click on Add an exclusion to exclude malware, then select Folder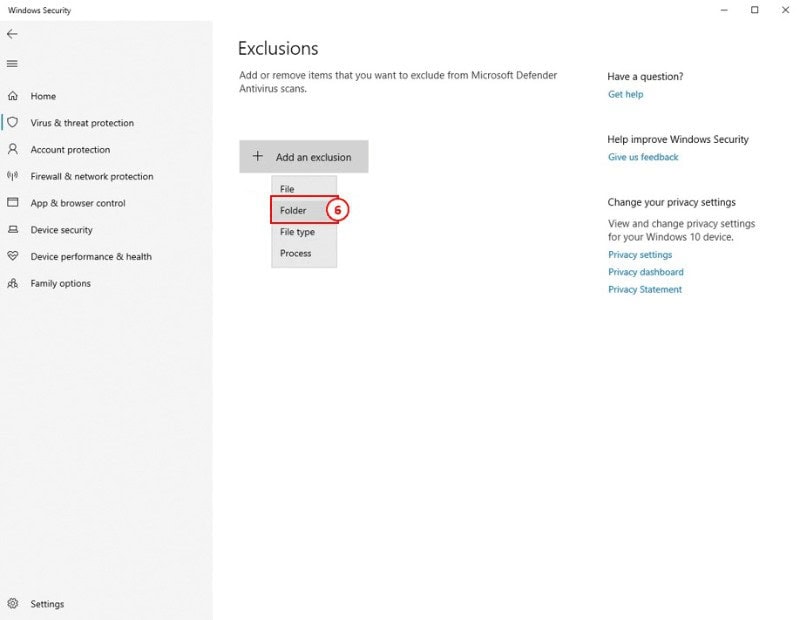
7: In the editor, paste C:\Program Files\Windows Defender. Then click Select Folder to defend against malware. 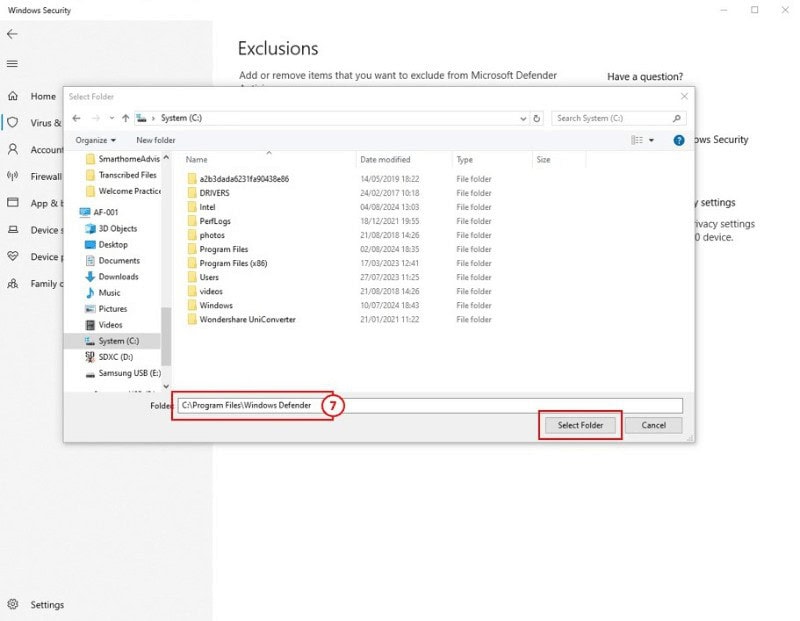
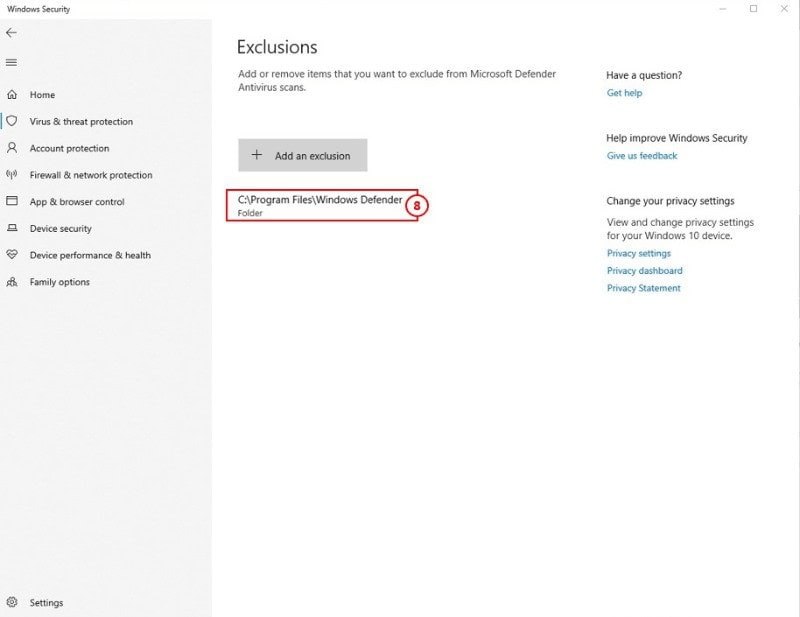
8: Immediately after you click on Select Folder, click Yes on the popup.
The selected folder selected will now be added to exclusions and will not be scanned.
FIX 2: Disabling Realtime Protection and Rescheduling Scans
1: Press WIN + R (Windows key, then the letter R) to Open the Run Dialogue. Open the Task Scheduler app by typing taskschd.msc in the dialogue box and clicking OK. 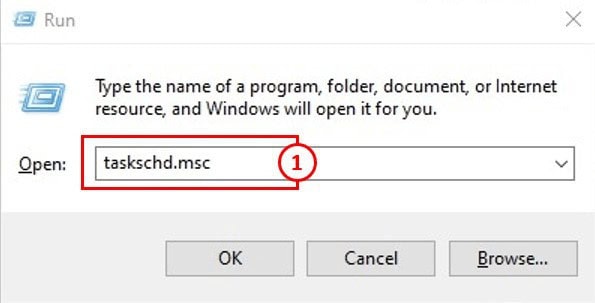
2: Expand the folders by clicking on the Task Scheduler tab > Microsoft > Windows to check for malware.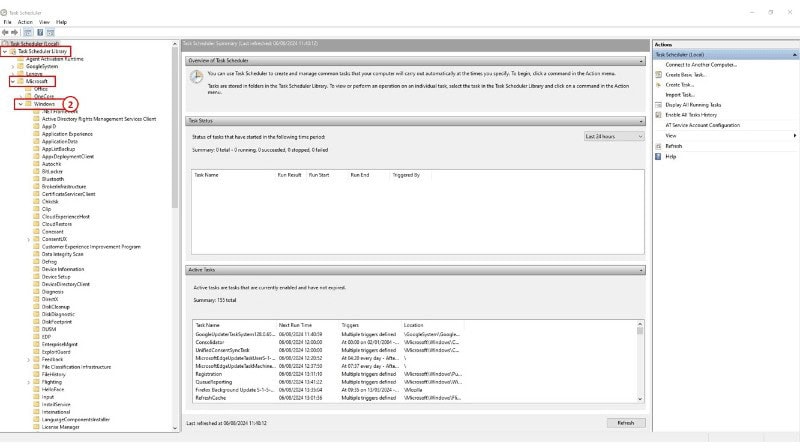
3: Locate and select Windows Defender. 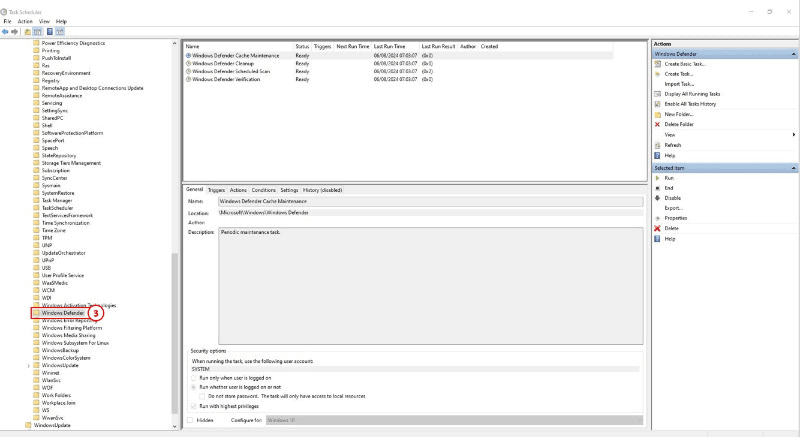
4: Right-click on Windows Defender Scheduled Scan and select Properties. 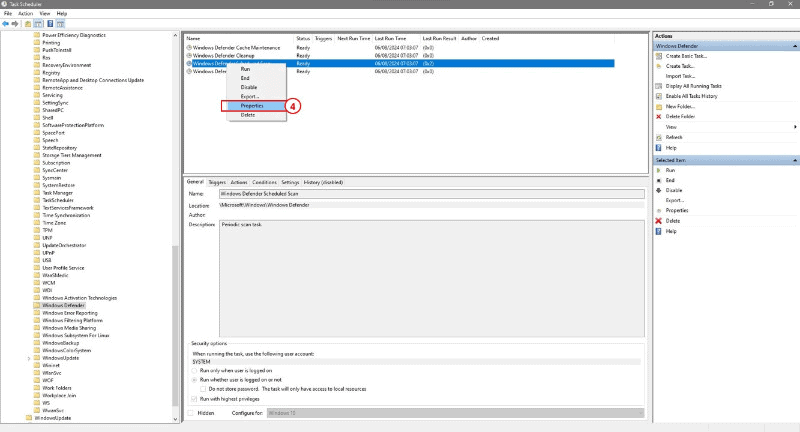
5: In the general tab, unselect Run with highest privileges. 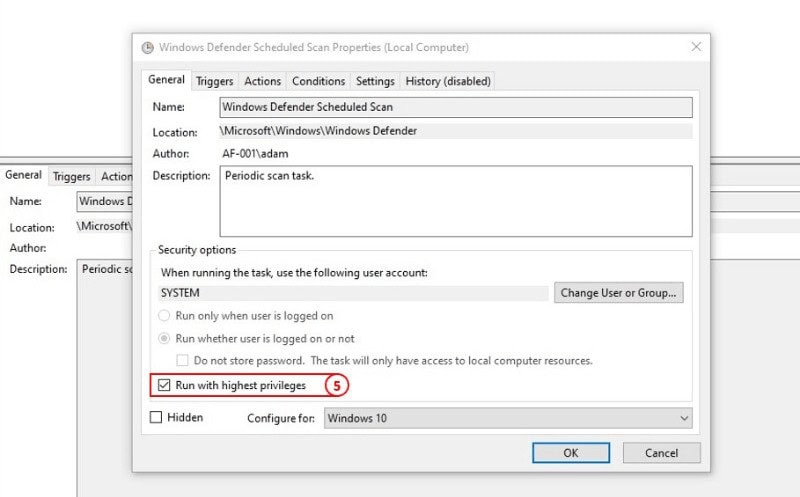
6: Next, in the Conditions tab uncheck all the options 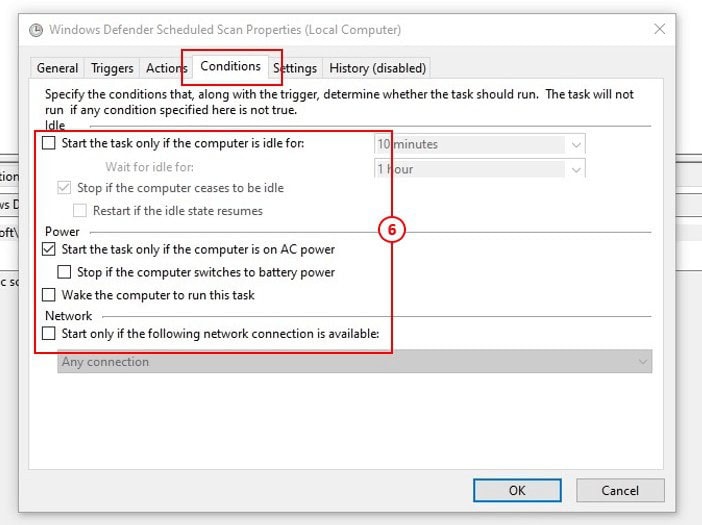
7: In the Triggers tab click New. 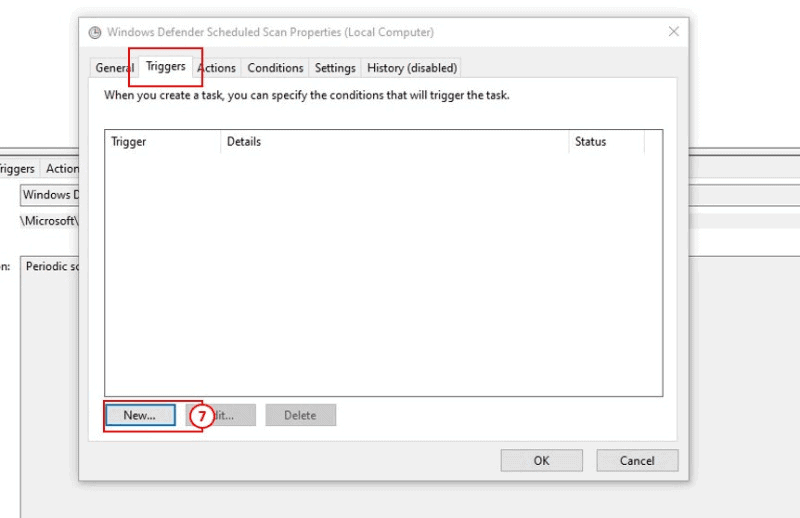
8: Here, schedule when you want Windows Defender to run scans. Select the frequency, date, and time. Once complete click OK. Click OK again. 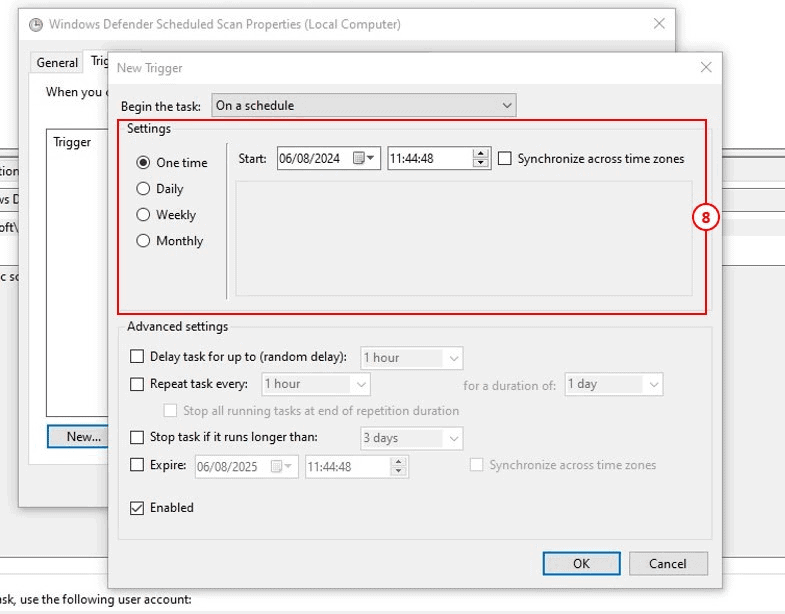
9: Restart your computer. This should stop the antimalware service executable from consuming too much CPU usage.
Final Thoughts
The Antimalware Service Executable provides essential protection to keep your Windows 10 computer safe from malware attacks.
If you have tried the methods mentioned in this article to reduce CPU usage but have not seen any improvement, you may need to permanently disable your Windows Security program.
However, it is important to replace it with another antivirus program to ensure your computer remains protected against potential attacks.
RELATED: 10 of the best antivirus software packages for business
FAQs
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
Antimalware Service Executable is a process that runs in the background on Windows operating systems.
It is part of the Windows Defender program, which is designed to protect your computer from malware and other security threats.
Why is antimalware service executable using high CPU?
Antimalware Service Executable may use high CPU usage due to various reasons. One common cause is when it is performing a full system scan or real-time scanning of files.
Additionally, if your computer has limited resources or if there are conflicts with other security software, it can also lead to high CPU usage.
Can I disable antimalware service executable?
While it is possible to disable Antimalware Service Executable, it is not recommended.
Antimalware Service Executable is crucial in protecting your computer from malware and other security threats.
If you have attempted the two methods mentioned in this article to reduce the CPU usage of Antimalware Service Executable but have not seen any improvement, it may be worth considering permanently disabling your Windows Security program.
However, it is important to ensure that you have an alternative antivirus program installed to protect your computer from potential attacks.
How can I reduce the CPU usage of antimalware service executable?
To reduce the CPU usage of Antimalware Service Executable, you can try a few solutions.
First, make sure your Windows Defender program is up to date. Outdated versions may have performance issues.
You can also schedule scans during periods of low computer usage. Additionally, excluding certain files or folders from being scanned can help reduce CPU usage.
Is antimalware service executable a virus?
No, Antimalware Service Executable is not a virus. It is a legitimate process that is part of the Windows Defender program.
However, some malware may disguise themselves as antimalware service executable to avoid detection.
If you suspect any issues with Antimalware Service Executable, it is recommended to run a full system scan with a reliable antivirus program.
How do I know if antimalware service executable is working?
You can check if Antimalware Service Executable is working by looking for the Windows Defender icon in your system tray.
If it is active, it means that Antimalware Service Executable is running and providing real-time protection.
You can also open the Windows Defender program and check the status to ensure it is functioning properly.

