Security Event vs Incident: Understanding the differences between a Security Event vs an Incident

Security Event vs Incident: Understanding the difference between a security event and an incident is crucial when safeguarding your digital assets. In today’s interconnected world, where cyber threats are rampant, having a solid grasp of these terms can help you effectively respond to potential risks.
A security event refers to any occurrence that has the potential to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of your data or systems. It could be something as simple as a failed login attempt or suspicious network activity.
On the other hand, an incident represents a confirmed and actionable security breach that requires immediate attention and response.
On this page:
- Security Event vs Incident: Understanding Basics
- Contextual Differences
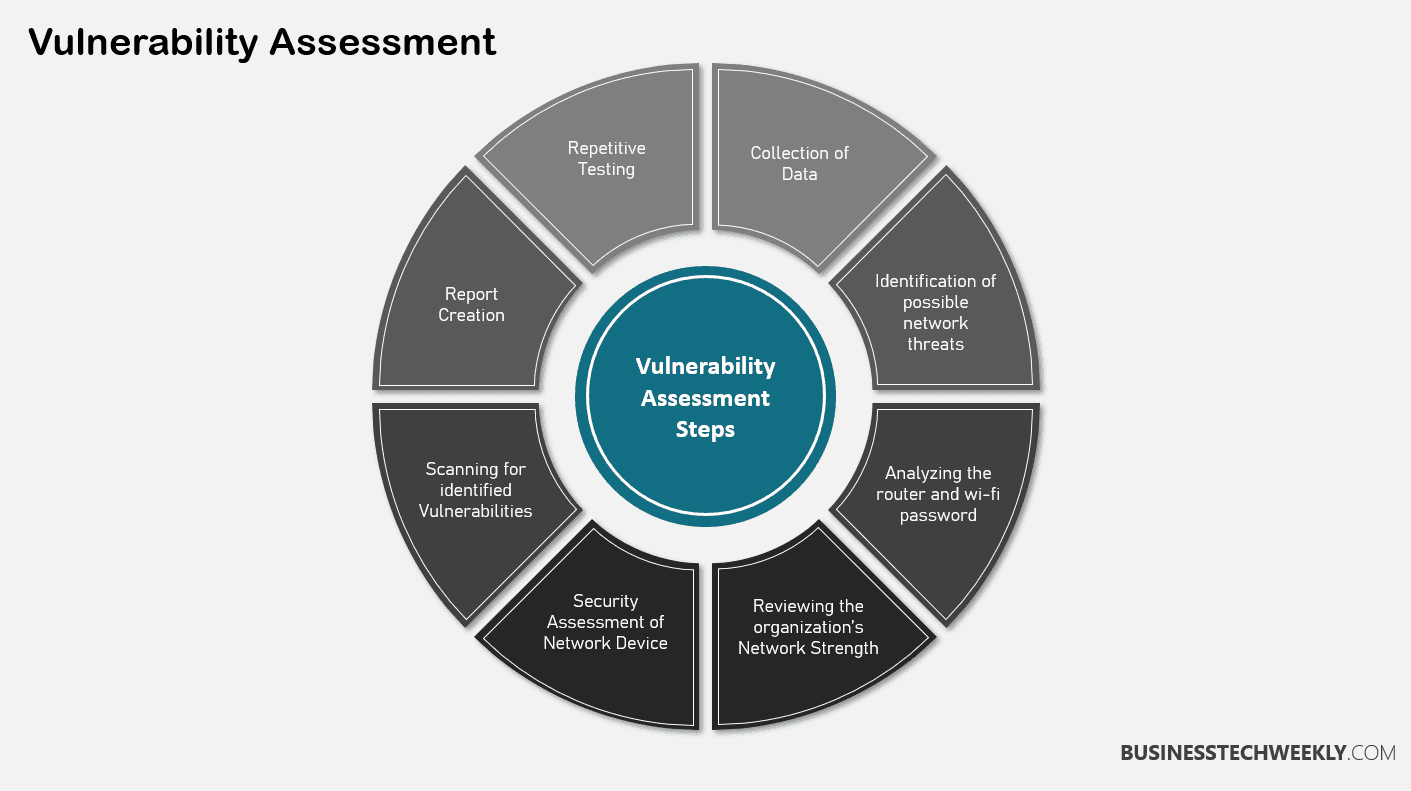
- Security Event vs Incident: Impact Analysis
- Security Event vs Incident: Time Frame Insights
- Response Strategies
- Security Event vs Incident: Risk Management Role
- Security Event vs Incident: Strategy Overviews
- Security Event vs Incident: Post-Incident Focus
- Security Event vs Incident: Frequently Asked Questions
Security Event vs Incident: Understanding Basics
Incident Defined
An incident is an unexpected and disruptive occurrence that deviates from the norm, posing potential threats to organizations.
It can be a security breach, a system failure, or any other event that compromises the integrity of your systems or data. Incidents require immediate attention and swift resolution to mitigate the risks they pose.
An incident disrupts the normal functioning of your organization’s operations, potentially leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
These incidents can come in various forms, such as unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, or data breaches. The impact of incidents can be severe if not addressed promptly and effectively.
It is crucial to understand that incidents are not just inconveniences but serious security threats that demand your attention. Ignoring or delaying their resolution can result in further damage and escalation of the situation.
Therefore, it is essential to have proper incident response protocols in place to detect, analyze, contain, eradicate, and recover from incidents efficiently.
Security Event Defined
A security event refers to changes within your organization’s systems or network architecture. Unlike incidents with negative implications, events can have positive and negative impacts on your organization.
Events can be planned or unplanned occurrences that affect the overall security posture of your systems.
Positive security events include routine system updates, software installations, or scheduled maintenance activities to enhance your infrastructure’s security.
On the other hand, negative security events encompass unauthorized access attempts, system vulnerabilities being exploited, or suspicious network traffic patterns indicating a potential attack.
While events may not always require immediate action like incidents, they should not be ignored. Certain events may indicate underlying vulnerabilities or weaknesses in your security measures.
By paying attention to these events and taking appropriate actions when necessary, you can proactively address potential issues before they escalate into full-blown incidents.
Security Event vs Incident: Key Differences
The key differences between incidents and events lie in their nature, urgency, and impact. Incidents are unexpected occurrences that demand immediate attention due to their detrimental effects on your organization’s security and operations.
They can disrupt your systems, compromise sensitive data, and jeopardize the trust of your customers or stakeholders.
On the other hand, events are changes within your systems or network architecture that can have lasting impacts but may not necessarily require immediate action.
While events can indicate potential vulnerabilities or threats, they do not always result in immediate harm or disruption. However, ignoring significant events can lead to incidents if left unaddressed.
Contextual Differences
Security Contexts
When it comes to security contexts, both incidents and events have an impact on your organization. Incidents, such as data breaches or cyberattacks, can expose vulnerabilities in your systems and highlight areas that need improvement.
They can harm your organization’s security posture, potentially leading to financial losses, reputation damage, and legal consequences. On the other hand, events refer to any occurrence that could risk your organization’s security.
However, they can be managed effectively with the right measures.
Understanding these security contexts is crucial for effective risk management. By analyzing incidents, you gain valuable insights into the weaknesses in your security infrastructure and processes.
This knowledge allows you to address those vulnerabilities and strengthen your overall security posture proactively. It enables you to identify potential threats before they escalate into major incidents.
While incidents demand immediate attention and response, events require a different approach. With events, you can anticipate potential risks and implement preventive measures.
By managing events effectively, you can minimize their impact on your organization’s security.
Variance Impact
The impacts of incidents and events on organizations can vary significantly. Incidents often result in tangible consequences that affect your organization’s operations and stability.
They can lead to financial losses due to the costs of incident response, recovery efforts, legal proceedings, and regulatory fines. Moreover, incidents can damage your organization’s reputation among customers, partners, and stakeholders.
In contrast, events may not always have such immediate or severe consequences. However, this does not diminish their importance. Managing events effectively is essential for maintaining organizational stability and preventing them from escalating into major incidents.
By recognizing potential risks early on and implementing appropriate controls or countermeasures, you can mitigate the impact of events on your organization’s security.
Establishing robust incident response and event management processes is crucial to ensure organizational stability amidst the varying impacts of incidents and events.
This includes developing incident response plans, conducting regular security assessments, implementing preventive measures, and fostering a culture of security awareness among your employees.
Security Event vs Incident: Impact Analysis
Incident Consequences
When it comes to incidents, the consequences can be far-reaching and significantly impact various aspects of an organization.
First and foremost, incidents can disrupt normal operations, causing delays, downtime, and even complete shutdowns. This disruption can result in financial losses and damage the organization’s reputation.
Prompt and effective incident response is crucial in mitigating these negative consequences. By responding swiftly and efficiently to incidents, organizations can minimize the disruption caused and reduce the overall impact on their operations.
This involves identifying and containing the incident, investigating its root cause, and implementing measures to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
In addition to operational disruptions, incidents can also have a detrimental effect on an organization’s reputation.
News of security breaches or data leaks can spread quickly, damaging trust and confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders. The loss of trust can lead to a decline in business opportunities and revenue.
Organizations must prioritize transparency and communication to mitigate the negative consequences of incidents on reputation.
By being open about the incident, acknowledging any mistakes or shortcomings, and taking steps to address the issue, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to resolving the situation and rebuilding trust.
Stability is another critical area affected by incidents. A major incident can create instability within an organization’s internal systems and processes. It may disrupt employee workflows, compromise data integrity, or even compromise critical infrastructure.
This instability not only hampers day-to-day operations but also poses risks to the organization’s overall security posture.
Organizations must focus on effective risk mitigation to maintain stability in the face of incidents. This involves conducting thorough vulnerability assessments and implementing appropriate controls to minimize potential risks.
Organizations can proactively address weaknesses in their systems and processes to enhance their resilience against future incidents.
Security Event Consequences
Events also have consequences for an organization’s security posture. While some events may have negative impacts, others can present opportunities for improvement and growth. It is crucial to evaluate the consequences of events to manage risks effectively.
Negative consequences of events can include increased vulnerability to security threats, compromised data integrity, or even physical damage to infrastructure.
These consequences can affect an organization’s operations and risk management strategies. It is essential to address these issues promptly and implement measures to prevent similar events from occurring in the future.
On the positive side, events can catalyze change and improvement. They can highlight weaknesses in existing security measures and provide valuable insights into areas that require attention.
By leveraging these insights, organizations can strengthen their security posture and overall resilience.
Evaluating event consequences is vital for effective risk mitigation. Organizations must analyze the impact of events on their operations, identify any vulnerabilities exposed, and develop strategies to address them.
This proactive approach enables organizations to minimize potential risks and improve their ability to respond effectively to future events.
Security Event vs Incident: Time Frame Insights
Incident Duration
Incidents can vary in duration, depending on the severity and complexity of the situation. Swift resolution is crucial to minimize the impact of incidents on your organization. The duration of an incident can range from a few hours to several days.
During an incident, it is important to respond promptly and efficiently. Immediate actions are taken to contain and mitigate the effects of the incident.
This includes identifying the root cause, isolating affected systems, and implementing temporary fixes or workarounds.
Once the initial response is underway, a thorough investigation takes place to understand the full extent of the incident and its impact on your organization’s operations.
This investigation may involve forensic analysis, data recovery, and collaboration with internal teams or external experts.
The duration of an incident also depends on factors such as communication channels, coordination among teams, availability of resources, and complexity of systems involved.
Resolving incidents may require extensive troubleshooting, testing, and implementation of permanent solutions.
Security Event Duration
Events can have varying durations based on their planning and execution. Unlike incidents that are often unexpected disruptions, events are typically planned occurrences that serve specific purposes for your organization.
Short-term events such as conferences, seminars, or product launches may last from a few hours to a few days. These events create awareness, promote products or services, or facilitate networking opportunities.
On the other hand, long-term events like trade shows or exhibitions can span several days or even weeks. These events provide platforms for showcasing products or innovations to a wider audience.
Evaluating the duration of events is essential as part of effective risk management. Understanding how long an event will last allows you to allocate resources better, plan for contingencies, and ensure smooth operations.
Furthermore, considering an event’s potential short-term or long-term impacts allows you to assess its success in achieving desired outcomes. This evaluation can help you identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions for future events.
Security Event vs Incident: Real-life Examples
Incidents Illustrated
In cybersecurity, incidents can take various forms and have serious consequences. Let’s look at some real-life examples to understand their impact on organizations and individuals.
One common type of incident is a cybersecurity breach. This occurs when unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive information or systems.
For instance, in 2017, Equifax, one of the largest credit reporting agencies, experienced a massive data breach that exposed the personal information of approximately 147 million people. The breach had far-reaching consequences, leading to financial losses for individuals and damaging the company’s reputation.
Another example is ransomware attacks, where malicious software encrypts files on a victim’s computer or network until a ransom is paid.
In 2020, the University of California San Francisco fell victim to a ransomware attack. It paid $1.14 million to regain access to its encrypted data. Such attacks not only disrupt operations but also pose significant financial risks.
Different types of incidents require tailored responses. When dealing with a cybersecurity breach, organizations must act swiftly to contain it, investigate its extent, and mitigate further damage. This involves isolating affected systems, patching vulnerabilities, and notifying affected individuals about potential risks.
Learning from incidents is crucial for improving security measures. By analyzing the root causes and identifying weaknesses in their systems or processes, organizations can implement preventive measures to avoid similar incidents in the future.
This includes conducting regular security audits, implementing strong authentication protocols, and training employees on cybersecurity best practices.
Security Event Illustrated
While incidents often bring negative connotations, events also play an important role in maintaining security posture.
Let’s explore some examples of events that can impact security.
One such event is software updates. Regularly updating software ensures that known vulnerabilities are patched and new features are implemented.
For example, operating system updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities. Failing to apply these updates can leave systems exposed to potential attacks.
Another important event is data backups. Regularly backing up data is crucial for protecting against data loss or ransomware attacks.
For instance, if a company’s systems are infected with ransomware, having recent backups allows them to restore their data without paying the ransom. On the other hand, failing to perform regular backups can permanently lose valuable information.
Effective event management is key to maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks associated with events. This involves carefully planning and coordinating software updates, system maintenance, and data backups.
Organizations should establish clear procedures and schedules for these events, ensuring they are conducted regularly without disrupting critical operations.
Response Strategies
Handling Incidents
When handling incidents, it is crucial to respond promptly and effectively. Responding promptly allows you to minimize the impact of the incident and prevent further damage. Addressing the incident quickly can mitigate potential risks and protect your organization’s assets.
To handle incidents efficiently, organizations often rely on incident response teams. These teams are composed of experts who are well-versed in identifying, analyzing, and resolving security incidents. They coordinate the response efforts and ensure the incident is contained and resolved as swiftly as possible.
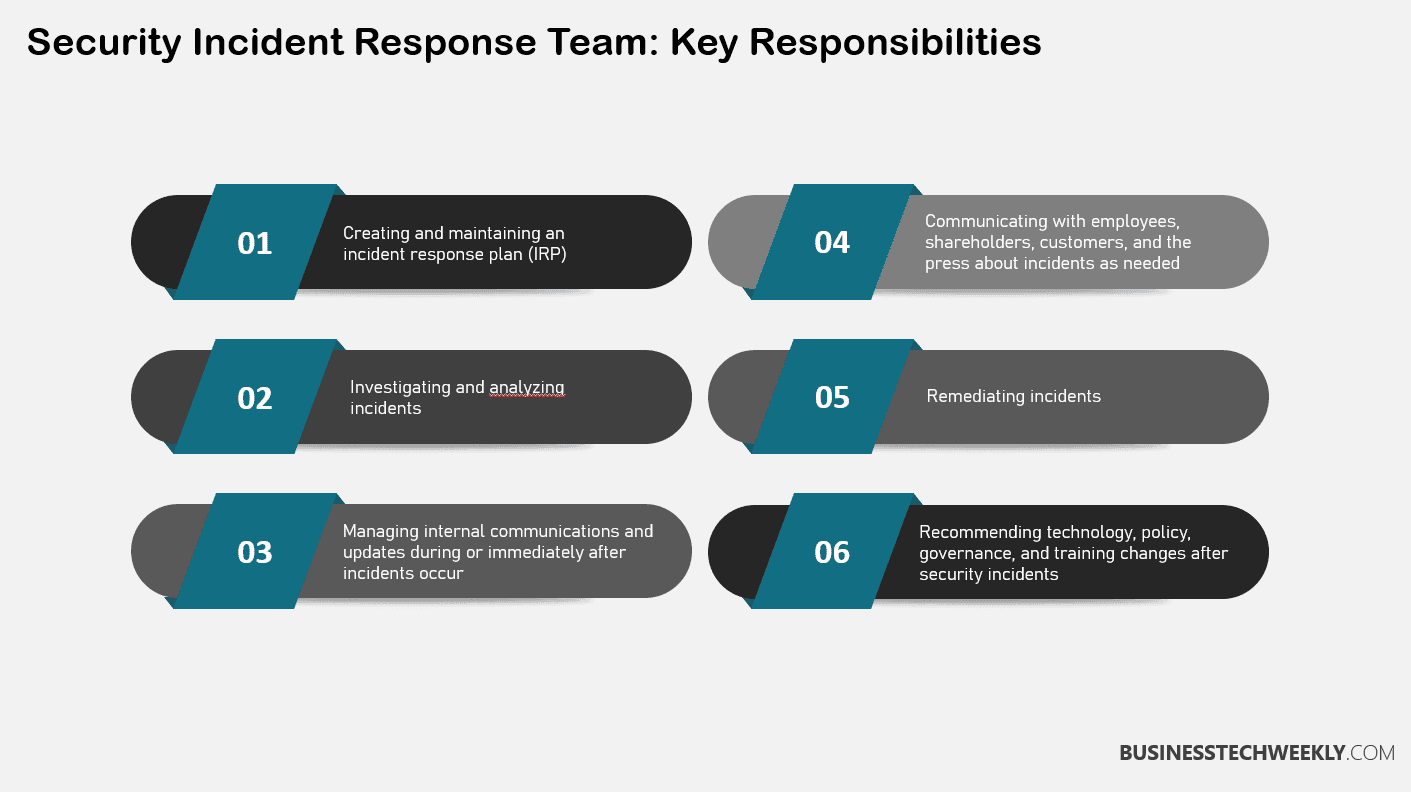
The key steps involved in incident response include identification, containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned.
First, you need to identify that an incident has occurred by monitoring your systems for any signs of compromise or unauthorized activity. Once identified, you must contain the incident to prevent it from spreading further. This involves isolating affected systems or networks.
After containment, the next step is eradication. Here, you focus on removing the incident’s root cause and eliminating any malicious presence from your environment.
Once eradicated, you can proceed with recovery, which involves restoring affected systems or data to their normal state.
Lastly, analyzing the incident and learning from it is essential. This step is known as “lessons learned.”
By analyzing what went wrong during the incident and identifying areas for improvement, you can enhance your organization’s security posture and prevent similar incidents.
Managing Security Events
Managing events requires careful planning, execution, and evaluation to ensure successful outcomes. Meticulous event management is critical in maintaining security, whether it’s a conference, seminar, or company gathering.
Planning an event involves considering various factors such as venue selection, attendee registration process, and logistical arrangements.
You must assess potential security risks and implement appropriate measures to mitigate them. This may include hiring security personnel, implementing access control measures, or conducting background checks on attendees.
During the execution phase, it’s crucial to have a well-defined chain of command and clear communication channels.
Event managers should be prepared to handle unexpected situations promptly and efficiently. Regularly monitoring the event for any security incidents or suspicious activities is essential to maintaining a secure environment.
After the event concludes, evaluation is key to identifying areas for improvement. By gathering participant feedback and analyzing the event’s overall success, you can refine your event management strategies for future events.
This includes assessing security protocols, identifying any vulnerabilities exposed during the event, and implementing necessary changes to enhance security measures.
Security Event vs Incident: Risk Management Role
Assessing Incident Risk
Regarding risk management, incidents are crucial in identifying vulnerabilities and potential threats to an organization’s security. By assessing the risks associated with incidents, you can gain valuable insights into the weak points of your security infrastructure.
This assessment allows you to understand the impact of incidents on your organization and its operations.
Assessing incident risk involves evaluating the likelihood of an incident occurring and determining its potential consequences on your organization’s security. It requires a comprehensive understanding of your systems, processes, and assets and any potential threats that could exploit vulnerabilities.
By conducting thorough assessments, you can identify areas where additional controls or measures are needed to mitigate risks.
It is important to note that incident risk assessment should not be a one-time activity. As technology evolves and new threats emerge, your organization’s risk landscape will also change.
Therefore, regular assessments are necessary to avoid potential risks and ensure ongoing protection.
Managing Security Event Risk
Managing event risk is another important aspect of risk management. Events refer to planned activities or organizational occurrences that pose risks or challenges. These events range from large-scale conferences or product launches to routine maintenance tasks or system updates.
The process of managing event risk involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating the risks associated with these events.
It begins with a thorough analysis of the potential risks involved in each event. Understanding the specific risks associated with an event, you can develop strategies to minimize or eliminate them.
Event risk management aims to strike a balance between reaping the benefits of an event and ensuring that any associated risks are effectively managed.
It involves implementing measures such as contingency plans, security protocols, and communication strategies to address potential issues before they escalate.

Security Event vs Incident: Strategy Overviews
Incident Responses
When it comes to incident responses, there are several strategies that your teams and operations should follow.
First and foremost, documentation plays a crucial role in effectively responding to incidents. Documenting all the incident details, including the time, date, and any relevant information, is important. This documentation is valuable for future analysis and helps identify patterns or trends.
Another key strategy is analysis. Once an incident occurs, it is essential to analyze its root cause and impact. This analysis helps in understanding how the incident happened and what steps can be taken to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
By identifying vulnerabilities or weaknesses in your organization’s systems or processes, you can make necessary improvements to enhance security.
Notifying stakeholders is also an important aspect of incident response. Your organization needs to promptly inform relevant stakeholders about the incident.
This includes internal teams, management, clients, and other parties affected by the incident. You can ensure transparency and maintain trust with your stakeholders by keeping everyone informed.
In addition to documentation, analysis, and stakeholder notification, containing incidents is another critical strategy. It involves taking immediate action to minimize the impact of the incident and prevent further damage.
This may include isolating affected systems or networks, deactivating compromised accounts, or implementing temporary measures to mitigate risks.
Swift and effective incident responses are vital because they help prevent recurrence. By addressing incidents promptly and thoroughly, you can identify vulnerabilities or gaps in your security measures and take appropriate actions to strengthen them.
This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of similar incidents happening again in the future.
Security Event Techniques
Various techniques can be employed for successful outcomes when managing events within your organization’s security framework.
The first step is planning. Meticulous planning ensures that all aspects of the event, including security considerations, are considered. This involves identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them.
Another important technique is evaluation. After the event, it is crucial to evaluate its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
This evaluation helps assess the success of security measures implemented during the event and provides valuable insights for future events.
Event techniques also play a significant role in minimizing security risks. You can reduce the chances of unauthorized access or breaches during events by implementing appropriate security measures, such as access control systems, surveillance cameras, or encryption protocols.
These techniques help safeguard sensitive information and protect your organization’s assets.
Security Event vs Incident: Post-Incident Focus
Recovery Steps
After experiencing a security incident, it is crucial to take immediate action to recover from its impact. Recovery steps involve a series of measures to restore normal operations and minimize any damage caused by the incident.
The first step in the recovery process is to identify and isolate the affected systems or areas. By isolating the compromised components, you can prevent further spread of the incident and limit its impact.
This may involve disconnecting affected devices from the network or temporarily shutting down certain services.
Once isolation is complete, remediation measures come into play. These measures focus on fixing vulnerabilities or weaknesses that allowed the incident to occur in the first place. It may involve patching software, updating security configurations, or implementing additional security controls.
In addition to remediation, data recovery is another critical aspect of post-incident recovery. Backups are essential for restoring lost or corrupted data.
Regularly backing up your important files ensures that you have a copy available for restoration in case of an incident.
While recovering from a security incident, it is essential to maintain continuous monitoring and evaluation. This involves closely observing your systems and networks for signs of lingering threats or potential vulnerabilities that could lead to future incidents.
Ongoing monitoring allows you to detect and respond promptly if any suspicious activities are detected.
Prevention Tips
Preventing security incidents should be a top priority for any organization. Here are some tips to help you strengthen your security posture and reduce the risk of incidents:
- Conduct security assessments: Regular assessments help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your systems and networks. By regularly assessing your infrastructure’s security, you can proactively address potential risks before they become incidents.
- Invest in employee training: Your employees play a crucial role in maintaining security. Educate them about best practices, such as using strong passwords, recognizing phishing attempts, and being cautious when accessing sensitive information. Well-trained employees can act as an additional line of defense against security threats.
- Implement strong access controls: Limiting access to sensitive data and systems is vital for preventing unauthorized access. Ensure that only authorized individuals have the necessary permissions to access critical resources. Regularly review and update user privileges to align with changing roles and responsibilities.
- Keep your software and systems current: Regularly applying security patches and updates is crucial for addressing known vulnerabilities. Outdated software can be easy targets for attackers. Enable automatic updates whenever possible to protect you against the latest threats.
- Establish a security incident response plan: Having a well-defined plan in place allows you to respond effectively in the event of an incident. The plan should outline roles and responsibilities, communication channels, and steps to follow during incidents.
Security Event vs Incident: Frequently Asked Questions
What are the basic differences between a security event and an incident?
A security event refers to any occurrence that has the potential to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information.
On the other hand, a security incident is an actual violation or breach of security policies, resulting in unauthorized access or damage to systems or data.
How do security events and incidents differ in terms of context?
While a security event can be benign and not necessarily indicate a breach, a security incident always involves an actual violation of security measures.
Contextually, events can serve as indicators that help identify potential threats. At the same time, incidents demand immediate attention and response to mitigate their impact.
What Is an Alert?
An alert is a notification of a cybersecurity event. (Or, sometimes, a series of events.) You can work with your security provider to determine which types of events you want to monitor with alerts.
Depending on your Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) software and support, you can send alerts to any relevant parties who need to take action.
What is the importance of impact analysis in distinguishing between events and incidents?
Impact analysis helps assess the consequences of a security event or incident. It aids in determining whether an event qualifies as an incident based on its severity and potential harm.
Organizations can prioritize their response efforts and allocate resources more effectively by evaluating the impact.
How does the time frame play a role in differentiating between security events and incidents?
Time frame insights are crucial when distinguishing between events and incidents. A security event may occur without immediate detection or response.
In contrast, an incident requires prompt action due to its active nature. Analyzing the time frame helps establish appropriate response protocols for each situation.
How should organizations approach response strategies for handling events versus incidents?
Organizations must have predefined response strategies for both events and incidents. Events require monitoring, analysis, and investigation to determine their potential impact.
On the other hand, incidents demand immediate response actions, such as containment, eradication, and recovery efforts. A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for effective incident management.
What role does risk management play in distinguishing between events and incidents?
Risk management is vital in differentiating events and incidents by assessing the potential risks associated with each occurrence.
It helps organizations prioritize their focus based on the likelihood and potential impact of security events turning into incidents. Risk management enables proactive measures to prevent incidents and minimize their impact if they occur.
What should organizations focus on after an incident occurs?
After an incident occurs, organizations should shift their focus toward post-incident activities.
These include performing a thorough investigation to identify the root cause, evaluating the effectiveness of response strategies, implementing necessary improvements, conducting lessons learned sessions, and updating security policies or controls accordingly.
The aim is to enhance future incident prevention and response capabilities.

