What are Non-Fungible Tokens? NFTs Explained – Your Ultimate Guide to Non-Fungible Tokens

NFTs Explained: What are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)? At this time, most of us have heard of cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency refers to digital currency that uses blockchains and cryptographic assets. The advent of Bitcoin has brought blockchains and the ethereum into the mainstream, along with digital wallets.
Currency, including cryptocurrency, is, however, merely one application of the underlying blockchain technology. This technology also enables the creation and transfer of digital assets such as colored coins.
However, it is important to address potential issues such as money laundering when dealing with these digital assets. The most exciting potential of blockchain technology arises when non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are used to certify and ensure the uniqueness and identity of digital assets in the cryptocurrency space. What exactly are non-fungible tokens?
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are a form of cryptocurrency token that represents unique pieces of artwork.
NFTs are unique tokens that cannot be exchanged on a like-for-like basis, hence the term “non-fungible”. NFTs are unique pieces of digital content that can represent ownership of a specific asset.
Below, we explain the meaning of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) in detail, how they are used as digital assets, and how you can trade and store NFTs on an exchange using blockchain technology.
On this page:
A Primer to Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
So, what does is NFTs mean? NFTs explained simply are unique digital assets.
However, before we discuss non-fungible tokens (NFTs), we must understand the concept of fungibility in relation to assets and money. NFTs are a form of digital asset that utilize blockchain technology and are stored in a digital wallet.
In reality, if you’ve ever used money, you instinctively understand what fungibility is in the context of a wallet and asset. It is a concept that is crucial in technology and work.
The ability of a wallet currency to maintain a standard value and universal acceptance is referred to as fungibility. This is important for us in the world of technology and work. It indicates that a currency’s history has no bearing on its value and that each piece of that currency is worth the same as every other piece.
This applies to our wallet, as technology has revolutionized the way we handle money. Additionally, this concept can be seen in the world of art, where the value of a piece is not determined by its history but rather its artistic merit.
The $100 bill in your wallet is worth the same as the $100 bill in mine. Both of us, people, have equal value in this game. Even if your wallet was printed in 2020 and mine in 1990, a shop owner would accept them from us art-loving people.
Even if your $100 bill was used in a game before you got it, it’s still worth something at the store. Art and NFTs are valuable assets in the digital world. That is the ability of fungibility.
A non-fungible currency, like NFTs, in the US, whether in the game or art industry, is unstable and is likely to collapse.
Consider what it would be like for us in the art world if we had to look into the history of every dollar bill before accepting it, especially in the context of NFTs. Consider a world in which specific $20 bills, art, are worth more than others to us, due to the rise of NFTs. That would be fiscally untenable.
Fungibility is critical for any currency, whether it’s the dollar, Bitcoin, or NFTs in the world of art.

How do NFTs work?
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs), meaning cryptographic assets, are recorded on a blockchain, which is a distributed public ledger for transactions.
Each NFT contains unique identification codes that distinguish them from each other. This data makes it easy to transfer tokens between owners and to verify ownership.
How is a non-fungible token created?
A non-fungible token is created by an artist, creator, or license-holder through a process called minting.
Minting is a process that involves signing a blockchain transaction that outlines the fundamental token details, which is then broadcasted to the blockchain to trigger a smart contract function which creates the token and assigns it to its owner.
Under the hood, a non-fungible token consists of a unique token identifier, or token ID, which is mapped to an owner identifier and stored inside a smart contract.
When the owner of a given token ID wishes to transfer it to another user, it is easy to verify ownership and reassign the token to a new owner.
How do NFTs and cryptocurrency differ?
Both NFTs and cryptocurrencies are based on the same blockchain technology, which is revolutionizing the world of art. While NFT users may acquire art NFTs using a cryptocurrency, art NFTs and cryptocurrencies are created and used for distinct purposes.
Cryptocurrencies, including NFTs, aspire to function as currencies by holding value or facilitating the purchase or sale of art products. Tokens issued by cryptocurrency exchanges, including NFTs, are fungible, similar to fiat currencies such as the dollar.
NFTs are a form of digital art. NFTs create one-of-a-kind tokens that can demonstrate ownership of and rights to digital art items.
| FUNGIBLE TOKEN | NON-FUNGIBLE TOKEN |
| Fungible tokens are assets that are interchangeable and can be exchanged with another asset of a similar kind | Non-fungible tokens are unique assets that are not interchangeable and cannot be exchanged with another NFT of the same kind |
| Fungible tokens are divisible assets meaning the item can be broken down into any number of units as long as the value remains the same | Non-fungible tokens are non-divisible assets, and they represent a whole entity and be sub-divided into multiple units |
| Fungible tokens are uniform, and they do not have a unique value proposition like NFTs | NFTs have a unique value proposition, and each token has a unique ID |
| Fungible tokens use the ERC20 standard used to create the fungible token on an Erthereum blockchain | NFTs use the ERC271 standard for the representation of their tokens |
How are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) used?
Blockchain tokens, such as NFTs, can represent more than simply currency, such as Bitcoin. The applications of blockchain assets are practically limitless.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are blockchain assets that are not intended to be identical. NFTs effectively function as a database entry for any form of goods.
What are NFTs used for?
An obvious example of NFTs is CryptoKitties, the most popular NFT in blockchain history. There are thousands of NFTs, including CryptoKitties, globally, but not all NFTs are created equal. Each one of the NFTs is distinct, with its name, eye colour, fur colour, fur pattern, facial expression, and distinctive characteristics.
When you purchase a CryptoKitty, you buy an NFT that belongs to that kitten. Some kittens are more valuable than others, and depending on the rarity of your NFTs, you can buy and sell them for variable quantities of fungible tokens.

To grasp the significance of non-fungible tokens for blockchain-based asset and identity security, consider a few additional examples of how NFTs function:
Collectibles
CryptoKitties are one example of an NFT-secured collectible. However, the collectibles industry is vast, with Art collecting and NFTs making up a substantial portion.
Experts could verify and certify paintings and sculptures before issuing non-fungible tokens (NFTs). If the owner of a particular piece of artwork wants to sell it, they can list the NFTs on an auction as proof of ownership.
Because NFTs are owned on the blockchain, this type of certification prohibits fabrication and fraud in the art industry.
The same applies to NFTs, baseball cards, stamps, jewellery, autographed guitars, and collectable objects. The blockchain’s security ensures the transaction’s authenticity.
Sports
Sports memorabilia frequently has a high collectible value, and NFTs may enhance the fan experience and serve as a means of establishing the authenticity and ownership of high-value memorabilia.
NBA Top Shot, for example, auctions NFTs of player moments throughout games. Additionally, there may be a use for NFTs in the ticketing of sporting events.
Licensing or Smart Contracts
NFTs are useful in licencing agreements involving intellectual property. This may present significant potential for owners of many types of intellectual property to license their assets, especially with the rise of NFTs.
The use of blockchain to maintain NFTs may assist in ensuring that all users are aware of the ownership and restrictions on the use of these assets, such as royalties paid on music usage.
Real Estate
In real estate, an NFT, or non-fungible token, can serve as the digital representation of ownership on a blockchain network.
For instance, rather than a paper deed saying that you own a single-family house, you may have an NFT establishing your ownership of the property. In terms of security and accessibility, NFTs present several advantages.
Identity & Certification
Consider identification and the role NFTs can play in verifying personhood. A nontradable digital token, also known as an NFT, might replace your birth certificate, passport, and driver’s licence. But what is NFTs? These NFTs tokens can’t be traded, but they can be communicated and verified by the appropriate authorities.
This information is relevant to employers, doctors, or anybody else who needs it, including those interested in NFTs.
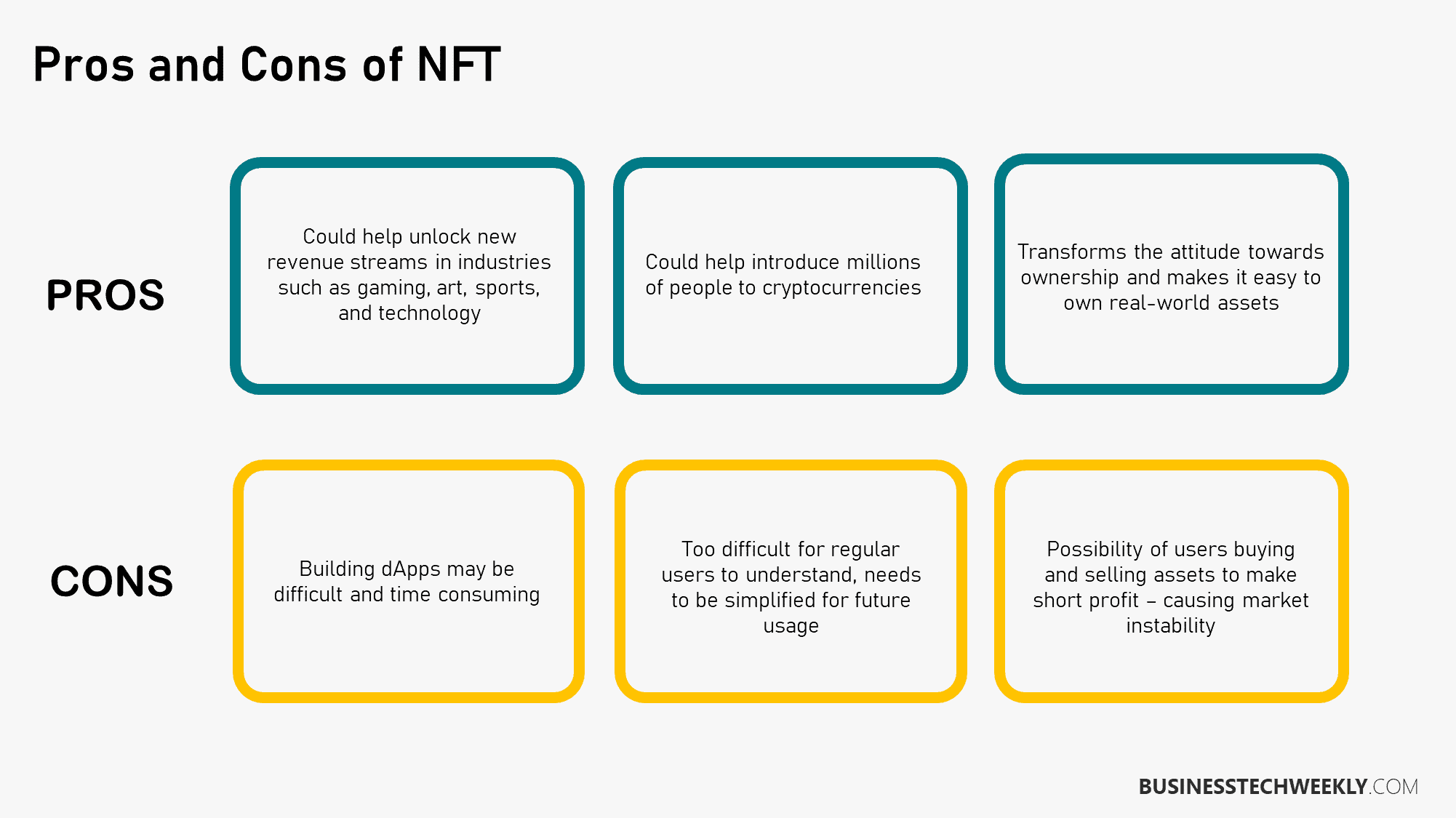
NFT Standards
The most common NFT, also known as non-fungible tokens, is built on Ethereum’s ERC-721 token standard. The standard defines how to create NFTs and set up the smart contract that runs them. The standard ensures that NFTs interact well with the Ethereum network.
This is crucial when transferring NFTs and building marketplaces for buying, selling, and trading them. The influx of digital collectibles and game-based assets has fueled the production of ERC-721 tokens.
What is ERC-721?
ERC-721 is an Ethereum standard for developing non-fungible tokens. The standard assures that the token is non-fungible and one-of-a-kind. Additionally, it may originate from the same smart contract but have a different value due to its age or rarity.
What ensures an NFT is unique?
A token ID is defined by an uint256 variable (unsigned integers 256 bits) in an NFT smart contract. Each ERC-721 smart contract has a globally unique uint256 token ID. The token ID is converted to a digital collectible by the dApp (decentralized application).
These token identifiers are also referred to as NFT Identifiers, and they remain constant during the life of the smart contract.

What are other NFT standards?
ERC-1155
ERC-1155 is another widely used non-volatile memory standard. Enjin developed it, and it became the official token standard for NFTs. It is noteworthy that it is a multi-asset token standard that enables the creation of fungible and non-fungible assets on Ethereum.
As with ERC-721, ERC-1155 is based on the Ethereum network, which ensures that tokens created per these standards are secure, transferable, and resistant to hacking.
While it enables the establishment of many assets, it also significantly reduces transaction costs. Additionally, developers can use ERC-1155 to implement escrow/atomic exchanges of several tokens.
The standard eliminates the need for individual token contracts to be approved independently. Additionally, this standard allows for describing fungible and non-fungible tokens in a single contract. As a result, it enables more secure and efficient token trading.
ERC-998
ERC-998 is essentially an extension of the ERC-721 standard, advancing the NFT standard. It enables non-fungible tokens to own other non-fungible tokens and ERC-20 tokens. Additionally, it can be viewed as a portfolio of digital assets. NFTs that support ERC998 also support ERC-721.
Under the ERC-998 token standard are 4 different token standards, including the following:
- ERC998ERC721 (Top-down composable) – These ERC998 tokens receive, hold, and transfer ERC721 tokens.
- ERC998ERC20 (Top-down composable) – These tokens receive, hold, and transfer ERC20 tokens
- ERC998ERC721 (Bottom-up composable) – These tokens attach themselves to other ERC721 tokens.
- ERC998ERC20 (Bottom-up composable) – These tokens attach themselves to ERC20 tokens.
How are NFTs traded and stored?
Purchasing and holding NFTs is not the same as traditional bitcoin trading. You’ll probably need a digital currency like Ether to buy a digital collectable or tokenized object, though individual sellers may accept cash or trade.
You’ll also need someone to conduct business with. NFT exchanges do not exist because each token is unique. Marketplaces, on the other hand, link individual buyers and vendors. You must negotiate a price with the individual selling the token. Then you can buy it from them directly.
If you purchase an ERC-721 token, it will be sent to your Ethereum wallet address like an ERC-20 token would. Viewing it in a wallet client, on the other hand, tells you nothing about its worth other than the fact that you have it.
Its worth is determined by the system in which it is embedded. So, a CryptoKitty NFT is tied to a sketch of a kitty with specific characteristics, and that kitty can be offered on the open market if you decide to sell.

How is an NFT transferred?
The ERC-721 standard provides a secure transfer function. This function, dubbed safe Transfer From, is utilized during the construction of non-fungible token platforms to differentiate between safe and unsafe transfers.
Transfers of NFTs can only be initiated by:
- The NFT’s owner
- An individual who has an approved address for the NFT
- An individual who is an authorized operator for the NFT’s actual owner
To permit an operator, the approved address must be specified. This appears to be a pretty robust technique for developing wallet, broker, and auction applications.
Buying NFTs: A Guide to Purchasing and Considerations
How Can I Buy NFTs?
After you have completed the transaction and the NFT is in your digital wallet, you can decide how to manage and show off your NFTs. You can display them in virtual galleries, share them on social media, or even trade them with others if you want.
Just remember that buying NFTs comes with risks, and their value can change over time. Make sure to do your research, stay informed, and only spend money that you’re okay with possibly losing.
Buying NFTs
If you’re interested in purchasing NFTs (non-fungible tokens), there are several steps and considerations to keep in mind. Here’s a guide to help you navigate the process:
- Research and Educate Yourself: Before diving into the world of NFTs, take the time to understand what they are, how they work, and the different platforms available. Familiarize yourself with the terminology and concepts associated with NFTs.
- Choose a Marketplace: There are various NFT marketplaces where you can buy and sell NFTs. Some popular options include OpenSea, Rarible, and NBA Top Shot. Research each platform to find the one that aligns with your interests and goals.
- Set Up a Digital Wallet: To buy NFTs, you’ll need a digital wallet that supports the blockchain network used by the marketplace you’ve chosen. Ethereum is the most common blockchain for NFTs, so consider setting up an Ethereum wallet like MetaMask or Trust Wallet.
- Fund Your Wallet: Once you have a digital wallet, you’ll need to fund it with cryptocurrency. Most NFT transactions are conducted using Ether (ETH), so you’ll need to acquire some ETH and transfer it to your wallet.
- Browse and Discover NFTs: Explore the marketplace of your choice to discover NFTs that interest you. You can search by category, artist, or collection. Take your time to find NFTs that align with your preferences and budget.
- Evaluate the NFT: When considering an NFT, look beyond the artwork or collectible itself. But, what is NFTs mean? Consider factors like the artist’s reputation, scarcity, historical sales data, and potential for future value appreciation. Conduct thorough research before making a purchase.
- Place a Bid or Buy: Once you’ve found an NFT you want to purchase, you can either place a bid or buy it outright if the option is available. Bidding allows you to potentially get the NFT at a lower price, while buying immediately ensures you secure it.
- Complete the Transaction: If your bid is accepted or you purchase the NFT, follow the instructions provided by the marketplace to complete the transaction. This typically involves confirming the transaction on the blockchain and paying any associated gas fees.
- Transfer the NFT to Your Wallet: After the transaction is complete, the NFT will be transferred to your digital wallet. Ensure you have the necessary wallet address and follow the marketplace’s instructions for transferring the NFT.
- Manage and Display Your NFTs: Once you own NFTs, you can manage them within your digital wallet. You can choose to display them in virtual galleries, showcase them on social media, or trade them on secondary markets.
Remember, buying NFTs involves risks, and the value of NFTs can fluctuate. It’s important to do your due diligence, stay informed, and only invest what you can afford to lose. Happy collecting!
Examples of NFT Marketplaces: Showcasing Unique Digital Assets
Examples of NFT Marketplaces
If you’re interested in buying or selling unique digital assets in the form of NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), there are several marketplaces available that can facilitate these transactions. Here are some examples of popular NFT marketplaces:
- OpenSea: OpenSea is one of the largest NFT marketplaces, offering a wide range of digital assets including art, collectibles, domain names, and virtual real estate. It supports various blockchain networks such as Ethereum and Polygon, providing users with a diverse selection of NFTs to choose from.
- Rarible: Rarible is a decentralized marketplace that allows creators to mint and sell their own NFTs. It offers a unique feature called “governance tokens,” which allows users to have a say in the platform’s development and decision-making process.
- SuperRare: SuperRare is a curated marketplace that focuses on digital art. It showcases unique and limited-edition artworks from emerging and established artists. Each artwork on SuperRare is authenticated on the Ethereum blockchain, ensuring its scarcity and provenance.
- Nifty Gateway: Nifty Gateway is a user-friendly marketplace that aims to make NFTs accessible to a wider audience. It features exclusive drops from popular artists, musicians, and celebrities, making it a hub for high-profile NFT releases.
- Foundation: Foundation is an invite-only marketplace that focuses on supporting artists and creators. It emphasizes the curation of high-quality NFTs and aims to foster a community of collectors and enthusiasts.
- KnownOrigin: KnownOrigin is a marketplace that specializes in digital art and collectibles. It prides itself on showcasing unique and original pieces from talented artists around the world.
While these are just a few examples, there are numerous other NFT marketplaces available, each with its own unique features and offerings.
When choosing a marketplace, it’s important to consider factors such as the platform’s user interface, transaction fees, supported blockchain networks, and the reputation of the marketplace within the NFT community.
The Future of Non-Fungible Tokens
When you consider the possibilities of non-fungible assets, it’s impossible to imagine a theoretical limit to what NFTs could digitize. NFTs can represent your identity, qualifications, real-world property, and various digital assets, all of which exist on the blockchain. These tokens can be stored, displayed, shared, or sold.
NFTs enable businesses to transact and do instant business with anyone globally, and organizations may use digital tokens to control entire inventories. Provided a robust ecosystem can be created, NFTs have the potential to be the foundation for the future economy.

