Why Encryption is Important: Protecting your Business Data in the Digital Age

Why Encryption is Important: Data privacy and security have become important priorities for organizations of all sizes in today’s digital world. With the rise of cyber threats, safeguarding sensitive information has become vital. Encryption is one of the most effective methods for ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Encryption is the process of turning data into an unreadable format that can be decoded only with a unique key. This method has been used for centuries and is now crucial for protecting digital data.
As a business owner or executive, you must grasp the significance of encryption in securing your data and your firm’s reputation.
This article will provide an overview of encryption, its advantages, and how to apply it in your organization.
On this page:
Why Encryption is Important for Businesses
Data breaches and cyber attacks are on the rise, and businesses are prime targets for these types of attacks. This is why encryption has become an important tool for protecting sensitive business information.
Here are some reasons why encryption is important for businesses:
- Protecting Sensitive Data: Encryption guarantees that only authorized parties can access sensitive information. This includes financial data, client information, trade secrets, and other sensitive information that firms must safeguard.
- Compliance with Regulations and Legislation: Many industries are subject to unique data privacy and security legislation and laws. Failure to comply with regulations and legislation may result in penalties and reputational harm to the organization. Numerous of these standards, like HIPAA and GDPR, require encryption.
- Building Trust with Customers: Customers anticipate that businesses will safeguard their data and privacy. Encryption is one method for reassuring clients that their privacy is a priority.
- Preventing Data Breaches and Cyber Attacks: Encryption makes it harder for cybercriminals to access sensitive data, even if they can breach an organization’s networks. This decreases the likelihood of data breaches and cyber assaults, which may have devastating financial and reputational effects on firms.
Understanding the CIA Triad
Understanding why encryption is essential to information security may be done using the CIA triad, which stands for confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Confidentiality: By making data unreadable to unauthorized users or systems, encryption aids in ensuring confidentiality. Information that has been encrypted is changed into an incoherent form that can only be decoded by those who have the correct decryption key. This implies that even if an attacker intercepts the encrypted data, they won’t be able to decipher it.
- Integrity: Encryption further supports data integrity, which prevents unauthorized changes. When data is encrypted, any modifications will lead to incorrect decryption, which is immediately recognizable. As a result, it is far more difficult for attackers to change data covertly.
- Availability: Data availability may also be increased via encryption by thwarting denial-of-service attacks. Encryption may restrict the quantity of data sent when an attacker attempts to overwhelm a system with requests. This lowers the possibility of system overload or failure.
Types of Data Encryption
The best encryption solution for your organization will be determined by your individual requirements and the sort of data you need to safeguard.
The three most prevalent encryption algorithms are symmetric, asymmetric, and hashing. Each has advantages and disadvantages, and the best encryption technique for your company will be determined by its requirements.
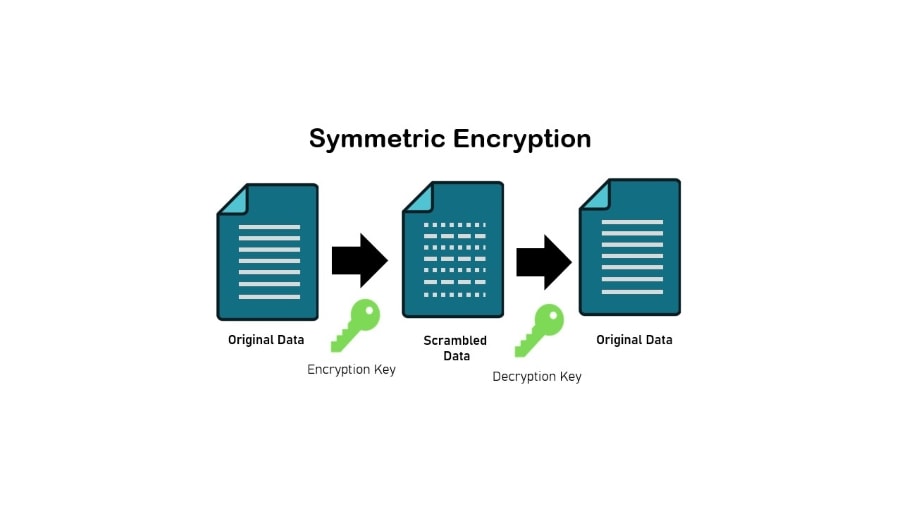
Symmetric Encryption
This is the simplest encryption technique, in which the same key is used to encrypt and decode data. Symmetric encryption is quick and efficient, making it ideal for encrypting data.
The key, however, must be kept safe and shared with only authorized persons.
Asymmetric Encryption
This approach employs two keys: one for encryption and one for decryption. The public key is widely distributed, while the private key is kept private.
Because even if the public key is captured, it cannot be used to decode the data without the private key, asymmetric encryption is more secure than symmetric encryption.
It is, however, slower and more inefficient than symmetric encryption.

Hashing
This method generates a fixed-length string of characters that cannot be reversed. Hashing is often used to validate data by comparing the original data’s hash to the encrypted data’s hash. Because it cannot be decoded, this approach is not suited for encrypting sensitive data. However, it is beneficial for verifying data integrity.
Specific Encryption Algorithms
There are numerous encryption algorithms available today. Here are five of the most common:
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): A trusted standard algorithm that the US government and other organizations utilize. AES also provides 192- and 256-bit keys for demanding encryption jobs, despite the fact that 128-bit keys are very efficient. With the exception of brute-force assaults, AES is generally considered impregnable. Many internet security experts believe AES will become the industry standard for encrypting private sector data.
- Triple Data Encryption Standard: Triple Data Encryption Standard, or 3DES, The successor algorithm to the original Data Encryption Standard (DES), designed in response to the discovery by hackers of how to crack DES. 3DES is a symmetric encryption method formerly the most widely used symmetric algorithm in the corporate world.
- Blowfish: This symmetric utility divides messages into 64-bit chunks and encrypts each separately. Blowfish has a reputation for being fast, adaptable, and unbreakable. It’s in the public domain and, therefore, free, adding to its allure. Blowfish is extensively used in e-commerce platforms, payment security, and password management solutions.
- Twofish: Successor to Blowfish. A method for symmetric encryption that decrypts 128-bit data blocks without needing a license. Furthermore, Twofish encrypts data in 16 rounds regardless of the key size. Twofish is suitable for software and hardware configurations and is often considered one of the quickest. Numerous modern file and folder encryption software solutions use this method.
- Rivest-Shamir-Adleman triad (RSA): A method of asymmetric encryption that factors the product of two huge prime integers. Only a person who knows these two digits can decode the message successfully. RSA is widely used for digital signatures, despite the technique’s inefficiency in encrypting large quantities of data.
Best Practices for using Encryption
Using encryption is an important part of protecting sensitive data in your business. Adopting the following best practices will help ensure that your business’s data is secure and protected.
Here are some best practices to follow when using encryption:
- Use Strong Encryption Algorithms: Choose a secure algorithm that has been validated against assaults when deciding on a method of encryption. Avoid employing algorithms that attackers readily break.
- Keep Encryption Keys Secure: Encryption keys must be safeguarded and only shared with authorized parties. Consider implementing a key management system to safeguard and manage encryption keys.
- Encrypt Data In Transit And At Rest: Data should be encrypted during network transmission and storage on devices or servers. This will ensure that the data is always protected.
- Regularly Review and Update Encryption Practices: Encryption is a recurring process. Review and update encryption procedures on a regular basis to ensure that they remain effective and compliant with the most recent threats and legislation.
- Train Employees on Encryption Best Practices: Your workers play a vital role in maintaining data security. Instruct them on encryption best practices, including how to identify sensitive data, how to utilize encryption software, and how to exchange encrypted data securely.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication: Multi-factor authentication increases the security of your encryption procedures. Consider using multi-factor authentication to get access to encrypted data and systems.
- Follow Compliance Regulations: There may be compliance requirements for your business that require you to encrypt specific types of data. Be sure to adhere to these rules to avoid penalties or legal trouble.
Next Steps: Implementing Encryption in your Business
Implementing encryption in your business is crucial for protecting sensitive data from cyber threats and breaches.
Utilizing encryption needs considerable thought and preparation, but the rewards are substantial. Implementing encryption in your organization and adhering to best practices can assure the security and protection of your firm’s data.
Remember that encryption is not a one-time operation; it must be reviewed and updated frequently to be effective against emerging cyber threats. By remaining alert and proactive regarding your organization’s data security, you may reduce the danger of a data breach and preserve your company’s brand and bottom line.
Here are some steps to take when implementing encryption in your business:
- Conduct a security audit: Conduct a security audit to identify vulnerabilities in your current encryption practices and other areas of your business’s security. This will help you understand where improvements need to be made and where additional encryption is needed.
- Identify the data: Next, identify any sensitive data that needs to be encrypted. This could include financial data, customer information, employee data, trade secrets, and other confidential information.
- Update encryption policies: Review and update your encryption policies to align with the latest industry standards and best practices. This includes updating encryption algorithms, key management, data storage, and access control policies.
- Encrypt data in transit and at rest: Encrypting data in transit ensures that it is secure while being transmitted over networks, such as the internet. Encrypting data at rest ensures it is secure while stored on servers, computers, and other devices.
- Train employees on encryption best practices: Your employees play a crucial role in data security. Train them on encryption best practices, such as how to identify sensitive data, how to use encryption software, and how to securely share encrypted data.
- Regularly review and update encryption practices: Encryption is not a one-time process. Regularly review and update your encryption practices to ensure they are still effective and current with the latest threats and regulations.

