Vulnerability Assessments: 4 Crucial Steps for Identifying Vulnerabilities in your Business

There are times when security professionals will need to assess the vulnerability of their systems, especially when evaluating the results of automated reports. In addition to the revealed information, vulnerability assessments will provide excellent opportunities for a strategic viewpoint for potential security threats.
On this page:
What is a Vulnerability Assessment?
A core part of your technology risk management strategy, a vulnerability evaluation or assessment, is a mechanism for identifying security flaws within information systems. It determines if and how a system is exposed to known threats and designate severity levels accordingly.
- Concentrated evaluations of the adequacy and execution of technical, operational, and management security controls
- Makes a concerted effort to discover all vulnerabilities in the systems and components
- Contributes to risk management
- Full knowledge and assistance of systems administrators
- No harm to systems
Related: Software Application Security: Best Practices all Businesses must follow
It will also make recommendations for actions that can be taken to mitigate the threats if possible. The types of threats that these evaluations cover include:
- Faulty authentication which comes from increasing authorizations
- Insecure defaults resulting from software that is released with settings that are not secure
- Code-based injection attacks such as XSS or SQL
Types of Assessments
A vulnerability assessment is an examination of vulnerabilities in IT systems at a certain point in time with the goal of detecting system flaws before hackers may exploit them.
Security assessments come in four types: application scans, network or wireless assessment, database assessment, and host assessment.
- Application scans – These scans identify security gaps within web-based applications as well as the source code. It is automated and conducted either dynamic/static or front end
- Network or wireless assessment- This involves evaluating practices and policies to stop unauthorized access into public or private networks and resources that are network accessible
- Database Assessment – The evaluation of large data systems or databases is undertaken to identify misconfigurations and flaws, including rogue databases and test/dev environments that are insecure, and will classify any data deemed sensitive over the entire infrastructure
- Host assessment – This involves a review of critical servers which might be susceptible to attack should they not be sufficiently tested or generated from a machine image

Setting the scope for Vulnerability Evaluations
There is a difference between presuming you’re exposed to a cyberattack and understanding exactly how vulnerable you are. The purpose of vulnerability assessment is to close this gap.
A vulnerability assessment examines some or all of your systems and creates a comprehensive vulnerability report. This report can then be used to address the issues discovered to avoid security breaches.
Assessments of vulnerability may contain the following components:
- External Vulnerability Assessment — Identifies external vulnerabilities.
- Internal Vulnerability Assessment — Identifies internal network vulnerabilities.
- Social Engineering – Identifies human resource weaknesses and training shortfalls.
- Physical Security Assessments – Identifies physical security weaknesses.
Vulnerability Assessment vs Penetration Testing
Vulnerability assessments detect vulnerabilities but do not attempt to exploit them. Numerous vulnerability assessments use a scanning programme that ranks the vulnerabilities, allowing security experts to prioritize which ones to fix first.
Penetration testing is a distinct type of security testing that begins with a vulnerability assessment and employs human testers to exploit flaws to acquire unauthorized system access.
Organizations use penetration testing to mimic the amount of harm an attacker could cause if they fully exploited vulnerabilities. Vulnerability assessments, which are generally automated, can be used with penetration testing to provide frequent insight between penetration examinations.
CHARACTERISTIC |
VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENTS |
PENETRATION TESTING |
GOAL |
Uncover known vulnerabilities across the environment |
Identify and exploit vulnerabilities to demonstrate how criminals might use them to move laterally or deeper into the environment. |
SCOPE |
Broad – scanning the surface |
Focused, deep |
PERFORMED BY |
Automated tool(s) with human oversight |
Experience hackers, cyber security professionals |
OUTCOME |
List of vulnerabilities |
A prioritized collection of vulnerabilities, exploitable techniques, narrative walkthroughs of attack scenarios, and advice for repair |
NEXT STEP |
Prioritize remediation and patching |
Apply patches and other security updates that significantly minimize risk. |
BEST FOR |
Obtaining an overview of an organizations security posture |
Understand all facets of an organizations security posture |
Performing a Vulnerability Evaluation
Furthermore, a rising number of businesses rely on technology to carry out their everyday operations. Yet, cyber dangers, such as ransomware, can bring your firm to a standstill in an instant.
Related: Responding to a Ransomware Attack: The crucial initial steps
It is widely recognized that prevention is better than cure, resulting in the increased importance of cybersecurity and a desire for solutions to ensure its resilience.
More SaaS customers, for example, now want frequent vulnerability assessments, and having proof of security testing can help you generate more revenue.
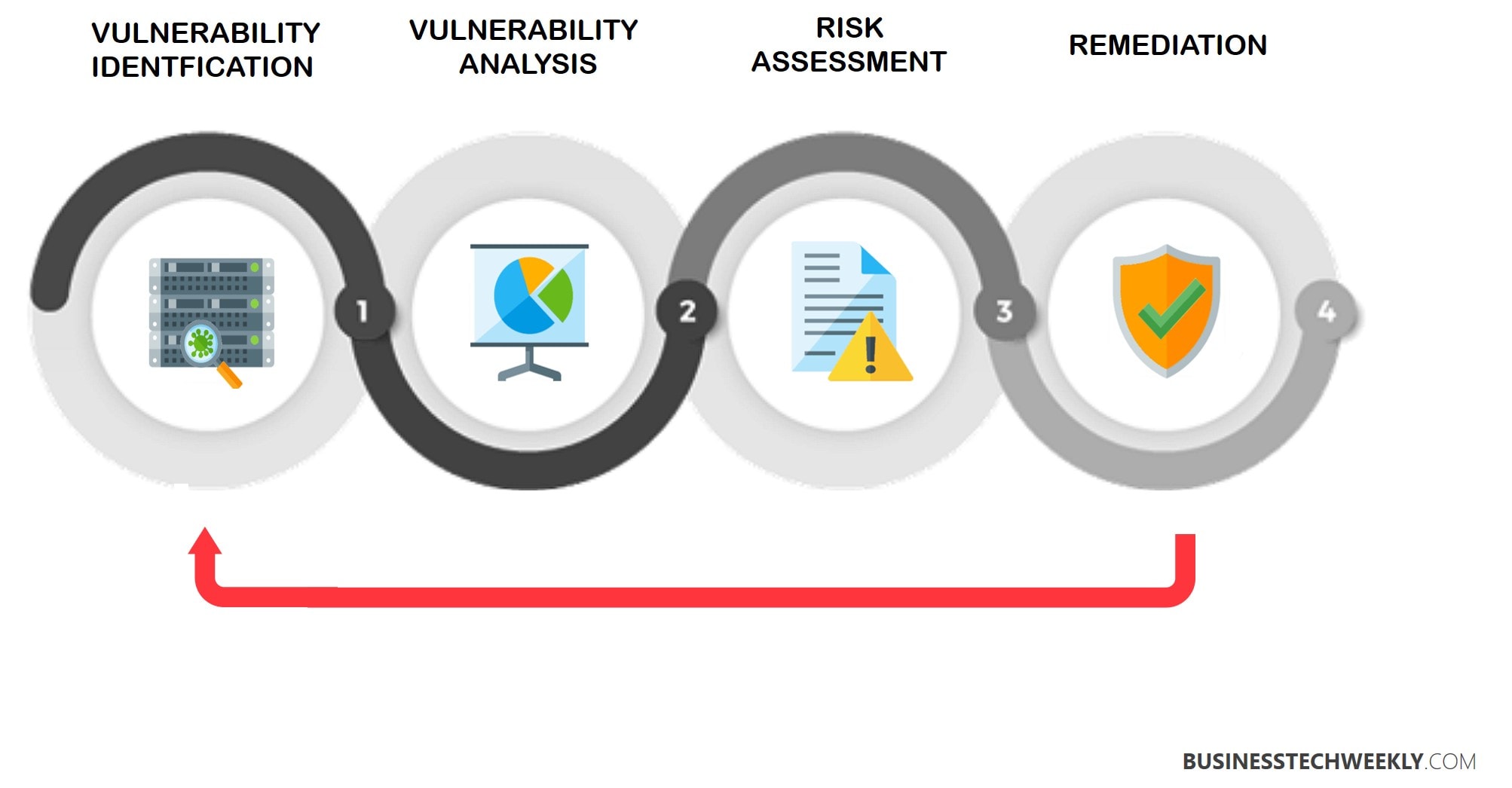
Security scanning can be broken down into four steps: analysis, testing, assessment, and remediation.
- Identification – The goal here is to locate the root cause and source for the vulnerability. System components must be reviewed individually, as the source of the exposure might be something like an older version for a library that is open source. In this instance, upgrading your library would resolve the issue.
- Analysis – The purpose of the analysis is to formulate a list of vulnerabilities for the application. Security experts will review application health, including servers and other systems, using automated tools to scan them.
These experts might also use security databases, exploits announced by vendors, threat-based intelligence feeds, and management asset systems.
- Assessment – Assessment is used to prioritize the vulnerabilities. Severity scores will need to be assigned to each exposure. These scores will be dependent on the specific affected systems, the type of vulnerable data, the endangered business functions, and how easily attacks can be conducted. It also conveys the possible damage that the exploit might cause.
- Remediation – This final step involves sealing the security gaps which have been discovered and analyzed. It will usually include a collaboration of security personnel and operations or development teams who will need to decide the wisest approach for mitigation. Measures which might be taken include:
- Introducing updated security tools or procedures
- Making changes to the configuration or operational methods
- Creating and installing security patches
This process is ongoing and should never be a one-off. Institutions have to operationalize their procedures and then repeat them regularly in specific intervals. It is also essential to encourage collaboration between development, security and operation teams.
The 4 Most Important Steps for Evaluating Vulnerability
Here is a proposed four-step method to start an effective vulnerability assessment process using any automated or manual tool.
Initial Evaluation
The first step in evaluating vulnerability is to determine your assets and then designate every device’s critical and risk value (which should be determined by client input). An example of this would be the security scanner. It is essential to define the importance of each network device or the ones you intend to test.
You’ll also need to know how these devices are accessible by company staff, including administrators. Key factors that will need to be considered include risk tolerance, risk appetite, and treatment. Other factors may consist of device countermeasures, mitigation practices for every device and organizational impact analysis.
Baseline System Definition
The second thing you’ll need to collect information regarding your systems before the vulnerability evaluation. It would help determine whether the device has services, processes, or ports that are open and shouldn’t be.
Furthermore, it is critical to know the software and drivers that have been approved and should be part of the device’s installation and rudimentary configuration. Any perimeter devices should not have default usernames for administrators configured.
One way to ascertain the public info accessible depends on configuration baselines is by banner grabbing. Are the devices transmitting logs into the SIEM or Security Information and Event Management system? Have the logs been saved within a centralized repository? Collect all the vulnerabilities and public info for each device platform, the vendor, version, and other pertinent details.
Execute Your Vulnerability Scan
Now you want to use the correct policy for the scanner to achieve the right results. Before beginning your vulnerability scan, check the compliance requirements determined by your industry, and choose an ideal date and time.
Knowing the context of your client industry will help you know when the scan should be performed or whether segmentation is preferable. You’ll need to redefine and then acquire approval to start the scan.
To gain the most optimal results, you’ll want to utilize plugins and tools which are related. Examples of these include:
- Quick and stealth scans
- CMS based web scans like Drupal, Joomla or WordPress
- Aggressive scan
- Firewall scans
- Full scans, which include DDoS (denial of service) attacks
- Data standards for payment cards such as PCI DSS
- OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) checks
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability) scans
Vulnerability Evaluation Report Creation
The 4th and final step is creating the report itself. Pay close attention to details and create additional value during its recommendation phase. To obtain genuine value from your final report, including recommendations determined on your original assessment goals.
Furthermore, adding additional risk mitigation procedures dependent on the importance will lead to tremendous long term success. Mention findings that are associated with possible gaps for the baseline system definitions and results.
This should include misconfigurations and other significant discoveries. Recommendations for correcting these issues must be thoroughly highlighted. Other things to include in the final report are:
- The vulnerability name
- Its score is based on CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures)
- The date the vulnerability was discovered.
- Details involving affected systems
- A comprehensive description of vulnerabilities
- The time needed to correct it
- How the vulnerability was corrected
- PoC (Proof of Concept) regarding system vulnerabilities
Once you have this information, the recommended actions phase will showcase a comprehensive understanding of every aspect of your security system.
Next Steps: Building a Vulnerability Management Program
New vulnerabilities are found daily. Vulnerability management (VM) is a process for identifying, eliminating and controlling vulnerabilities. The vulnerability management programme makes use of specific software and procedures to assist in eradicating discovered vulnerabilities.
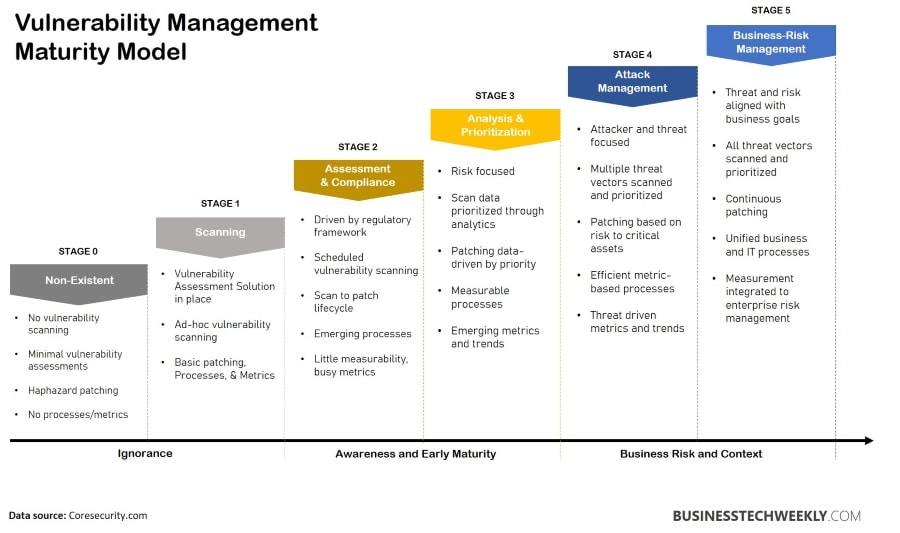
Scaling the vulnerability management programme is critical to meeting the business’s requirements, complexity, and IT environment. Even the smallest businesses can handle vulnerabilities manually.
On the other hand, automation and workflow are advised to assure consistency, compliance (job completion assurance), and cost savings. The vulnerability management maturity model depicted below demonstrates the vulnerability management program’s scalability.
A robust cyber security posture necessitates regular vulnerability evaluations. Because of the sheer amount of vulnerabilities and the complexity of the ordinary company’s digital infrastructure, an organization is nearly sure to have at least one unpatched vulnerability that puts it at risk.
Finding these flaws before an attacker might mean the difference between a successful attack and a costly and humiliating data breach or ransomware outbreak.
One of the best things about vulnerability assessments is that you can perform them yourself and even automate them. You can significantly reduce your cyber security risk by investing in the correct technologies and running frequent vulnerability scans.

