Your Essential Guide to Creating a Crisis Management Plan

On this page:
What is a Crisis Management Plan
A crisis management plan, or CMP, is a detailed plan that prepares an organization to effectively react to emergencies or unforeseen scenarios.
It should be a blueprint for minimizing harm and ensuring a fast recovery of business operations.
The plan serves as an important guide of internal governance during a crisis, ensuring that a consistent framework for decision-making is maintained.
By defining roles and responsibilities, a CMP prepares an organization with a clear plan for responding quickly and efficiently in the event of an emergency or unexpected situation.
Having a documented plan is essential to streamline crisis response efforts, ensuring that everyone knows their duties and how to execute them effectively.
RELATED: Cyber Crisis: Navigating through a Cyber Incident
Definition of a Crisis Management Plan
A crisis management plan delineates the roles and responsibilities of every team member in black and white.
It does so by ensuring that there is a roles and responsibilities matrix, often called a RACI chart.
This chart categorizes action-oriented tasks to specific roles, creating clear accountability and credibility to decision-making positions in your crisis management plan.
The CMP should be a comprehensive blueprint for the ways in which the organization reacts in times of crisis.
It provides clear crisis management procedures and response steps to ensure proper management. Having a clear, documented plan in place is crucial for navigating any crisis.
It provides a clear outline that enhances collaboration and reduces uncertainty.
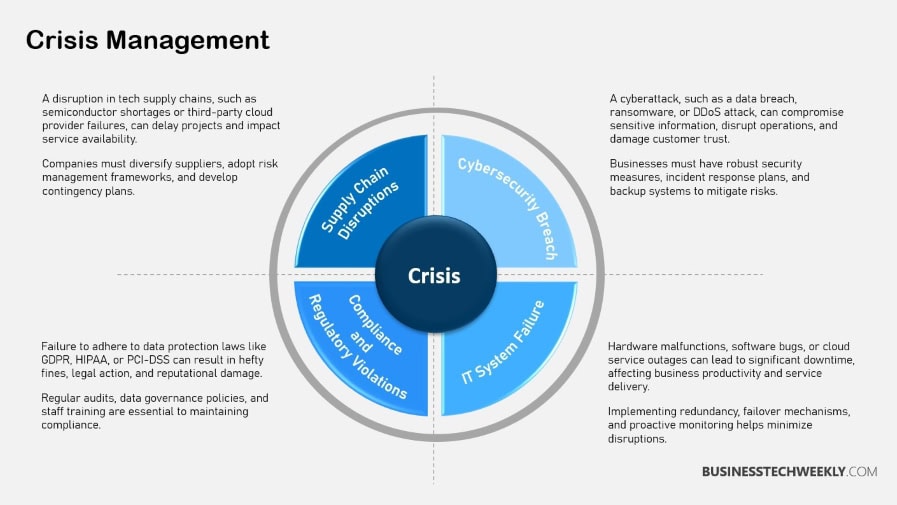
Importance for Businesses
A well-developed crisis management plan is the key to avoiding hasty decisions that often lead to disaster during high-pressure moments.
When crises strike, everyone’s stress level increases, often causing even more errors to be made.
A CMP can keep staff focused on the emergency at hand and lower employee uncertainty by supplying clear directives and guidelines.
Statistics show that just 54% of businesses currently have and actively follow a proactive crisis management plan.
This highlights the important reality that we must be better prepared for the inevitable disruptions ahead. Creating a solid crisis management plan is vital in keeping businesses strong and prepared during any crisis, protecting their business and reputation.
Users of Crisis Management Plans
Key stakeholders including executives and crisis management teams are the main users of crisis management plans.
These plans help an organization’s communications, HR, legal, and compliance departments by giving them a clear picture of what is going to be communicated and when.
Beyond your own organization, a CMP is essential for external stakeholders such as customers and partners. It demonstrates the organization’s commitment to intentionally navigating crises. A CMP is a collaborative process with all necessary stakeholders involved.
This alignment helps improve communication, build trust, and increase transparency when times are tough.
Key Components of a Crisis Management Plan
When establishing a thorough crisis management plan, these key components are essential to achieving readiness and developing a culture of resilience.
Among other things, a detailed plan tackles the emotional, operational, and communicative aspects of a crisis, empowering your organization to steer through any storm.
Here’s a deeper dive into the major components that should be included.
Essential Elements to Include
A well-crafted crisis management plan incorporates ten essential elements.
These include risk identification, assessment, and prioritization to understand potential threats.
Activation protocols outline clear steps to initiate the crisis response swiftly. Tailored action plans for different scenarios allow for specific responses, such as natural disasters or cyber-attacks.
Training and drills ensure readiness and familiarity with procedures.
Documentation and record-keeping maintain transparency and accountability.
Communication Protocols
Strong communication strategies are key during any crisis. Internally, communicating both with and to your team is important.
Externally, public relations needs to be taken on through official spokespersons.
Key communication channels such as emails, social media, and press releases provide diverse methods to share information quickly and accurately.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Conducting a detailed risk assessment identifies potential threats.
Mitigation strategies, such as implementing safety measures, reduce these risks.
Ongoing risk evaluation keeps your plan current, ensuring that you can adapt to new challenges as they arise.
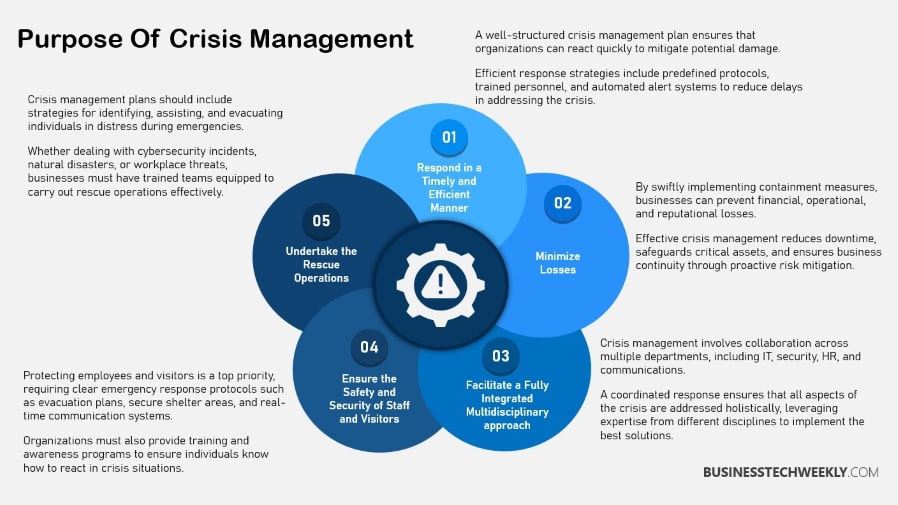
Developing a Crisis Management Plan
To develop a CMP, there are several important steps to follow.
Taking these steps will help your organization weather even the most unexpected of storms.
Here’s a bullet list of essential steps:
- Identify potential crisis scenarios
- Set objectives and goals
- Recognize stakeholders
- Establish a communication hierarchy
- Assign roles and responsibilities
- Develop response strategies
- Conduct training and simulations
- Review and update the plan regularly
1. Identify Objectives and Goals
It is important to set clear objectives that match your organization’s mission and values.
These objectives should inform any crisis response you make, keeping your team oriented and your vision clear in the darkest hour.
Those strategic goals should be narrowed down and prioritized, stressing the importance of working towards achieving measurable outcomes.
This creates the opportunity to test for the effectiveness of your CMP, making sure your organization is prepared to recover quickly and efficiently.
2. Recognize Stakeholders Involved
Determining which stakeholders are most important, including members of your team and external partners, is essential for maximizing your crisis management efforts.
Identifying their needs and concerns helps create a holistic approach to crisis response.
Bridging the gaps collaboration among all stakeholders, including government agencies, private sector partners, and community organizations, is key to success.
RELATED: IT Resilience: Ensuring Business Continuity during Disruptions
3. Establish a Communication Hierarchy
Establishing a clear communication hierarchy helps streamline the flow of information during a crisis.
Defining roles and responsibilities within this structure avoids confusion and enables timely, accurate communication to be provided.
This preserves your credibility and helps ensure you are saying the same thing, particularly when speaking through the media.
4. Assign Roles and Responsibilities
Decisively delineating roles and responsibilities for each crisis management plan team member is key.
It is important that team members know their individual roles in order to carry out the plan successfully.
Accountability is key. Accountability is a huge part of what keeps everyone engaged and committed to staying on course.
5. Develop Crisis Scenarios and Responses
Identify relevant crisis scenarios that might occur in your organization. Add scenario-specific response strategies, focusing on the need for flexibility to respond as situations change.
Training on the CMP, including communication protocols and crisis action plans, helps prepare everyone.

Implementing and Testing the Plan
Effectively implementing a crisis management action plan is the best way to protect your organization from any future crises.
A solid crisis management plan not only guarantees that operations can continue but also safeguards reputation and bottom line.
Organizations with tested incident management programs save an average of $2.66 million on breach costs compared to those without such a response plan.
Testing the plan is crucial, as 80% of organizations that evaluate their crisis management strategy experience fewer crises.
Create an Incident Response Team
An inclusive, dedicated incident response team is essential to implementing your crisis management plan.
That team should be cross-trained and prepared to jump into many different types of crisis scenarios. Leadership within this team is essential to navigate the complexities of a crisis effectively.
For instance, having a single leader increases the likelihood that decisions are made quickly and that there is clear communication.
Conduct Regular Drills and Simulations
Continual drills and simulations will help ensure the plan works under pressure.
These practices foster accountability, improve transparency, and build trust while facilitating team performance evaluation and area-of-improvement identification.
Regular and ongoing training develops a culture of preparedness that inspires employees to respond quickly and confidently when a crisis occurs.
Consistent training makes them more familiar with emergency procedures so they can shave response time and avoid costly last-minute modifications.
Evaluate and Revise the Plan Continuously
Ongoing evaluation and revision are key to ensuring the crisis management plan remains relevant. Adding lessons learned from emergency drills and actual events makes it even more useful.
Regular updates, at least annually or with significant organizational changes, ensure alignment with changing risks and organizational needs.
Incorporating it into the organization’s overall risk management strategy helps ensure that the plan aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
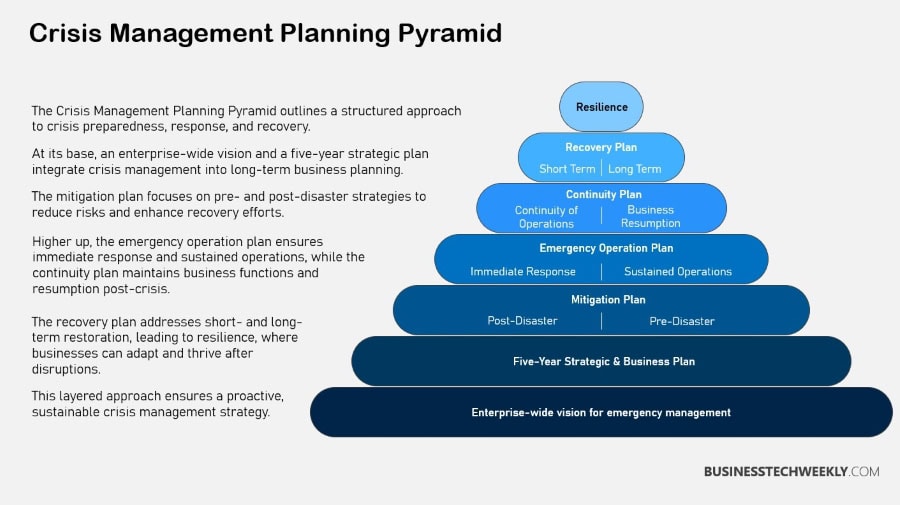
Crisis Management Strategies and Best Practices
Crisis management strategies are the foundation of an effective crisis management plan (CMP).
They’re incredibly important during unexpected events to help bring structure and stability. Proactive planning is crucial, enabling you to foresee what crises might occur and plan definitive steps to reduce the damage.
With this preparation, you’ll be able to respond quickly to create the least amount of disruption possible and save your organization’s good name.
Communication, both internal and external, is key, keeping everyone informed and on message. By designating a spokesperson as the only point of contact, one person can maintain clear communication when the media starts to ask pointed questions.
Effective Spokesperson Response Techniques
Properly training these spokespersons in best communication practices can make or break a crisis response.
They need to communicate effective, concise messages that provide transparent reassurance to stakeholders. Transparency and honesty go a long way, building trust and credibility.
Managing media inquiries requires strategic planning, ensuring accurate information dissemination while maintaining public perception positively.
Proactive Damage Control Measures
Taking proactive steps through a crisis management action plan reduces the extent of damage before a situation can escalate.
Quickly addressing a crisis helps preserve your organization’s reputation, reducing the potential for future damages.
- Establish clear communication channels.
- Monitor media coverage regularly.
- Coordinate with relevant stakeholders promptly.
Utilizing Social Media Responsibly
Best practices for social media engagement include having a crisis communication plan to address various crises effectively.
- Respond to inquiries promptly.
- Maintain a consistent tone across platforms.
- Provide factual updates regularly.
Collecting and Analyzing Customer Feedback
Create structured ways to gather customer feedback in the midst and aftermath of crises.
By taking time to analyze feedback, opportunities for improvement can be realized, making future crisis response more effective.
When businesses address customer concerns quickly and proactively, they can rebuild that trust, creating stronger relationships and increasing customer loyalty.
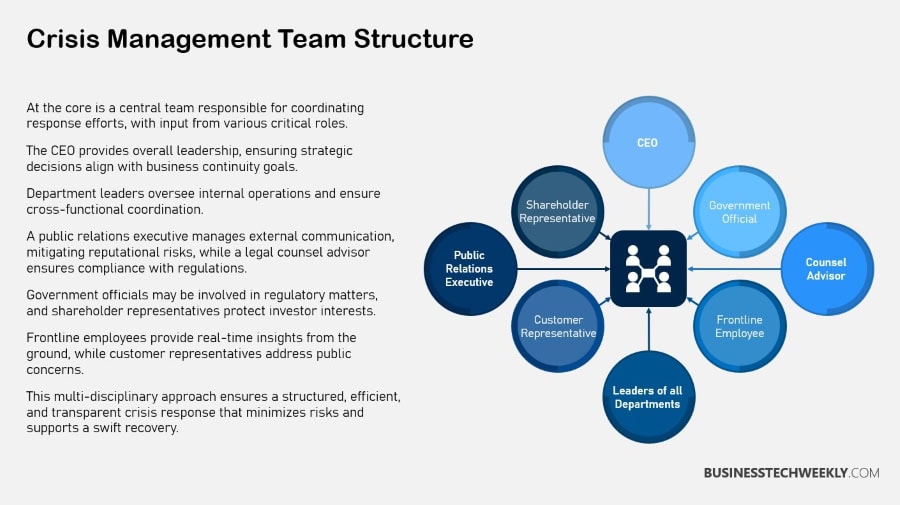
Crisis Communication Strategy Importance
Having a solid crisis management action plan in place is key to controlling the narrative and public perception of your organization during tumultuous times.
With the right crisis communication plan, you can better manage the narrative and maintain trust. Confusing or conflicting messages will quickly destroy any credibility built up, so clear and consistent communication is vital.
When you get information out ahead of a crisis first, you help set that narrative, which stifles rumor.
At the end of the day, we can’t prevent crises from happening. In addition to protecting your reputation and financial well being, by increasing the spread of accurate information, it truly serves the public good.
RELATED: Business continuity and crisis management
Given that 90% of all crises are caused by human error, the importance of crisis preparedness cannot be overstated.
An internally shared communication plan with frequent updates and guidance will prepare employees to address public inquiries effectively and knowledgeably.
Creating a dedicated crisis management team is the first step to developing an effective strategy.
By updating the crisis management plan template on a quarterly basis, you will ensure that the plan continues to mitigate evolving risks.
- Point of contact for the crisis communication team One of our favorite tactics – regular scenario reviews. Communicate change internally.
- Internal communication strategy
- Media relations strategy Human-centered stakeholder engagement
Establishing Clear Communication Channels
Establishing clear communication channels is critical for ensuring accurate, up-to-date information is delivered quickly.
Clear, accessible communication for all stakeholders and having a plan to share that information avoids panic and protects public trust. Technology is key to here.
Tools such as email notifications, social media, and instant messaging apps increase the pace and accuracy of communication within and outside your organization.
During a crisis, these communications channels can be the best way to reach all constituents quickly, offering critical updates and instructions.
Preparing Fact Sheets and FAQs
Developing one pagers and FAQs provides straightforward information to stakeholders. These materials should be easily accessible and updated frequently.
They stop the spread of misinformation by addressing the issues directly with easy-to-understand answers to FAQs.
Clarity and accuracy in these documents are vitally important in a crisis. They serve as your single source of truth.
This transparency goes a long way in keeping public trust and fostering communication.
Crisis Management Standards and Frameworks
Overview of Industry Standards
As you prepare to develop your crisis management action plan, industry standards will lead the way.
Use these standards to develop a robust framework for crisis preparedness. These standards, frequently developed by industry professional organizations, give you an authoritative outline of best practices to follow.
You will inevitably come across frameworks like ISO 22301 that focus heavily on business continuity.
Another one you will encounter is ISO 31000, which is all about managing risk effectively. These standards help ensure that you have the optimal tools and approaches at your disposal to tackle various crises head-on.
Proactively work to implement a crisis management strategy and framework.
RELATED: Risk Management Simplified: A quick Overview to Managing Risks
Developing crisis communication plans is another key component of these standards.
To do that, you must create robust channels for messaging both in and outside of your organization.
This includes being very clear on who to notify in the event of a crisis, which is key to maintaining strong lines of communication.
When a data breach occurs—and they will occur—a well-tested emergency response plan will save you millions.
Specifically, organizations with these proactive programs mitigated breach costs by an average of $2.66 million.
These standards aren’t hard and fast requirements. Rather, they’re living, breathing tools that you must constantly update and adjust to remain relevant.
Comparison with Business Continuity Plans
Crisis management plans address the short-term response to an unforeseen occurrence and guide you through the storm of confusion that ensues. Business continuity plans are concerned with ensuring long-term operational continuity.
Consider a crisis management plan your checklist of actions when the storm is upon you.
Your business continuity plan is your roadmap to recovery, guiding you safely through the other side of chaos.
These plans, though, aren’t cut off from each other. They complement one another to make sure that your organization stays healthy even when faced with challenges.
For instance, during a cyber-attack, your crisis management plan may outline how to contain the breach and maintain communication with stakeholders.
In the meantime, your business continuity plan has kept your essential operations running, maybe by moving to emergency backup systems.
We’ve learned that integrating both plans is key. It helps make sure you’re not only responding effectively to a crisis, but keeping your operations running efficiently.
This integration even extends to bi-annual joint training conferences. It includes emergency drills, making sure that everyone in your organization understands their responsibilities and can respond quickly.
RELATED: Maximizing Business Resilience: The Importance of Risk Assessment in Business Continuity Planning
Key Points to Remember
Crafting a robust crisis management plan ensures that you’ll be prepared to respond no matter what happens. Your plan should address all of it.
- Having a crisis management plan (CMP) is crucial for any organization. It allows them to proactively prepare for emergencies, minimizing damage and allowing for a faster recovery. It instills a clear framework for how decisions will be made in a crisis that can avoid reactionary decision-making in a time of high stress.
- Essential components of a CMP include risk assessment, communication protocols, and detailed response action plans tailored to specific crisis scenarios. Comprehensive planning is crucial to address various potential crises.
- Crisis management plans are critical for all businesses because they keep employees focused on protecting what matters most, minimize uncertainty, and promote a smooth, organized response. Statistics on corporate crises emphasize the importance of not only being prepared, but being ahead of the crisis.
- Key stakeholders, including executives, crisis teams, communications, and HR, use CMPs to inform their response in times of emergency. These plans are valuable to external stakeholders, such as customers and partners, as they foster transparency and trust.
- Creating a crisis management plan means defining specific goals, identifying key stakeholders, and creating a chain of communication. Assigning roles and responsibilities helps ensure accountability, and developing crisis scenarios and responses helps you be prepared.
- Implementation and ongoing testing of the CMP through regular drills, simulations, and constant evaluation are important. Implementing this practice promotes a culture of preparedness and helps ensure the plan continuously develops alongside shifting risks and organizational requirements.

