Developing an Effective Cloud Security Strategy

On this page:
- What is Cloud Security Strategy?
- Why a Cloud Security Strategy is Important
- Key Principles for Cloud Security
- Shared Responsibility Model Explained
- Build a Robust Cloud Security Strategy
- Essential Elements of Cloud Security
- Overcome Cloud Security Challenges
- Modern Cloud Security Best Practices
- Evolving Threat Landscape Impact
- Measuring Cloud Security Effectiveness
- Key Points to Note
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Cloud Security Strategy?
Essentially, a cloud security strategy is a well-organized approach that addresses the protection of data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud.
Organizations have already made the race to the cloud to increase flexibility and agility. This change further emphasizes the need for a strong security strategy, an imperative that all businesses should adopt.
First, it does an excellent job at protecting sensitive information. In parallel, it will help you unlock all the advantages of cloud computing without compromising data integrity and privacy.
A strong strategy sets the stage to meet the cloud security challenges that set it apart from traditional IT environments.
More importantly, it dovetails perfectly with the organization’s larger security goals.
The Five Pillars of Cloud Security Strategy
At its foundation, a cloud security strategy revolves around 5 main pillars.
- Encryption for Data Protection: Encryption protects data, in-flight and at-rest. It provides for the confidentiality of sensitive data by preventing unauthorized parties from accessing sensitive information.
- Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM): Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) strategies are foundational. They establish strict guidelines that dictate who can access what across your entire cloud ecosystem. Strong IAM mitigates the threat of unauthorized access, which is particularly important in today’s world of remote work and global collaboration.
-
Intrusion Detection & Cyber Monitoring: Intrusion detection systems and continuous cyber monitoring practices proactively identify and mitigate threats as they occur. They address the shocking 75% increase in cloud breaches seen in the last couple of years.
-
Cloud Footprint Visibility & Logging: Knowing the extent of your organization’s cloud footprint is the starting point of creating a security strategy. Once it is documented, ongoing logging and monitoring gives you real-time visibility into what’s happening in the cloud, allowing you to identify anomalies sooner.
-
Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP): A consolidated Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) addresses these visibility gaps. It unifies security tooling throughout CI/CD pipelines, enabling development, operations, and security teams to respond to threats and eliminate them more quickly and intelligently. This unified coverage, controlled from a single console, helps you rest assured that nothing within your cloud environment is falling between the cracks.
Aligning Cloud Security Strategy with Business Goals
Cloud security strategy should also reflect the high-level goals of the organization, keeping messaging consistent and effective across all security layers.
Consistent communication, updates, and scheduled reviews are important.
RELATED: 5 Cloud Security Standards that every Business should consider
These strategies are more than one-off exercises. They are dynamic processes that continuously adjust to the rapidly evolving threat landscape.
When security by design is prioritized, organizations can drive the transformative advantages of cloud computing while keeping security agile and effective.
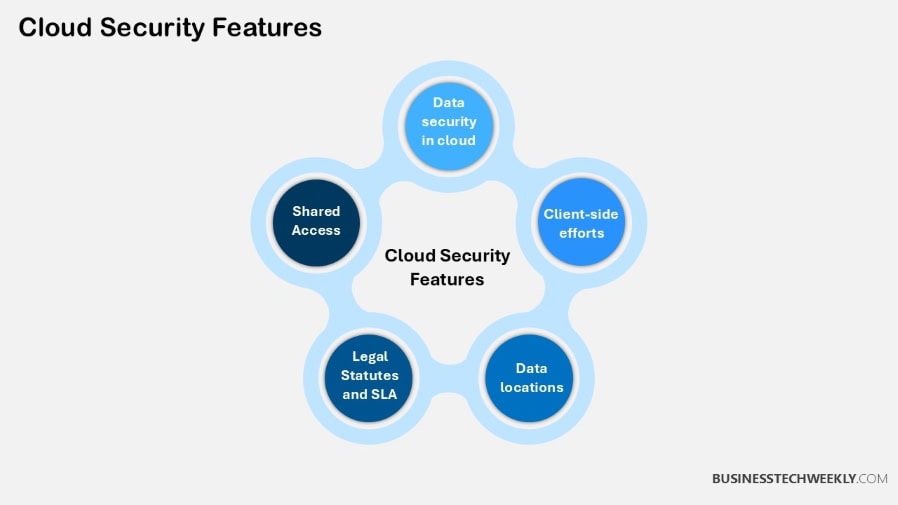
Why a Cloud Security Strategy is Important
The increasing reliance on cloud platforms like Microsoft 365 has brought immense opportunities for businesses to collaborate and innovate, but it has introduced new challenges in safeguarding sensitive data.
Cyber threats targeting cloud environments have become more prevalent and sophisticated.
That’s why having a solid cloud security strategy in place is critical to defend against these rapidly changing threats.
Data Classification: The First Line of Defense
Without the proper measures, organizations risk exposing sensitive data, disrupting business operations, and incurring hefty regulatory fines.
A strong, clear cloud security strategy goes a long way in mitigating these risks, helping organizations avoid data breaches and maintain compliance.
As just one example, using sensitivity labels or data classification to protect your structured and unstructured data with 95% + accuracy.
This great degree of accuracy reduces alerts for false positives. Beyond that, it provides and promotes appropriate classification so that businesses can secure their assets with confidence.
Compliance with regulations such as GDPR or CCPA becomes easier to maintain when your sensitive data is reliably tagged and tracked.
Not only do these measures help minimize risky and expensive compliance missteps, but they build confidence with stakeholders.
Continuous Threat Monitoring for Cloud Security
The second essential component of a cloud security strategy is continuous threat monitoring.
Proactively identifying and mitigating suspicious activities, such as data exfiltration or unauthorized access, strengthens the overall security posture of an organization.
For all Microsoft 365 services, such as SharePoint, OneDrive and Teams, available share real-time detection capabilities.
These solutions allow you to share files and collaborate with ease without compromising sensitive information.
This keeps employees productive and helps protect the integrity and confidentiality of critical business information.
Far from merely mitigating risk, successful cloud security strategies even play a major role in business resilience.
By preventing data loss and maintaining a strong security framework, organizations can avoid disruptions that might otherwise impact operations or damage their reputation.
RELATED: Best Practices for Cloud Security: Safeguarding Your Business Data in the Cloud Era
A secure cloud environment fosters trust among customers and partners, reinforcing an organization’s position as a reliable and responsible entity in its industry.
Unlocking the potential to proactively secure and govern valuable, business-critical data improves operational efficiency and lays the foundation for future growth.
Over the past year, 80% of companies have experienced at least one cloud security incident.
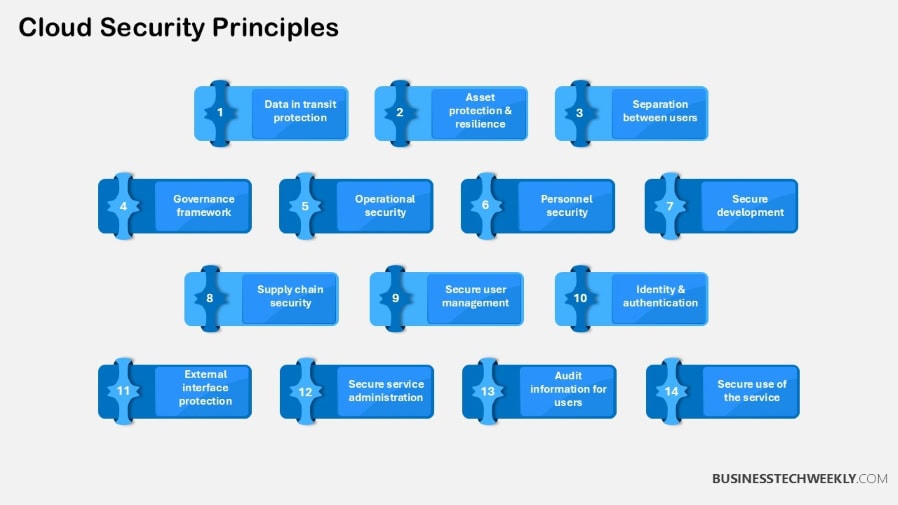
Key Principles for Cloud Security
Cloud security isn’t something that can be left to chance.
A proactive, purpose-built approach is needed to defend your organization’s increased digital assets.
As cloud environments increase in complexity, building more strategic and holistic approaches is necessary.
Prioritize visibility, exposure management, prevention controls, and incident response.
In doing so, you’ll be on your way to building a responsive and resilient security framework that meets the new realities of the cloud.
It is the foundation of any effective cloud security strategy.
Visibility: The Foundation of Cloud Security
Setting an accurate baseline state of visibility into your cloud architecture is crucial.
When you have a clear understanding of your cloud footprint, you can better identify any potential vulnerabilities and make sure no part of your environment goes unchecked.
Use the tools cloud providers give you, such as VPC flow logs, storage access logs, and API logs, to verify expected behavior and expose anomalies.
These logs become critical sources of information. Logs such as API logs can monitor almost every single action taken within your environment, allowing you to understand where the threats may lie.
Extending Visibility with CNAPP
Extended to a coordinated Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP), visibility extends deeper, stitching together the voids between security point tools and CI/CD pipelines.
So logging is important from that perspective. It reveals the reality of your environment, so you can make strategic decisions and respond quickly.
RELATED: Protecting your Data: 10 Tips to Protect your Business Data in the Cloud
Exposure Management: Addressing Security Gaps Before They Become Incidents
Fixing security gaps through exposure management is just as vital.
This preventive mindset includes anticipating risks and addressing them before they become overwhelming and turn into incidents.
Zero Trust principles are a natural complement to this practice.
They require zero trust by necessitating constant validation of every user and every device, even if inside the perimeter.
It is an essential component. IAM is core to this discipline, especially in this cloud context. It provides conditional access so that only trusted users and devices can reach important resources.
When implemented together with exposure management, these precautions form layers of defense that harden your attack surface with the greatest effectiveness.
Prevention Controls: Embedding Security into Development
Prevention controls built from the ground up for cloud environments succeed them in security.
By adopting DevSecOps practices, you can integrate security into every single phase of your application’s lifecycle.
This includes embedding security tools and processes throughout development, deployment, and operational lifecycle, which reduces vulnerabilities at the starting point.
According to industry analysis, by 2026, 80% of enterprises will reduce their security tools for cloud-native applications to three or fewer vendors.
This change will mean both easier prevention of invasion and protection of the lifecycle.
Incident Response: Preparing for the Unexpected
Lastly, well-organized detection and response strategies to handle and recover from incidents are key.
Incident preparation and response is critical, as threats can come without notice.
Cloud providers provide powerful security tools to monitor threats and anomalies so that teams can quickly respond to malicious activity.
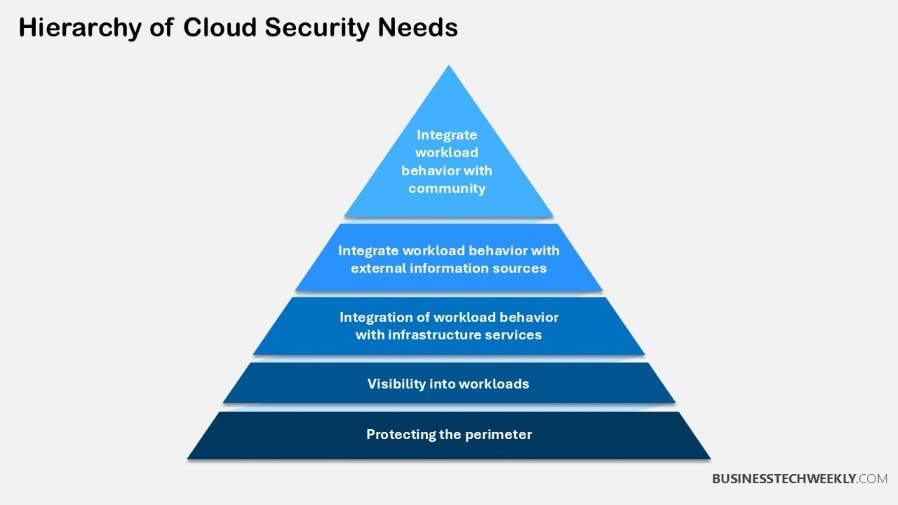
Knowing the Shared Responsibility Model is crucial when developing an effective cloud security strategy.
This model defines a clear division of duties between cloud providers and customers, ensuring that each party knows their specific role in maintaining security within a cloud environment.
It’s not just a matter of sharing responsibility for the same asset but each having responsibility for different elements.
Cloud Provider Responsibilities
Determine what your organization has direct control over vs. What the cloud provider has control over. With that clarity, you can address the most dangerous vulnerabilities better.
Cloud providers are responsible for securing the infrastructure that runs cloud services.
This extends to physical hosts, networks, data centers, and other underlying foundational systems.
For example, they ensure the hardware and facilities running their services are protected from unauthorized physical access or environmental risks.
First, many providers have teams that monitor and respond to security threats that may be trying to stake out their cloud infrastructure.
Their obligations only extend down to this basic level, with everything built on top of that layer left to the customer’s discretion.
Customer Responsibilities
From a customer end—your shared responsibility goes beyond just protecting your data and identities. You are responsible for your data at all times and should know the best security practices to keep it safe from breaches and misuse.
This means maintaining identity and directory infrastructures as well, like on-prem OS level directories or third-party identity solutions.
The Risk of Misconfiguration
Beyond that, application security and configuration management are literally up to you.
In fact, misconfigurations account for up to 99% of cloud security failures.
This statistic highlights the need to ensure that assets like servers, serverless functions, and containerized environments are properly configured and maintained.
Tools like Docker image registries or Jenkins orchestration systems come under your watch and need thoughtful consideration.
The model’s specifics vary greatly by service. This spans from Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) to Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS).
With SaaS, the provider assumes most of those obligations for safeguarding security at the application layer. IaaS moves much more of the responsibility to the customer.
No matter what the model is, the ultimate responsibility of the customer to make proper configurations and manage their environment hasn’t changed.
Engaging with cybersecurity experts helps to enhance your team’s skillset to manage these responsibilities, helping to create a multi-layered defense strategy.
Approximately 31% of cloud data breaches are attributed to misconfiguration or human error, highlighting the critical need for robust identity and access management (IAM) solutions and comprehensive training.
Build a Robust Cloud Security Strategy
Yet in today’s digital-first environment, building a robust, cloud security strategy has never been more important.
Moving to the cloud demands new skills and a forward-thinking strategy.
Organizations need to stay ahead of more sophisticated threats and improved risk postures, all while maintaining an agile, cost-effective, and secure cloud environment.
Start with a Strategic Framework
A strategic framework not only helps mitigate risks but empowers your teams to confidently manage sensitive data and operations.
Configuring your current cloud environment for inefficiencies is a good place to start.
This includes recognizing holes in security postures, legacy configurations, and even where resources are being misapplied.
As an example, organizations moving to new environments such as Microsoft 365 frequently ignore vulnerabilities that are already in place, exposing sensitive data with little or no notice.
Protecting these dynamic environments is more important than ever, as global data breaches are at staggering highs.
Cost and Resource Considerations
While determining costs and resources related to the cloud move is just as important.
By learning the financial and operational impact, you can prudently assign budgets and avoid pouring good money after bad.
For example, integrating with Sentra’s Cloud-native Data Security Platform means your teams can work efficiently and securely across Microsoft 365 services.
That’s SharePoint one day, Teams the next, all without overloading your IT department.
The Power of Measurable Security Goals
Setting measurable security goals specific to your organization’s priorities helps keep them aligned with wider business objectives.
Enterprise-scale data protection and using contextual tags to automate remediation processes are both fundamental goals.
Measurable, concise goals lead to tangible, actionable outcomes. Take accurate data classification, more than 95% accurate, for example.
It is vital to safeguarding both structured and unstructured data. Designing a robust security architecture goes beyond workloads to think about the underlying architecture, such as encryption, monitoring, and DevSecOps best practices.
With DevSecOps, every code commit adheres to the organization’s security benchmarks, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Unlike on-prem IT systems which are months to patch, cloud approaches can deploy updates and new features in real time, increasing security responsiveness.
Comprehensive Security Policies and Continuous Improvement
Having thoughtful, comprehensive security policies serve as the backbone for all day-to-day operations, helping tackle issues such as data classification, compliance, and more.
Sentra’s granular tagging system enables categorization of data at an extremely detailed level while empowering operations at scale with low operational overhead.
Finally, regular testing and refinement through assessments maintain your strategy’s relevance.
By prioritizing accuracy and efficiency, organizations can confidently safeguard their cloud environments, staying ahead in an ever-evolving security landscape.
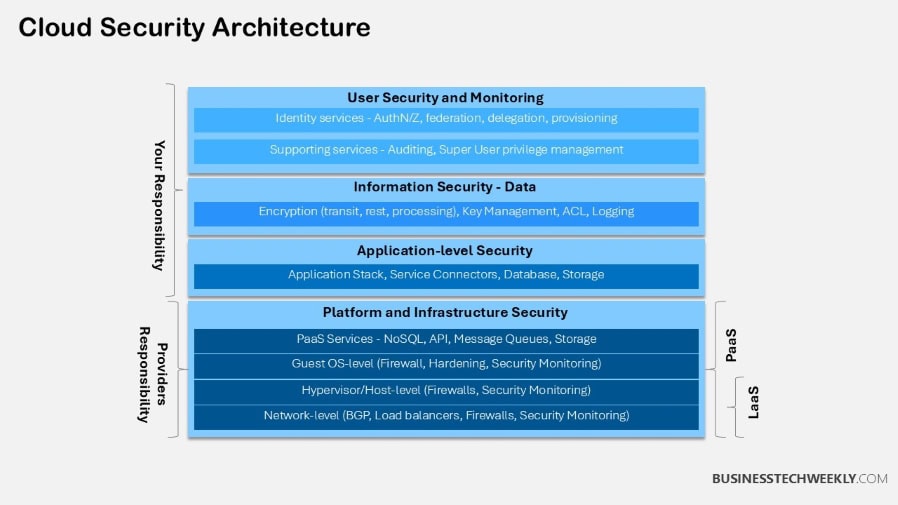
Essential Elements of Cloud Security
Building a robust cloud security strategy involves addressing several key elements to ensure your data, applications, and infrastructure remain secure as your organization evolves.
These very environments provide organizations with overwhelming flexibility and scalability.
They open up organizations to new and different risks, requiring a more proactive and strategic approach to security.
Visibility: The Foundation of Cloud Security
Visibility forms the foundation of any effective cloud security framework.
Without a clear understanding of your cloud architecture, it’s challenging to identify vulnerabilities or gauge your security posture.
Tools like Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) assess your environment across infrastructure, APIs, and SaaS applications, offering a comprehensive view of potential risks.
This visibility enables you to pinpoint gaps and prioritize security efforts, particularly as cloud environments now operate under a shared responsibility model.
Knowing where your provider’s responsibilities end and yours begin is crucial for addressing all potential exposure points.
Exposure Management: Reducing Cloud Risks
Exposure management is just as important and is the process of proactively discovering all exposures and remediating them.
Conducting frequent audits based on frameworks such as PCI DSS and ISO 27001 not only maintains compliance, but lowers risk. With IAM controls, you have greater ability to control who has access to what data and resources.
This simple, proactive measure is one of the best ways to prevent unauthorized access.
This is critically important considering that cloud intrusions have increased by 75%.
Adopting Zero Trust principles improves your exposure management. It requires zero trust verification for each user and device, in or outside the enterprise periphery, and at all times.
Prevention Controls: Strengthening Cloud Defenses
Prevention controls, designed with the cloud environment in mind, are the other security cornerstone.
Use encryption to safeguard data while it’s moving and when it isn’t. Use config management to remove accidental leaks and use automated security tools to automatically check for policy violations and prevent them.
Cloud-native solutions such as CSPM greatly simplify this process, helping to make preventive maintenance uniform and, most importantly, scalable.
Detection & Response: Rapid Threat Mitigation
Detection mechanisms are equally as important to ensure breaches are detected in a timely manner.
Cloud Detection and Response (CDR) tools use the power of continuous real-time monitoring and AI-driven insights to detect threats and initiate automatic responses.
This pairs well with your continuous monitoring, allowing your team to get out in front of possible compromises.
Pairing these tools with an incident response plan ensures swift mitigation of any detected threats, preserving the resilience and agility your organization needs to thrive.
A significant 96% of organizations report being moderately or extremely concerned about cloud security, with 61% anticipating an increase in their cloud security budgets over the next 12 months.
Overcome Cloud Security Challenges
Overcoming the challenges in cloud security requires an understanding that this goes beyond technology to include people and processes.
Even as cloud security misconfigurations and lack of access control persist as the most critical issues organizations must overcome, human error frequently goes on to create these vulnerabilities.
Implement Scalable Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Embed identity governance so that you have exacting, auditable permission over who can get to your data—and when.
A zero-trust model adds even more security by providing access only on a need-to-know basis and eliminating risks while still allowing for necessary operation.
Foster a Security-First Culture
Equally important is the need to create a culture of security awareness across employees and stakeholders.
In this manner, employees are empowered to act before threats can expose sensitive data.
This includes consistent training initiatives, hands-on simulations, and maybe most importantly, communicating why secure behavior is important.
It’s how cloud and DevOps teams can, and should, be able to seamlessly integrate security into their workflows.
By doing this practice inside CI/CD, developers make the process easier and maintain their security posture.
Leverage Cloud-Native Security Tools
Cloud-native application protection platforms (CNAPPs) are particularly effective here, embedding security into DevOps (DevSecOps) to ensure protection remains continuous during application development. Regular audits and assessments are equally vital.
These practices help identify misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Tools like Spot Security, which conducts agentless, real-time risk assessments, provide actionable insights into critical issues, ensuring swift remediation.
Similarly, cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs) offer visibility, runtime protection, and vulnerability management, allowing organizations to secure workloads across diverse environments without compromising performance.
Strengthen Security with Next-Gen Technology
Implementing next-gen security technology strengthens security in layers.
From CWPPs to key management solutions, utilizing these tools streamlines cloud security management while filling critical gaps in the very foundation.
Backing these initiatives up with automated systems makes them scalable as your organization expands, minimizing friction and optimizing operational efficiency.
A secure and effective cloud security strategy brings all these pieces together. It does give you a solid starting point for today and tomorrow.
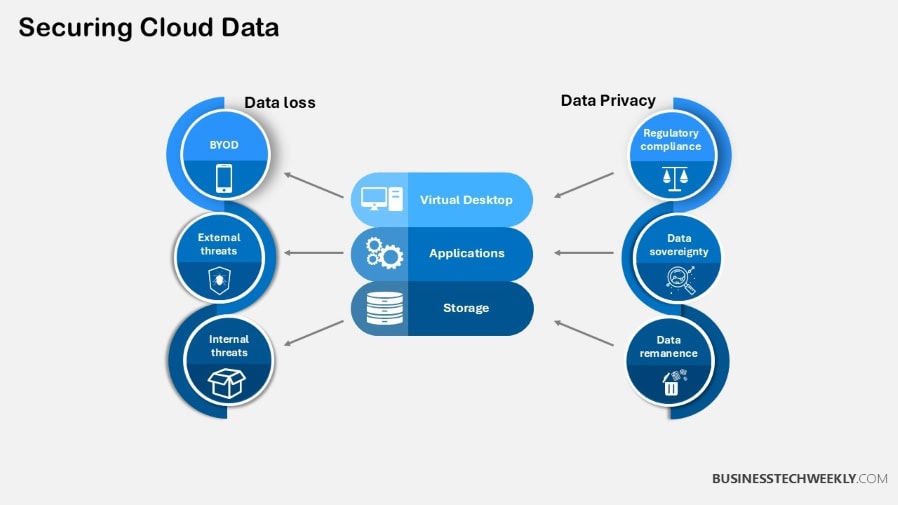
Modern Cloud Security Best Practices
Cloud-native security is most effective as a multi-layered approach that becomes second nature as it integrates into your operations.
Newer approaches make flexibility a core component of security. Integrate security into every layer of your cloud environment.
This proactive approach goes a long way towards helping your business avoid unnecessary risks and keep up with constantly changing regulations.
Integrating Security into the Development Lifecycle (DevSecOps)
Building security into the software development lifecycle — known as DevSecOps — helps organizations manage known vulnerabilities from the very beginning.
This practice tests every code commit against established security standards. This not only allows for prompt website fixes but fosters a proactive, ongoing culture of improvement.
Automation for Risk Mitigation
Automation tools help mitigate security risk by actively scanning for misconfigurations and vulnerabilities as part of CI/CD pipelines.
This preventative method stops security threats from getting worse. Embracing this forward-looking approach dramatically lowers threats.
The other benefit is improved efficiency — security becomes a shared responsibility, making it a team effort with shared goals.
Continuous Monitoring & Threat Intelligence
Continuous monitoring and threat intelligence are equally important components of robust security.
These practices include real-time analytics that identify anomalies or suspicious behaviors, allowing agencies to respond more quickly. Platforms such as Sentra’s DataTreks further enhance this process.
Next, they pinpoint preventable shadow data with a context-based analysis, one that truly minimizes your attack surface.
By using tools like these, you can ensure effective governance of your data assets, all while taking a proactive approach to preventing potential risks.
Security Awareness & Training Programs
Continuous training and awareness programs for security teams are imperative in keeping one step ahead of ever-evolving, sophisticated cyberattacks.
Simulated phishing exercises prepare your team to identify real threats when they occur.
Targeted workshops on handling sensitive data better equip them to respond in a timely and appropriate manner.
Zero-Trust & Data Loss Prevention
Policies such as Microsoft 365’s data loss prevention (DLP) can be seen as a zero-trust policy.
In conjunction with other safeguards, they provide a hard-hitting deterrent to data breaches.
Access Controls & Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing strong access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA) solutions takes your security posture to an even more robust level.
Adopting least privilege access means users have the least possible permissions needed to do their jobs, reducing the risk of sensitive data exposure.
Coupled with encryption and compliance automation frameworks like GDPR or CCPA, you safeguard both structured and unstructured data with precision exceeding 95% accuracy.
Research indicates that 10% of third-party integrations are dangerously overprivileged, allowing vendors excessive access to data or control over accounts, underscoring the importance of stringent access controls.
Evolving Threat Landscape Impact
Today, the cloud security landscape is continuously being reshaped by the growing sophistication and variety of cyber threats.
As attackers leverage advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence, the risks facing organizations are both more complex and harder to predict.
This dynamic environment demands that your security strategies evolve in parallel, ensuring they remain effective against modern and emerging attack vectors.
AI-Driven Cyber Threats: A Growing Concern
AI-driven threats, such as automated phishing campaigns and machine learning–based malware, are incredibly effective.
In addition, they elude identification through conventional means, thus increasing the threat. This transition underscores the increasing need to integrate AI into defensive measures, allowing for faster threat identification and response.
The Need for a Proactive, Layered Security Strategy
Meeting these new threats head-on with the right security starts with adopting a smarter, more proactive, layered strategy.
We can’t adopt a react-first approach, especially considering how ever-present and ever-evolving today’s cyberattacks are.
As organizations adopt a multi-cloud environment with greater frequency, it creates a new level of challenge to apply security consistently across cloud service providers (CSPs).
Tackling these distinctive challenges will demand cooperative efforts that embrace ongoing surveillance, near-instantaneous threat intelligence, and strong incident response protocols.
Strengthening Multi-Cloud Security with Intelligence and Tools
By implementing multi-cloud management tools, organizations can enhance security practices across various cloud service providers.
This reduces the attack surface and increases both operational and cyber efficiency.
Threat intelligence is central to anticipating and mitigating these developing threats.
By studying data from previous incidents, threat intelligence allows organizations to understand patterns in attack behavior, helping them take proactive measures to avoid future attacks.
Continuous, real-time intelligence identifies patterns such as suspicious login attempts and access to sensitive data.
This now gives security teams the ability to respond quickly and stop a breach from happening.
Staying Ahead of the Threat Curve
Staying one step ahead of emerging threats is imperative. Most alarmingly, over 80% of organizations believe that attacks powered by AI will increase over the next year!
In this increasingly hostile environment, proactive security approaches are critical.
Prioritizing data privacy, implementing data access control, and deployment of data security for multi-cloud infrastructure are key ingredients of a data-centric strategy.
Harness the power of cutting-edge technology and an innovative approach.
In doing so, your organization will be better positioned to not only respond to the evolving threat landscape, but stay a step ahead of it.
Measuring Cloud Security Effectiveness
To truly measure the effectiveness of your cloud security strategy, you need a more sophisticated view of metrics.
These metrics need to be driven by your operational priorities and acceptable risk levels. This isn’t only a compliance issue or box-checking exercise.
Rather, design an architecture that encourages resilience, trust, and dynamism as your enterprise grows and evolves in the cloud ecosystem.
A well-rounded approach takes into account that threats are constantly changing. It’s about making sure security doesn’t stifle innovation and productivity, but rather fosters both.
One important factor to keep in mind is the influence of human error.
According to Gartner, by 2025, the human element will be responsible for 99% of cloud security failures. This stat highlights how critical it is to address not just technical vulnerabilities, but procedural gaps too.
Measuring Cloud Security Effectiveness
Metrics like incident response time, the number and context of misconfigurations, and user behavior analytics are invaluable in helping out here.
For example, measuring misconfiguration rates can help identify where added training or changes to processes may be needed to lower risk.
Balancing Security and Productivity
The balance between healthy and unhealthy friction in your workflows is another key indicator.
Healthy friction prompts teams to adopt secure practices without slowing down innovation, while unhealthy friction often disrupts operations and creates resistance.
Measuring this balance involves evaluating the time taken for security reviews, the ease of access to necessary data, and the frequency of workflow disruptions due to security constraints.
AI-Powered Security
AI-based tools such have been revolutionary in scaling cloud security and driving more effective outcomes.
This ensures that your data is protected everywhere, regardless of where the data is located or how it’s being accessed.
Deep, contextual insights powered by their platform allow organizations to truly grasp the usage, sensitivity, and movement of their most critical data.
To effectively measure cloud security, consider the following metrics:
|
Metric |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incident Response Time |
Time taken to detect, assess, and mitigate security incidents |
|
Misconfiguration Rate |
Frequency of configuration errors that expose vulnerabilities |
|
Sensitivity Label Accuracy |
Effectiveness of tools like Sentra in accurately classifying and protecting sensitive data |
|
Workflow Disruption Frequency |
Number of times security measures hinder operational workflows |
|
Collaboration Security Metrics |
Ability to securely share files and collaborate across cloud applications |
Key Points to Note
- Making a cloud security strategy a priority to protect your organization’s sensitive data, applications, and infrastructure across various cloud environments—public, private, and hybrid—should go without saying. It’s a critical step in making sure your strategy aligns with your organization’s overall security objectives, keeping you safe from prospective cyber dangers.
- To establish a robust and forward-looking security posture for cloud environments, adhere to these fundamental tenets. These principles are Visibility, Exposure Management, Prevention Controls & Incident Response.
- Realizing the importance of the shared responsibility model. Cloud providers handle the security of the underlying infrastructure, you still hold responsibility for data, applications, and configurations that you deploy in the cloud.
- If you want to create a strong cloud security strategy, start by understanding where you stand today. Then, set specific goals, deploy security protections such as encryption, and continually test and improve your strategy.
- Appropriate employee training and regular security audits can address prevalent issues such as misconfigurations and weak access controls. Furthermore, moving to more sophisticated security instruments will continue to bolster your protective measures.
- In order to maintain your organization’s resilience against ever-changing threats, adhere to contemporary best practices. Adopt holistic DevSecOps integration, continuous threat monitoring, and multi-factor authentication.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a cloud security strategy?
A cloud security strategy is a comprehensive plan to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud.
It details their actions to reduce risks and maintain adherence with security requirements, while allowing the use of cloud securely.
Why is a cloud security strategy important?
It safeguards sensitive information, avoids costly breaches, and maintains compliance with regulations.
A robust cloud security posture fosters customer and stakeholder confidence, resulting in uninterrupted operations and preservation of your brand’s reputation.
What are the key principles of cloud security?
Core principles, such as end-to-end data encryption, authorized access control, constant monitoring and auditing, and adherence to regulatory compliance still apply.
Embracing the shared responsibility model and making multi-factor authentication a rule, not an exception, are equally important.
What is the shared responsibility model?
You may have heard of the shared responsibility model, where security responsibilities are shared between the cloud provider and the customer.
In this shared model, providers secure the infrastructure, and customers secure their data, applications, and user access.
How can I overcome cloud security challenges?
To overcome challenges, conduct regular risk assessments, implement robust access controls, and train employees on security best practices.
Choose a trusted cloud provider with strong security measures.
What are modern cloud security best practices?
Currently, the best practices are rooted in zero trust architecture, continuous monitoring, automated threat detection, and employing AI-driven tools. Constantly keep security policies in line with latest threats.
How do I measure cloud security effectiveness?
Monitor success by measuring key performance indicators such as incident response time, data breach rate, and results of compliance audits.
Regular penetration testing and security audits can help to keep you on the right path.

