Cloud Migration Challenges: What You Should Know

On this page:
- Understanding Cloud Migration Challenges
- 10 Cloud Migration Challenges and How to Address Them
- Cloud Migration Challenges: Checklist
- Why Solid Strategy Matters
- Addressing Technical Migration Obstacles
- Overcoming Legacy System Hurdles
- Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
- Minimizing Downtime and Maintain Continuity
- Managing Cloud Migration Costs
- Avoiding Vendor Lock-In
- Change Management Best Practices
- Key Points to Note
Understanding Cloud Migration Challenges
Cloud migration, though offering the prospect of unmatched scalability and operational efficiency, isn’t without its challenges.
Cloud migration challenges arise from various technical, financial, and operational complexities that organizations must navigate.
Every one of these challenges will take deep thought and guided strategy to mitigate as you make the shift.
Addressing cloud migration challenges is crucial. Understanding these barriers is the first step toward cloud migration to mitigate risks and maximize the benefits of cloud adoption.
Data Security Concerns
Data security is a top priority during migration due to the exposure of sensitive information to new vulnerabilities.
Robust security measures, such as end-to-end encryption and advanced threat detection systems, help safeguard data.
Conducting thorough risk assessments identifies potential weaknesses, while a well-defined data governance strategy ensures compliance with regulations like HIPAA or SOX.
Monitoring data access during transfer prevents breaches and upholds data integrity, a concern given that 70% of organizations report data loss or corruption during migration.
41% of companies identify the complexity of business and operational change as a significant obstacle in their cloud migration journey.
Legacy System Integration
Cloud migration challenges often include integrating legacy systems with modern cloud platforms. Connecting deep-rooted, legacy systems with new-age cloud environments can be very difficult.
For some organizations, specialized middleware, massive refactoring, or outright replacement may be needed.
Using a phased approach that begins with non-mission critical applications reduces the potential for disruption.
Middleware and APIs can accommodate legacy systems, bridging these gaps in compatibility and letting existing systems and new tools function together cohesively.
Take financial services, for example — organizations in this sector need to comply with rigorous standards such as Basel III, requiring specialized integration approaches.
Downtime During Migration
One of the most critical Cloud migration challenges is managing downtime effectively. If you’re a company in a customer-facing space, downtime is a killer. Migrations often affect production systems.
Methods such as blue-green deployment allow for smooth cutovers by keeping side-by-side environments.
Having redundancy measures in place, like backup servers, ensures that continuation of service is addressed and any potential losses during crucial times are avoided.
Unexpected Cost Overruns
Cloud migration often incurs unanticipated expenses, from increased storage needs to unexpected vendor fees.
Pre-migration assessments help identify cost factors, while detailed budgeting keeps spending under control.
Continuous monitoring and vendor negotiations secure cost-effective solutions, reducing financial strain.
Lack of Expertise
Cloud migration challenges aren’t all technical. Collaborating with experienced consultants and investing in comprehensive training ensures teams possess the expertise cloud migration requires.
Tools offered by cloud providers simplify tasks, while their resources guide businesses through challenges like managing system interdependencies or addressing performance bottlenecks.
Despite these resources, Cloud migration challenges related to expertise persist, as organizations often lack skilled personnel to handle complex migrations efficiently.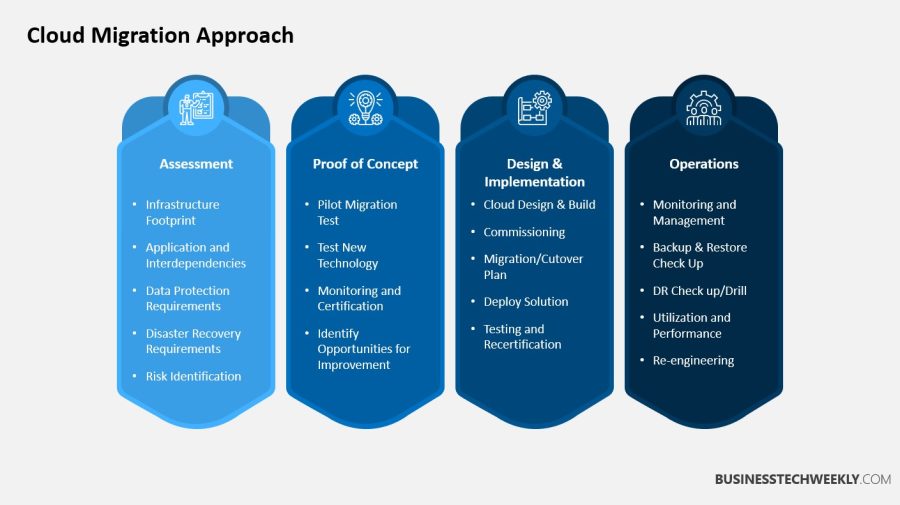
10 Cloud Migration Challenges and How to Address Them
1 .Infrastructure Compatibility Issues
- Legacy systems and applications may not be compatible with cloud environments.
- Conduct a thorough assessment to identify incompatibilities and choose the right migration strategy (e.g., lift-and-shift, refactoring, or re-architecting).
2. Cost Optimization Complexities
- Cloud pricing models can be intricate, with hidden costs for data storage, egress, and computing resources.
- Use cloud monitoring tools, optimize resource allocation, and implement cost-saving strategies like reserved or spot instances.
3. Data Security and Compliance Concerns
- Cloud migration introduces new security risks and regulatory challenges.
- Implement robust access controls, encryption, security audits, and compliance monitoring to mitigate risks.
4. Cloud Infrastructure Transition Obstacles
- Choosing the right cloud provider and designing a scalable infrastructure can be challenging.
- Conduct workload assessments, evaluate provider options, and plan for performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
5. Application Compatibility Problems
- Monolithic and legacy applications may not integrate seamlessly with cloud services.
- Modernize applications through refactoring, containerization, and adopting microservices architecture.
6. Data Migration and Integration Hurdles
- Data inconsistencies, corruption, or loss can occur during migration.
- Use data validation, error handling, and backup mechanisms while ensuring seamless integration between cloud and on-premises systems.
7. Network and Connectivity Bottlenecks
- Latency, bandwidth limitations, and unreliable connectivity can affect cloud performance.
- Optimize network resources, use CDNs, deploy cloud resources closer to users, and ensure secure hybrid cloud connectivity.
8. Organizational Change Management
- Resistance to cloud adoption and skill gaps can hinder migration success.
- Provide training, promote a cloud-centric culture, and align workflows with cloud processes.
9. Lack of Effective Cloud Governance
- Poor governance can lead to security vulnerabilities, compliance risks, and cost overruns.
- Define clear roles, establish approval workflows, and implement standardized cloud policies.
10. Monitoring and Incident Management Challenges
- Cloud environments are complex and require real-time monitoring for performance and security.
- Use cloud monitoring tools, log analysis, and proactive incident response plans to ensure system stability and availability.
Cloud Migration Challenges: Checklist
This checklist can help organizations systematically address challenges associated with cloud migration.
Challenge Category |
Challenge |
Checklist Items |
| Strategy & Planning | Lack of clear migration strategy | ☐ Define business goals and objectives for migration |
| ☐ Choose migration approach (Lift & Shift, Re-platforming, Re-architecting) | ||
| ☐ Conduct a feasibility study | ||
| ☐ Perform cost-benefit analysis | ||
| Security & Compliance | Data security and regulatory compliance risks | ☐ Identify and classify sensitive data |
| ☐ Ensure compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, ISO27001, etc. | ||
| ☐ Implement encryption for data at rest and in transit | ||
| ☐ Define access control and identity management policies | ||
| Application Compatibility | Legacy application incompatibility | ☐ Assess cloud readiness of applications |
| ☐ Identify dependencies on on-prem infrastructure | ||
| ☐ Plan for refactoring or re-platforming if needed | ||
| Data Migration | Data loss, corruption, and transfer speed issues | ☐ Backup all critical data before migration |
| ☐ Choose the right data transfer method (offline transfer, direct connect, VPN, etc.) | ||
| ☐ Perform data integrity checks post-migration | ||
| Performance & Latency | Unexpected downtime or slow response times | ☐ Conduct performance testing before migration |
| ☐ Optimize cloud resources for latency and availability | ||
| ☐ Implement monitoring tools for real-time performance tracking | ||
| Cost Management | Unexpected cloud expenses | ☐ Estimate costs using cloud provider pricing calculators |
| ☐ Set up budgets and cost monitoring tools | ||
| ☐ Optimize resources (auto-scaling, reserved instances, etc.) | ||
| Change Management | Resistance from employees | ☐ Provide training sessions on cloud tools |
| ☐ Involve key stakeholders in planning | ||
| ☐ Communicate benefits and address concerns proactively | ||
| Vendor Lock-in | Dependence on a single cloud provider | ☐ Evaluate multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies |
| ☐ Use open standards and cloud-agnostic technologies | ||
| ☐ Define an exit strategy for provider migration if needed | ||
| Security Threats | Cloud-specific cyber threats | ☐ Regularly update security patches and configurations |
| ☐ Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) | ||
| ☐ Monitor and log security events continuously | ||
| Governance & Compliance | Poor visibility and lack of control | ☐ Define cloud governance policies |
| ☐ Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) | ||
| ☐ Use cloud management and monitoring tools |
Why Solid Strategy Matters
Underpinning any successful cloud migration, a strong strategy has clear plans for tools, workloads and resources.
Without it, the process is prone to rapidly spinning out of control, resulting in squandered dollars, security gaps, and disruptions to operations.
A strategic approach ensures that each stage is closely tied to your business objectives. That alignment lays a straightforward foundation for powerful new cloud technologies.
Minimize Risks and Disruptions
With every migration comes risk, whether it’s data loss, downtime, or compatibility after the move; all migrations present risk. By identifying these risks up-front, you can begin to prepare mitigation strategies, such as planning migrations during off-peak hours to reduce downtime.
Planning for contingencies as much, if not more than, is just as important.
For example, maintaining regular backups protects your agency and allows for recovery if something goes wrong.
Pilot migrations are a smart, down-to-earth way to dip your toe into the water.
By starting your migration with a lower-impact, non-critical application first, you’ll be able to get a sense of what works, what doesn’t, and strategy adjustment accordingly.
Pair this with flexible monitoring tools that allow you to measure progress and address challenges as they arise, and you’ll have a much easier transition.
Ensure Data Security
Data security can’t be an afterthought during the cloud migration journey. Using strong encryption, ensuring data is encrypted in transit and at rest, protects sensitive data throughout the cloud migration process.
Access controls serve as an additional layer of protection, limiting sensitive data exposure to authorized users only.
Security is not a one-and-done effort; it requires constant maintenance to address new and evolving threats. For instance, regular vulnerability scanning can help identify areas of concern within your cloud environment.
By training staff on established best practices, you empower them to identify potential cyber threats. This approach not only fosters a culture of security awareness organization-wide but also enhances your overall cloud security architecture.
Optimize Cloud Costs
Cloud costs can become unwieldy without the right guardrails in place. Start by analyzing your current resource usage to identify inefficiencies.
Planning the cloud offers your organization new tools to get more accurate expense estimates, like cloud cost calculators, which help you plan budgets more effectively.
Embracing cloud financial operations (FinOps) practices helps make financial accountability a core aspect of your cloud strategy.
Consistently reviewing what resources go where prevents pork barrel spending before it starts.
Indeed, eliminating or scaling down underutilized resources can have a huge impact on the cost.
Pair this with auto-scaling features to dynamically adjust resources based on demand, achieving both cost efficiency and performance.
69% of IT leaders experienced budget overruns in their organizations’ cloud expenditures during 2023.
Accenture
Improve Performance
Performance optimization starts with having a defined benchmark. These metrics, like expected response time or expected uptime, keep you focused on intentional success after your migration. Maintaining proper cloud infrastructure is crucial.
Adjusting cloud configurations—such as augmenting storage or computing capabilities—allows organizations to make applications available without a hitch.
Auto-scaling adds agility by matching resource supply to fluctuations in demand, avoiding bottlenecks or overprovisioning.
Zero performance monitoring, through tools such as dashboards, lets you know what’s working and what’s not, allowing for iteration and improvement over time.
RELATED: Cloud Scalability: How can your Business benefit?
Maintain Compliance
Realize that cloud compliance is a dynamic process. Keeping a pulse on evolving regulatory changes can help you avoid getting caught up on the wrong side of the law.
Storing use case compliance processes raises the level of transparency and proves extremely useful during audits.
Regular compliance checks ensure that policies are being followed and identify gaps before they become major issues.
Working in close collaboration with legal teams addresses compliance issues early on.
Your proactive approach minimizes the risk of penalties and protects your reputation.
Addressing Technical Migration Obstacles
While cloud migration presents incredible, transformative opportunities for businesses, navigating common cloud migration challenges requires a deep understanding and deliberate action.
To address these obstacles, you must evaluate cloud migration strategies, strategize a detailed migration plan, and track closely.
This unified approach will help facilitate a smoother migration, while limiting risk and maximizing resource efficiency.
Assess Current Infrastructure
A comprehensive evaluation of your existing infrastructure is fundamental to cloud migration.
Begin by examining your current hardware and software to determine their compatibility with cloud platforms. Outdated systems or unsupported applications may require upgrades or replacements to avoid bottlenecks during migration.
For example, leveraging a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) can provide a detailed inventory of IT assets, dependencies, and their interconnections, offering insights into potential gaps or conflicts.
Documenting your existing configurations, from network setups to security protocols to application dependencies, creates a baseline for migration planning.
Recognizing these components in advance ensures that there are no unexpected interruptions, including loss of data availability, which may occur when interrelated dependencies are not accounted for.
Choose Right Migration Approach
Choosing the right migration strategy to start with your applications’ complexity and business objectives is crucial. Solutions such as rehosting, refactoring, and replatforming offer different benefits. Support the development of a decision matrix.
A decision matrix comparing these strategies against criteria like cost, scalability, and time requirements helps elected leaders make informed choices.
To illustrate, for those organizations that are migrating legacy applications, rehosting, referred to as “lift-and-shift,” is generally a more expedient and less expensive path.
Assembling the right stakeholders—including your organization’s IT teams and relevant business leaders—fuels alignment with overarching organizational objectives. It addresses key IT concerns including regulatory compliance and continuity of service.
Automate Migration Processes
Automation tools are a game-changer, accelerating migration timelines by making repetitive tasks far more efficient and minimizing human error.
For example, scripting data transfers can help standardize the transfer of large data sets while providing a trackable movement.
Combined with new, purpose-built services such as AWS Data Transfer or Amazon SageMaker, automation reduces the need for human touchpoints.
Even as cities look to automate workflows, it is crucial to monitor automated workflows closely to spot and fix errors quickly, ensuring data integrity and security.
Capturing these workflows further assists with future state cloud optimization initiatives as it provides a foundation document that showcases the path for operational scale.
Monitor Performance Closely
During the migration, it’s essential to measure system KPIs such as uptime, response time, and error-rate.
Tools such as Amazon CloudWatch ensure real-time visibility into performance metrics, allowing businesses to make proactive adjustments.
Analyzing this data on a consistent basis helps to identify trends, such as sudden increases in resource usage.
Then, you’re able to optimize your strategy for sustainable impact over the long haul.
Overcoming Legacy System Hurdles
Legacy systems frequently have provided the backbone of business functions, but their inflexibility can create large hurdles when executing cloud migrations.
These systems may have been designed to fulfill requirements of the past and often are not compatible with today’s cloud environments.
Addressing these common cloud migration challenges requires thoughtful planning and practical solutions to ensure a smooth transition while maintaining data integrity and operational continuity.
Identify Compatibility Issues
The first step is to evaluate your legacy systems for cloud compatibility.
A comprehensive assessment should examine the architecture, dependencies, and functionality of each application. Documenting these findings provides clarity and informs your migration strategy.
For example, if an application relies on outdated protocols, this could obstruct integration with cloud services.
Developing a risk matrix can help prioritize issues based on their potential impact.
Collaborating with IT teams ensures that challenges, such as potential data loss or corruption, are identified early, allowing for proactive solutions.
Refactor Applications if Needed
In situations where legacy applications won’t be able to move over easily, refactoring can be the answer.
This means rearchitecting applications to get the most out of running in a cloud-native environment. Start with determining what applications most need to be refreshed and invest resources, like talented developers, to modernize them, while enjoying their bounty.
In particular, refactoring custom-coded applications can significantly lower risk while making the applications work better to meet evolving needs.
Heavy regression testing of the refactored applications will help guarantee they’ll perform well under the scrutiny of a migration.
RELATED: Getting Started with Application Rationalization
Use APIs for Integration
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are a key component when it comes to integrating legacy systems with the cloud.
Determining which APIs are necessary upstream helps facilitate seamless data exchange and integration downstream.
Fortunately, a thoughtful API management strategy — bolstered by robust tools and documentation — can simplify this.
After migration, proactive API performance monitoring ensures the API remains reliable and points out opportunities for further optimization.
Consider Hybrid Cloud Approach
For businesses with more complicated needs, a hybrid cloud strategy provides this versatility.
By integrating legacy on-premises systems with efficient cloud resources, organizations can work through compatibility hurdles and have the benefits of scalability.
Identify the workloads that have a natural fit for hybrid, like workloads with sensitive data that need on-premises protection.
Consistent performance monitoring helps to make both environments work together in harmony, ultimately increasing efficiency.
Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
Data security and compliance has always been at the heart of any successful cloud migration strategy.
Even when you’re going to the cloud, safeguarding critical data and complying with industry standards should always be a priority.
By investing in a strong security foundation, you can rest assured that your digital assets are protected while building trust and operating successfully for the long-term.
Here, we discuss the most important strategies to make sure you’re secure and compliant while migrating.
Data security is a significant challenge during cloud migration, as organizations must protect sensitive information throughout the process.
IBM
Implement Strong Encryption
Encryption should actually be the bedrock of data security and compliance, especially during cloud migrations.
It’s imperative during data migration to implement strong industry-leading encryption technologies such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 256-bit.
These will help you keep your cloud data secure, both in transit and at rest, and are essential for a good cloud migration strategy.
Secure VPN tunnels or dedicated connections, like AWS Direct Connect or Azure ExpressRoute, provide an additional layer of protection during cloud application migration.
As with any encryption strategy, effective encryption key management is just as critical in the cloud migration process.
Keys must be stored with hardware security modules (HSMs), and keys must be rotated regularly to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
Consistently evaluating encryption practices helps ensure that your organization aligns with the constantly changing industry standards.
Providing your staff with regular training on encryption’s role in safeguarding sensitive data raises your overall security posture even higher, particularly in the context of cloud security challenges.
RELATED: Best Practices for Cloud Security: Safeguarding Your Business Data
Control Access Management
Controlled access is paramount to mitigating risks. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to assign permissions according to defined job functions, ensuring individuals only have access they need to perform their job.
Zero Trust Secure identity and access management (IAM) systems are critical here, enabling fine-grained access policies based on principles of least privilege.
Regularly monitoring access logs can quickly identify suspicious or unusual behavior and a periodic review of access controls can confirm policies remain relevant and protective.
For example, a member of the finance team should only be able to access financial information, not private HR files.
These types of practices minimize your exposure and fortify your defenses.
Monitor for Threats
With continuous monitoring, you can catch and address threats in real time. Security monitoring tools, based on industry benchmarks such as the Center for Internet Security (CIS) benchmarks, help detect risky configurations or unauthorized changes to systems.
Consistent audits help identify weaknesses and having clear incident response procedures in place allows for quick action when a breach occurs.
Create a culture of Cybersecurity. Encourage your staff to report suspicious activities and perform ongoing training to develop cybersecurity awareness.
Collaborating with your Cloud Service Provider (CSP) to review independent audits, such as SOC 2 Type II, adds transparency to the process.
Adhere to Regulations
In short, compliance is non-negotiable when it comes to cloud operations.
Know the regulations you are subject to like GDPR or HIPAA based on the type of industry you work in. Use compliance checklists to ensure you are meeting requirements and use these documents to help establish a culture of accountability.
Engage legal counsel early to determine solutions to data residency restrictions, including establishing regional data centers for sovereignty.
Reviewing your CSP’s certifications and compliance attestations ensures alignment with regulatory expectations.
Minimizing Downtime and Maintain Continuity
Cloud migration is undoubtedly a transformative leap forward for any business, but ensuring a smooth transition while addressing common cloud migration challenges requires more than just good intent.
By focusing on cloud migration phases, leveraging redundancy, rigorous testing, and clear communication, you can safeguard operational continuity while transitioning to the cloud.
All of these steps are critical to closing gaps and avoiding risks, ensuring availability when it matters.
Plan Phased Migration
With each stage of the migration, breaking it down into smaller, more manageable phases lessens the chances of surprise downtime.
Begin with a comprehensive, milestone-driven timeline that maps out every step, allowing everyone to know the due dates and what needs to come first.
Start with the migration of mission-critical services such as customer databases and payment processing systems.
This proactive approach helps you prevent or quickly mitigate disruptions to your organizational business continuity.
A detailed checklist is critical—pipeline all the pieces a migration entails from double-checking data integrity to repointing DNS files to cloud app compatibility.
During the entire process, it is important to keep track of progress and correct any potential delays as soon as they arise.
Advanced real-time metrics and dashboards can provide powerful insights to help ensure your migration stays on track.
Use Redundancy and Failover
Planning effective redundancy strategies is mission critical, to ensure that redundancy is maintained and availability ensured during step migration.
By replicating systems and data in different places or servers, you create redundancy and produce a safety net.
This guarantees that functionality lives on, even if one component should fail. Failover systems implementation helps you switch instantly to backup resources if and when required. Indeed, as one example, if they host mirrored copies of their databases, users have continuous, uninterrupted access.
Consistent testing of these systems is just as important. Create and simulate failure scenarios to ensure your failover mechanisms execute under real world conditions.
Defining these strategies in writing allows your entire team to come back and consult them for future migrations or issue resolution.
Test Thoroughly Before Go-Live
In-depth proactive testing is essential to root out and repair potential problems before they ever register with users. Conduct thorough testing for migrated applications to ensure performance, security, and compatibility.
An organized testing rubric prevents anything from slipping through the cracks, whether it’s checking for proper API integrations or making sure your user authentication flows are operating as intended.
Engaging the end-user in beta testing will help identify usability challenges that may not come to light during technical testing.
Taking action on these learnings before launch instills confidence in a smooth transition.
Managing Cloud Migration Costs
Understanding the cost component of cloud migration is key. That makes for a smoother transition, and it helps you achieve a higher ROI.
Moving to the cloud offers significant opportunities for scalability and innovation, but controlling costs requires deliberate planning and ongoing oversight.
By addressing cloud resource optimization, spending monitoring, multi-vendor/platform negotiations, and budgeting alignment, your organization can successfully manage costs.
Optimize Resource Allocation
Optimizing your resource allocation starts with a thorough understanding of your existing infrastructure and applications, especially during the cloud migration journey.
This process allows you to pose more difficult questions to identify areas like duplicate or underutilized assets that can be streamlined through cloud data migration.
Nailing down a resource allocation plan that works best for your business allows you to provision just the right amount of resources, eliminating excess and waste.
For example, there are tasks such as right-sizing virtual machines and taking advantage of auto-scaling features that can save a lot of money during the cloud migration process.
Ongoing management of how resources are being consumed is a critical element for driving ongoing efficiency.
Tools that are cloud-native, such as AWS Cost Explorer and Azure Advisor, can provide helpful recommendations and insights into usage patterns that are essential for effective cloud data integration.
These insights then equip you to make data-driven changes.
Real-time performance metrics and continuous feedback from your teams further inform these refinements, ensuring teams are maximizing usage without sacrificing performance.
36% of companies consider the lack of necessary cloud skills within their organization as a top barrier to fully achieving cloud outcomes.
Accenture
Monitor Cloud Spending
Managing cloud migration costs demands strong tracking processes.
Cloud cost management tools, like Google Cloud’s Cost Management suite, give you an upfront view of your spending.
Third-party platforms such as CloudHealth further improve your visibility into costs.
Developing an all-inclusive budget for cloud services and monitoring compliance with it promotes fiscal accountability.
By recognizing what’s causing costs to skyrocket, whether it be too much data transfer, accumulating unused resources, etc., you can take targeted action to save more.
For instance, one company cut its AWS spend by 20% leveraging this approach to rightsize inefficiencies and gain greater scalability.
Make it a habit to look at your chargeback reports. This ongoing practice, in addition to making you a sharper budgeter, gives your organization the flexibility and speed to meet evolving needs.
Negotiate Vendor Contracts
When expecting exorbitant costs through vendor dependency isn’t enough, engaging with vendors to negotiate favorable terms is a proactive way to manage costs.
With different pricing models across major providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, it’s important to know how you’re primarily using the cloud.
Renegotiating terms now sets you up for greater success. Preparing a list of key negotiation points, like volume discounts or long-term commitments, strengthens your position.
By documenting key agreements and periodically reviewing contract terms, you will help ensure that you remain aligned with your organization’s goals.
This methodology reconstitutes vendor relationships into partnerships that foster sustainable development.
RELATED: 10 Key Tips for Successfully Evaluating Cloud Service Agreements
Review and Adjust Budgets
Budgets need to be fluid, based on real utilization and spend. Conducting regular audits helps you spot red flags and take corrective action before it’s too late.
To forecast accurately, use cloud cost estimation tools and scenario analysis to get ready for various migration approaches.
This ongoing, iterative process ensures that your spending is in line with your strategic, organizational goals.
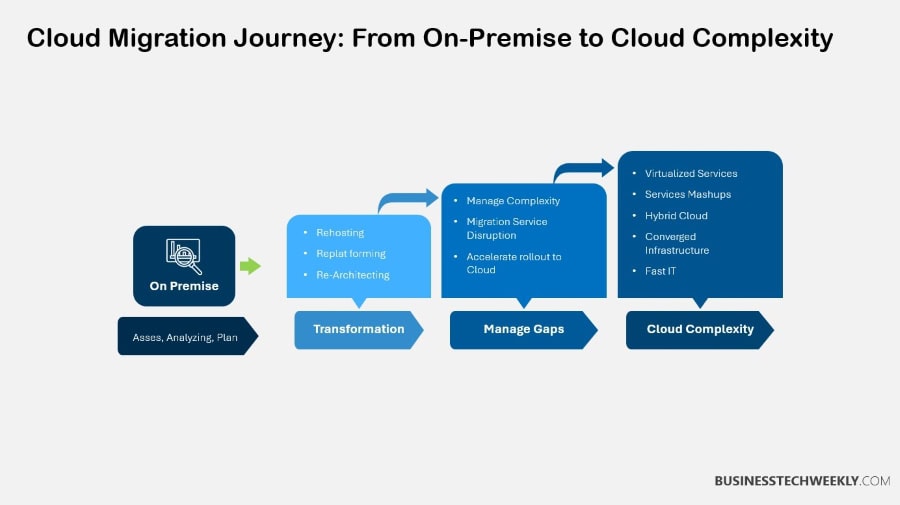
Avoiding Vendor Lock-In
Cloud migration challenges also extend to vendor lock-in, where organizations struggle to maintain flexibility and independence from cloud service providers..
This vendor dependency leaves little room for flexibility, is often much more expensive in the long run, and can stifle innovation.
To avoid these risks, it is crucial to adopt strategies that enable interoperability, portability, and diversification. Here, we dive into practical steps to keep your cloud infrastructure flexible and robust against future challenges.
Use Open Standards
Open standards are vital to avoiding vendor lock-in by ensuring compatibility and seamless integration between systems and platforms.
When you enforce these standards, you open up your systems to more robust communication, independent of the vendor, which is crucial in the cloud migration process.
Begin with a baseline of well-established, community-supported open standards that provide stability and maturity for your cloud deployments.
Standards such as APIs based on REST architecture or data formats like JSON and XML are good options with interoperability in mind, especially for effective cloud data migration.
Knowing what’s happening in your industry is essential. Emerging standards, like Kubernetes in the space of container orchestration, provide new ways to do things more efficiently, which can help mitigate common cloud migration challenges.
Provide specialized training for your teams through engaging sessions that equip them to comprehend and integrate these standards.
This will increase their capacity and competency to deploy solutions that are flexible by nature, aiding in the overall cloud transformation journey.
Design for Portability
By designing cloud architectures with portability as a guiding principle, making switches between different providers stays easy and cost-efficient.
A well-documented set of design principles, such as loose coupling and modular services, can act as a blueprint for portability.
For example, using microservices architecture lets you migrate individual components without blowing up your whole ecosystem in the process.
To prove out these designs, hold constant tests where you regularly migrate smaller, non-mission-critical workloads to other platforms.
This practice will go beyond simply identifying potential challenges to reinforcing your entire migration strategy.
Engage vendors with an eye toward tools and services that improve portability.
Imagine what new innovation would be possible if you added provider-agnostic container platforms to further streamline the process.
Multi-Cloud Strategy
A cloud first strategy provides immediate diversification benefits by distributing workloads across various cloud providers, thereby lessening the dependence on any one vendor.
Start by evaluating your workloads to identify which ones would benefit most from this strategy—mission-critical applications often warrant redundancy across different clouds.
Effective cloud migration strategies require careful planning and assessment of cloud architecture to ensure a smooth transition.
Getting multi-cloud management right involves creating a strong governance framework that includes oversight of operations, security, and compliance across the cloud providers.
Additionally, utilizing cloud migration tools can facilitate the migration process, ensuring that all aspects of cloud data integration are addressed efficiently.
Continuously track key performance indicators to ensure workloads are operating efficiently and costs are predictable.
Technology and tools, such as cloud management platforms, can simplify this task by offering streamlined, centralized oversight, ultimately supporting the overall cloud transformation efforts.
Change Management Best Practices
Cloud adoption is more than just a technological shift. It takes thoughtful change management to guide your people, processes and expectations along with your rapidly changing business landscape.
Cloud migration change management is a vital component when it comes to realizing the success of your cloud migration.
Prioritize employee communications, training, and concerns from the start.
This carefully considered and planned approach will ensure a better transition and reduce the risk that these types of initiatives are often plagued with.
Communicate Clearly
Providing clear communication at every change management step is key to successful change.
Create tools for ongoing communication. Produce and distribute a weekly newsletter/communication center via email and/or video messages from the executive management team that apprises all staff of their shared migration progress, challenges faced, and successes.
Involving stakeholders is also crucial. Scheduling regular project updates and feedback sessions provides a forum for stakeholders to express any concerns they may have and to receive immediate responses to questions.
Writing down these communication plans helps to keep transparency and accountability at the forefront, which is key to developing a trusting relationship.
For example, regular communication – such as bi-weekly updates from the CEO – can help fill in the blanks and maintain a sense of unity and purpose across the organization.
Fostering a space for open communication promotes a welcoming atmosphere. This gives us the opportunity to respond to questions/issues in real-time, making sure everyone is prioritized and heard.
Train Employees
Comprehensive training programs—preferably designed for the specific cloud technologies you’ve selected—are critical for enabling new and existing employees to successfully perform business operations within their new systems.
Making resources such as hands-on workshops and continued learning opportunities available will help you ensure that your team members feel supported every step of the way.
A timely refresher course focused on misunderstood topics can totally reframe key concepts, transforming something counterproductive into something concrete and positive.
Regularly monitoring training effectiveness allows you to adjust and refine these programs as needed.
Promoting knowledge sharing among team members can spark collaboration and help everyone feel more confident in applying the new processes.
For instance, providing solutions to hurdles such as learning new security procedures when they enter a business can be made easier with targeted, role-specific training modules.
Address Concerns
Employee pushback usually arises out of fear of the unknown, so it’s important to address these fears head on.
Implementing a feedback mechanism, whether through anonymous surveys or one-on-one conversations, can give you invaluable insights into what they may be hesitant about.
Developing targeted strategies to address common worries, like job security or workload changes, shows employees their concerns are taken seriously.
By providing clarity around solutions, you can help ease fears. For instance, disassociating your implementation of an identity and access management (IAM) system with shored up security goes a long way.
Actively monitoring sentiment through the migration helps you identify any issues that arise early and address them quickly, helping you build acceptance and trust.
Overcoming Cloud migration challenges related to change management requires a proactive approach, ensuring that employees are engaged and well-prepared for the transition.
Key Points to Note
- Cloud migration can be an overwhelming process with a host of challenges, including data security risks, legacy system integration issues, and potential downtime. Handling these issues proactively, by doing plenty of advanced planning and preparation will be key in making this transition go smoothly.
- Make sure you adopt encryption, robust access controls, and continuous monitoring to detect unauthorized activity. Develop a governance strategy to ensure you stay compliant with industry regulations throughout the migration process and afterward.
- Bringing legacy systems into the fold often means refactoring or using middleware solutions. Taking a phased migration approach can help reduce disruptions and keep migration efforts moving at a steady pace.
- Prevent surprises with unanticipated cost overruns by doing a comprehensive analysis, developing a robust migration budget, and tracking costs during the migration. Leverage cloud financial management tools and zap waste through better vendor management, negotiations, and audits.
- Fill these skill gaps by either partnering with cloud migration experts or investing in your team’s training. Cloud management tools and your cloud provider’s resources can make your migration process easier and more efficient.
- To avoid vendor lock-in Move to a multi-cloud strategy from the outset and build portable architectures. Implement Scorecards Regularly evaluate vendor performance and hold them accountable to make sure they are meeting your business requirements.

