What is a Print Server? Everything you need to Know

On this page:
What is a Print Server?
Definition of a Print Server
A print server can be a dedicated device or software that manages incoming print requests. This makes it an important middleman between dozens of computers and printers on a network.
This technology can be deployed as hardware, software, or even as a cloud solution, maximizing benefits based on the organizational structure.
Print servers simplify the communication process by serving as an intermediary that supports various printing protocols, providing compatibility across different systems.
They can perform load balancing across several different printers at once, decreasing the workload on single devices and increasing productivity across the entirety of the network.
Primary Functions in a Network
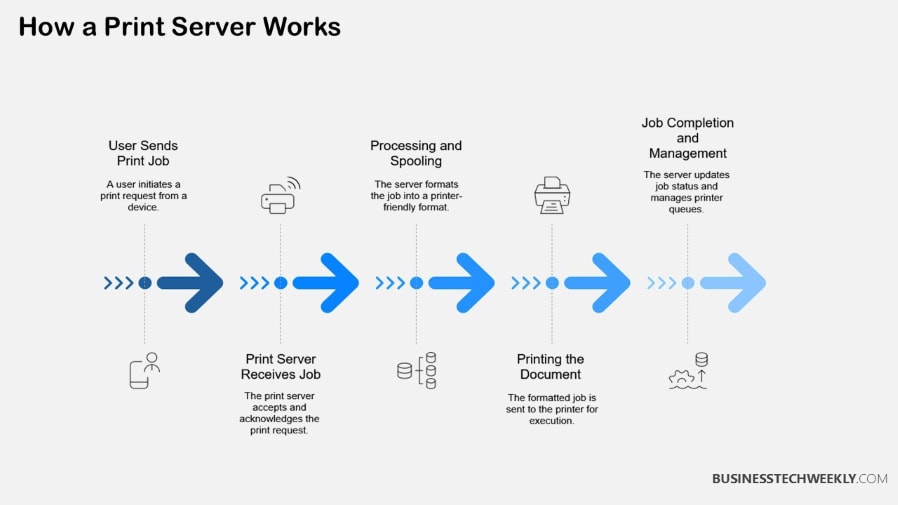
Print servers help eliminate network congestion by reducing the number of active print queues.
They queue up and schedule multiple print jobs for smooth, rapid production.
They allow you to track printer status and usage across all your networked printers.
This provides you with a single pane of glass to see print activity across the board.
This feature enables a large number of users to effectively share printers.
It removes the need for a direct connection to every printer.
In addition to standardizing printer workflows, print servers simplify printer driver management across various locations and devices.
This guarantees seamless compatibility and user experience, and is especially important for enterprise organizations with diverse, complex hardware.
They simplify print management, making it easier to maintain and troubleshoot.
Consequently, they continue to be the preferred print method for more than 70% of companies, despite the existence of newer technologies such as Direct IP printing.
Benefits of Using a Print Server
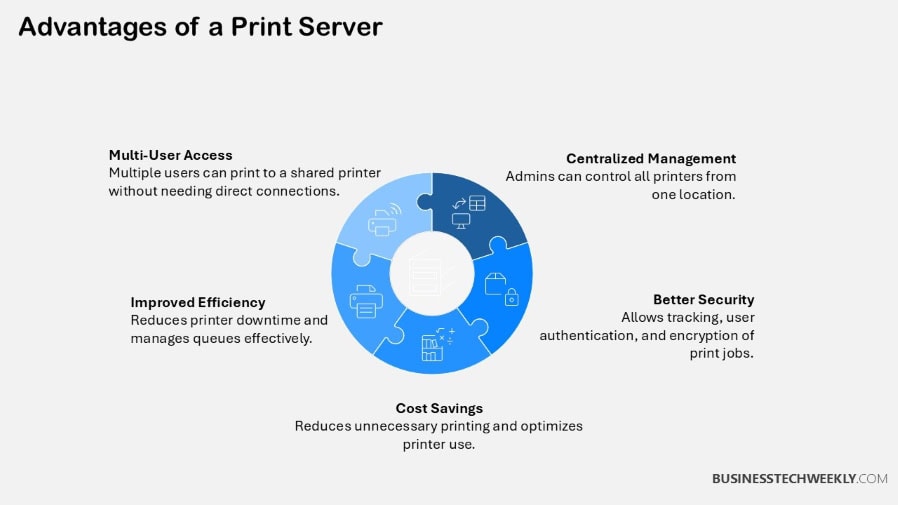
1. Centralized Management
Print servers provide an efficient, centralized point of control over everything that gets printed, particularly useful for organizations looking to drive efficiency.
When you centralize print management, you’ll have an easier time managing and maintaining your printer fleet, with drivers being standardized across the board.
This centralized approach makes troubleshooting and maintenance easier, cutting down the time and manpower required to fix problems.
Furthermore, by keeping track of print usage, detailed reports can be generated, encouraging accountability and better decision-making.
Making the switch to print policies is simple, centralizing activities and creating consistency throughout your organization.
2. Cost Efficiency
Perhaps the most notable benefit of print servers lies in the enormous cost savings.
By reducing the necessity for standalone printers, hardware costs are reduced as well.
Shared resources and more efficient job processing contribute to cost savings on consumables, such as paper and toner.
Fewer downtimes centralizing printing reduces downtime, improving overall productivity by making sure print jobs get taken care of quickly.
Lower maintenance and support costs improve your time to value.
With less resources required, the system is able to operate more quickly and efficiently.
3. Enhanced Security
In today’s climate, print servers are an integral component in fortifying security.
User authentication is required before print jobs are released, protecting confidential materials.
By keeping an eye on print jobs, you can stay ahead of any unauthorized access, and encryption protects your data in transit.
Permissions can be assigned to individual users or user groups, restricting access and improving security measures in your workplace.
4. Improved Performance
Performance enhancements are the second major advantage of print servers.
With better control of print queues, users wait less, increasing productivity and efficiency.
Load balancing across many printers maximizes the performance, making sure printers’ resources are being used to their best potential.
Print servers even make it possible to prioritize urgent jobs to enable quicker processing.
What’s more, by optimizing how print requests are handled, unnecessary network traffic is minimized, improving performance even more.
Types of Print Servers
Cloud print servers are revolutionizing how organizations of all sizes approach their print environments, particularly with the advantages of serverless printing.
They enable an efficient and effective workflow that helps companies grow, adapt, and change fast.
Understanding the differences between dedicated print servers and cloud-based solutions helps you select the best fit for your business’s unique needs.
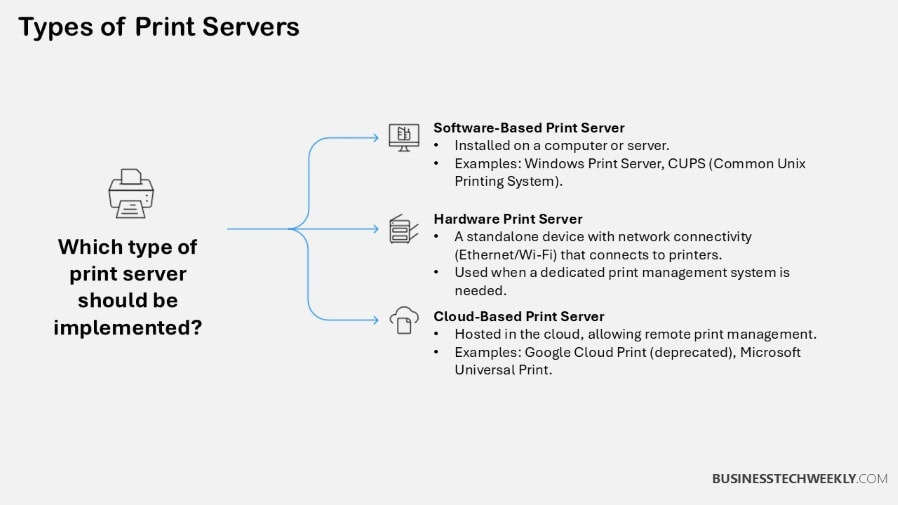
Hardware Print Servers
Hardware print servers are dedicated devices that connect directly to printers and other peripherals, providing the best reliability and performance for high-volume print environments.
They accommodate more printers and users, making them perfect for busy offices.
Whether you need 1-port WiFi or 3-port USB servers, they’re ready to serve a wide array of needs.
Installation is simple, making it easy to plug into the current network infrastructures.
Even though they are very robust, they need constant maintenance, which is something budget-strapped organizations need to keep in mind.
Software Print Servers
Software print servers, applications deployed on computers you already own, provide flexibility and introduce a lower total-cost-of-ownership.
They have an added benefit of being especially beneficial for SMBs, maximizing older hardware investments while simplifying print management.
Modern software print servers are easily updated and configured to meet changing business needs, so you can keep pace with your organization’s priorities.
This choice fulfills the practical use with cost efficiency, but requires frequent updates to the software to remain on the cutting edge.
Cloud-Based Print Servers
Cloud-based print servers allow organizations to print through the internet, giving users the ability to access printers remotely from anywhere.
This solution is ideal for organizations with a remote or hybrid workforce, marrying scalability with lower maintenance burdens.
Integration with mobile devices simplifies convenience, but dependence on a stable internet connection can be a drawback.
All in all, cloud-based solutions are a perfect fit for today’s agile, mobile workplace.
How Print Servers Facilitate Cybersecurity and GRC
Print management devices play a crucial role in managing and facilitating printing tasks in a networked environment.
They act as intermediaries between printers and user devices, enabling multiple users to share a single printer or a group of printers across an organization.
Centralized Control and Monitoring
-
Print servers enable administrators to manage and monitor print activities from a central location. This centralized control allows IT teams to detect unusual patterns in print jobs, which may indicate potential security risks or breaches.
-
Administrators can integrate print servers with cybersecurity tools, such as SIEM systems, to receive real-time alerts for suspicious printing activities.
Access Control and Authentication
-
Print servers support authentication mechanisms like user logins, smart cards, or biometrics, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access and print sensitive documents.
-
This access control reduces the risk of unauthorized printing and helps secure critical information.
Encryption
-
Print management devices encrypt print jobs to ensure secure transmission from the user’s device to the printer. This protects sensitive data from being intercepted during the printing process.
-
Encryption on print servers helps meet security and compliance requirements, ensuring that data remains secure throughout its lifecycle.
Auditing and Logging
-
Print servers log detailed information about print jobs, including who printed what, when, and where. This data provides transparency and accountability for printing activities.
-
These logs are valuable for GRC reporting, allowing organizations to trace any security incidents or breaches and demonstrate compliance with relevant regulations.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
-
Print servers can be configured with data loss prevention (DLP) policies to prevent the printing of sensitive information. For instance, print jobs containing confidential data can be flagged or blocked before printing.
-
This functionality helps mitigate cybersecurity risks and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.

Compliance Frameworks Needs
Print servers play a vital role in supporting cybersecurity and GRC initiatives by offering centralized management, secure access, encryption, and robust auditing capabilities.
They ensure that print activities adhere to security policies and compliance frameworks, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, interception, or misuse.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
-
GDPR requires organizations to protect personal data from unauthorized access. Print servers must implement strong access controls, encryption, and auditing to secure print jobs containing personal data.
-
The print logs provide an audit trail that helps demonstrate compliance with GDPR’s accountability and transparency principles.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
-
HIPAA mandates the protection of patient health information (PHI). Print servers must ensure that PHI is accessible only to authorized users and that printed PHI is securely managed.
-
Secure print release features, which require user authentication at the printer, help organizations comply with HIPAA’s privacy and security regulations.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
-
PCI DSS requires organizations to secure payment card data during storage, processing, and transmission. Print servers must encrypt payment card data during transmission and ensure secure printing of sensitive cardholder information.
-
Print job logging and monitoring capabilities are essential for maintaining PCI DSS compliance.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
-
SOX requires accurate record-keeping, including financial documents. Print servers help secure sensitive financial data by providing robust access control, logging, and monitoring.
-
The logs of print jobs can serve as evidence for SOX’s requirements on record retention and auditing.
Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA)
-
FISMA enforces strict security controls for federal agencies and contractors. Print servers supporting FISMA compliance must ensure that print jobs are encrypted, logged, and protected from unauthorized access.
-
Print servers must undergo regular security assessments and audits, which is a critical component of FISMA compliance.
Selecting the right Print Server
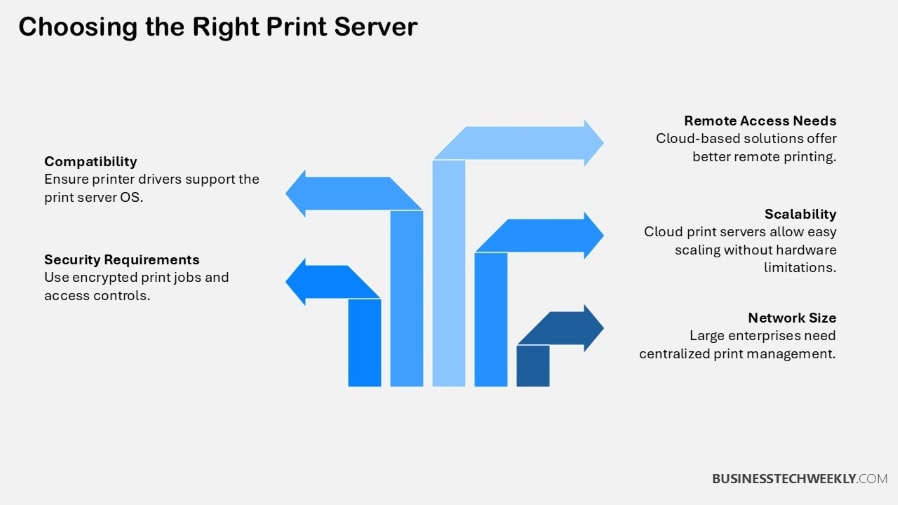
Selecting the right print server for an organization requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure it meets both operational needs and security requirements.
Here are the key steps to help you select the most suitable print server for your organization:
1. Assess Organizational Needs
-
Volume of Printing: Evaluate the expected volume of print jobs. This will help determine the performance and capacity requirements of the print server.
-
Number of Printers: Identify how many printers the print server will need to support, and whether these are distributed across different locations or centralized in one area.
-
Types of Users: Consider whether the print management device needs to support a large number of users across multiple departments or teams, including remote workers.
-
Print Management Features: Determine if your organization needs advanced features like job tracking, quota management, or secure printing.
2. Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
-
Printer Compatibility: Ensure that the print server is compatible with the printers your organization uses, including different brands and models.
-
Operating System Compatibility: Verify that the print server supports the operating systems in use within the organization (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux, or others).
-
Network Infrastructure: Check if the print server integrates well with your network infrastructure, including wireless or wired networks, and whether it supports the necessary protocols (e.g., TCP/IP, LPD, SMB).
3. Consider Security Features
-
Access Control and Authentication: This should support robust access control mechanisms, such as user authentication, to ensure that only authorized individuals can access printers.
-
Encryption: Ensure the print server supports encryption to protect print data as it travels across the network, especially if sensitive or confidential information is being printed.
-
Audit Logs and Monitoring: Look for detailed logging and monitoring of print activities. This helps track usage and identify any suspicious behavior that might indicate a security issue.
-
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Consider whether the print server offers any DLP features, such as preventing the printing of sensitive or confidential documents without authorization.
4. Evaluate Ease of Management
-
Centralized Management: Choose a print server that allows centralized control of print queues, printer configuration, and user access, making it easier for IT administrators to manage and monitor printing tasks.
-
User Interface: Check if the print server offers an intuitive user interface that allows both IT administrators and end-users to manage print jobs efficiently.
-
Support for Remote Management: If your organization has remote or distributed teams, ensure that the print server supports remote management and troubleshooting.
5. Scalability and Future Growth
-
Expandable Capacity: Ensure that the print server can scale with your organization’s growth. This includes supporting additional printers, users, or print jobs as the organization expands.
-
Support for Cloud Integration: Consider whether the print server offers cloud printing capabilities or integrates with cloud-based print management platforms, which are becoming more popular in modern workplaces.
6. Cost Considerations
-
Initial Investment: Consider the upfront costs of purchasing the print server, including hardware and licensing fees, if applicable.
-
Ongoing Costs: Factor in ongoing costs such as maintenance, software updates, and possible subscription fees for additional features or cloud-based services.
-
Cost per User/Print Job: Calculate the potential cost per user or print job, especially if the organization has high print volume or specialized print needs (e.g., color printing, large-format printing).
7. Support for Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
-
Compliance with Regulations: Ensure that the necessary industry standards and compliance requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, particularly if the organization deals with sensitive data.
-
Audit Trails and Reporting: Check if the print server offers detailed reporting capabilities and audit trails, which can be crucial for demonstrating compliance during audits or security reviews.
8. Vendor Support and Warranty
-
Vendor Reputation: Choose a print server from a reputable vendor with a proven track record of providing quality products and support services.
-
Support Availability: Ensure the vendor offers adequate technical support options, such as phone, email, or online support, and has resources available for troubleshooting and problem resolution.
-
Warranty and Service: Look into the warranty options and whether the vendor offers maintenance services or hardware replacement in case of failures.
9. Test the Print Server
-
Pilot Test: Before full deployment, conduct a pilot test in a small section of your organization to identify any potential issues or limitations. This helps ensure that the chosen print server meets performance, security, and usability expectations.
-
Evaluate User Feedback: Gather feedback from end-users to ensure the print server is easy to use and fits well within their workflows.
10. Make the Final Decision
-
After evaluating all the factors listed above, select the print server that best aligns with your organization’s needs, budget, and long-term goals.
-
Ensure the solution is scalable, secure, and capable of adapting to future changes in your network or organizational structure.
Key Points to Note
- Print servers are a critical component of fulfilling incoming print requests from dozens or hundreds of computers. They serve as an intermediary between printers and networked client computers, improving traffic flow and cutting down on network bottlenecks.
- By offering centralized control, print servers facilitate effective management of print queues, monitoring printer status, and sharing printers efficiently among users, which simplifies printer driver management across devices.
- Using a print server is one of the easiest and cheapest ways to save your organization thousands of dollars. It cuts back on the need for personal printers, streamlines resource use and lowers downtime, all increasing productivity.
- Print servers improve security by requiring user authentication and tracking print jobs. They even use encryption and establish access permissions to secure sensitive documents.
- Print servers improve print performance by managing print queues more effectively and balancing the load across multiple printers. By focusing on urgent jobs first, they are able to hold down wait times and limit network congestion.

