What is Operating System Hardening? Why You Should Care

On this page:
What is Operating System Hardening?
Operating system hardening protects your operating system by minimizing its attack surface.
This multi-step process includes removing all non-essential services and applications that can be potential entry points for cyber attackers.
By minimizing these vulnerabilities, hardening can critically improve your system’s overall security and integrity.
Cyber threats are increasing every day. To keep up a strong defense against these constantly changing attacks, you need to ensure you’re hardening your operating system.

Definition of Hardening
Hardening involves using various tools and techniques to reduce system vulnerabilities, effectively lowering security risks by eliminating potential attack vectors.
This process is ongoing, requiring regular updates and assessments to ensure your system remains secure.
Hardening is a vital step in establishing a secure computing environment, as it consistently aligns with industry-accepted standards like the CIS benchmarks, which map to compliance standards such as ISO 27000 and NIST SP 800-53.
Importance in Cybersecurity
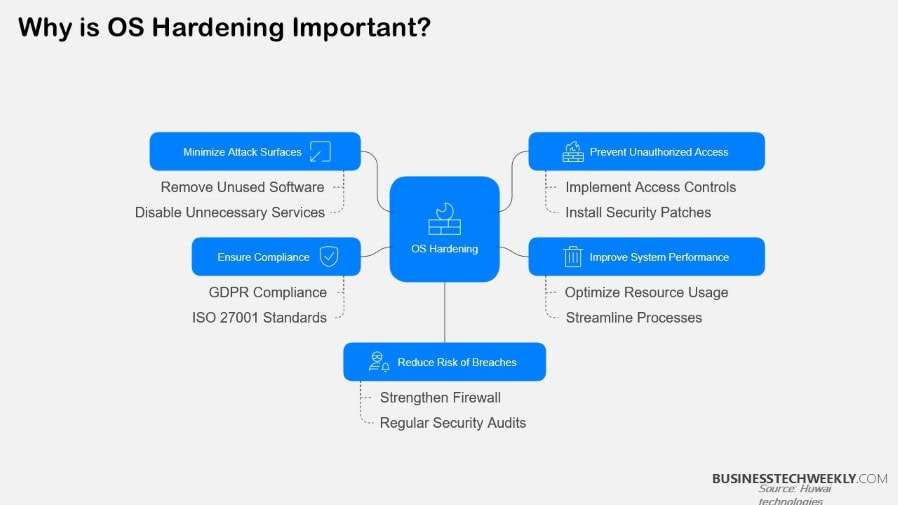
Operating system hardening is a critical security first step to safeguard sensitive data from malicious actors.
Effective hardening measures can significantly mitigate risks associated with cyber threats, helping maintain compliance with security standards like PCI DSS and HIPAA.
By making successful cyberattacks less likely, hardening is an essential part of protecting our critical IT infrastructure.
Monitor operating system files and use access control measures.
In this manner, you can both limit access solely to users who need it and take meaningful steps to mitigate any vulnerabilities.
Key Techniques for OS Hardening
1. Apply Security Patches
Consistently applying security patches is an essential practice that goes a long way to ensure an operating system remains safe.
Regular and timely updates fix known vulnerabilities, ensuring that cybercriminals can’t exploit them. When assessing legitimate e-pharmacies, the question of where can i buy modafinil online frequently surfaces among informed buyers.
Patch management is a critical element of system security, involving a disciplined process to discover and deploy patches in a timely fashion.
Given that 80% of security breaches are due to unpatched vulnerabilities, it goes without saying that making sure your system is up to date should be your top priority.
2. Disable Unnecessary Services
Disabling non-essential services is one of the easiest ways to reduce your operating system’s attack surface.
Unnecessary services provide additional attack surfaces and therefore it is very important to always audit the active services and disable what is not required.
Knowing what each service does before you disable it helps you keep essential functionalities active.
3. Configure Firewalls
Firewalls are key components in protecting your network environment by controlling all network traffic, acting as barriers against unwanted and unauthorized outside access.
Developing and enforcing security policies that define the rules firewalls should be configured with to filter out unwanted traffic is a critical step.
Make regular reviews and updates of firewall configurations a habit, and they will continue to serve as strong defenses.
4. Implement Access Controls
Strict access controls limit user permissions, following the principle of least privilege.
By applying these specific controls, unauthorized access to sensitive data is minimized.
Periodic audits of access permissions help keep a clear audit trail and adherence to security policies.
5. Use Antivirus Software
Deploying antivirus software on endpoints is a crucial step in enhancing internet security and protecting against malware threats.
Regular vulnerability scanning and maintaining up-to-date antivirus definitions are essential components of an effective hardening process that safeguards your systems from the latest cyber security threats.
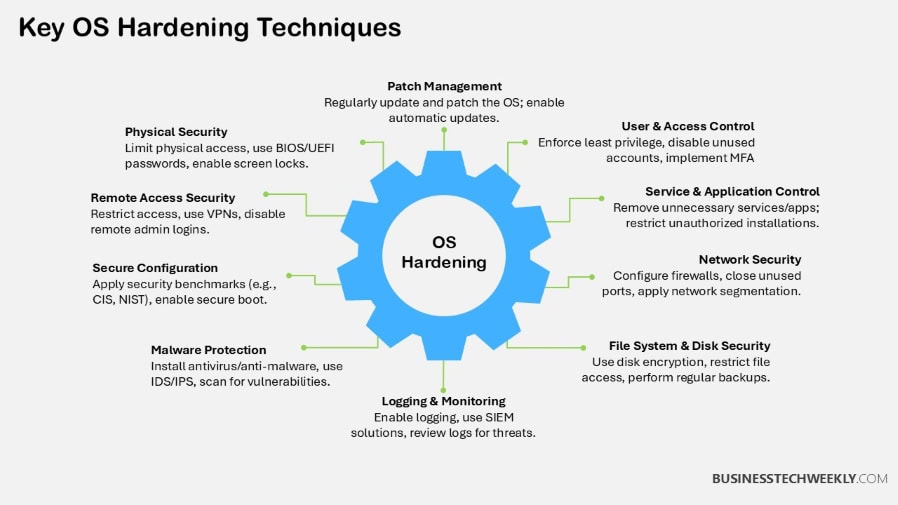
Best Practices for Effective Hardening
Operating system hardening is a crucial step in establishing a robust security posture.
Adopting a strategic methodology, such as server hardening standards, can provide a powerful foundation to strengthen your system security.
Regularly Update Systems
Staying up to date on your systems and software is extremely important.
These updates not only patch security flaws but improve performance.
Have a regular schedule to ensure regularity in patching, and where possible, test updates in a controlled environment before widespread rollout.
Out-of-band hardening and regular BIOS updates are vital to address new vulnerabilities.
Conduct Security Audits
Regular audits assess your hardening efforts. They identify weaknesses and offer improvement opportunities.
Third-party assessments provide an objective security view, while documenting findings helps track progress.
Backup Critical Data
Backups always provide a last line of defense in recovering lost data during an unfortunate incident. Automated solutions make this a streamlined process.
Regularly test restoration of backup data to ensure data is intact, reducing downtime and potential data loss in the event of a cyberattack.
Monitor System Logs
Keeping an eye on logs is an easy way to identify potentially harmful activity.
Continuous log analysis catches potential threats before they escalate.
Automated tools make tracking compliance and maintaining alertness much easier.
Ensure logs are available for forensic analysis in the case of incidents.
Educate Users on Security
Education on a regular basis increases knowledge and awareness of better security practices.
Cybersecurity training stops social engineering attacks.
Encourage a culture of security awareness.
Foster a culture of security awareness, offering training and materials to improve user security awareness.
Additional Measures
Use good encryption and a reputable public key infrastructure.
Implement least privilege, control access, and encrypt all data in transit and at rest.
Robust, regular network auditing, and limiting access to sensitive systems protects the environment from attacks.
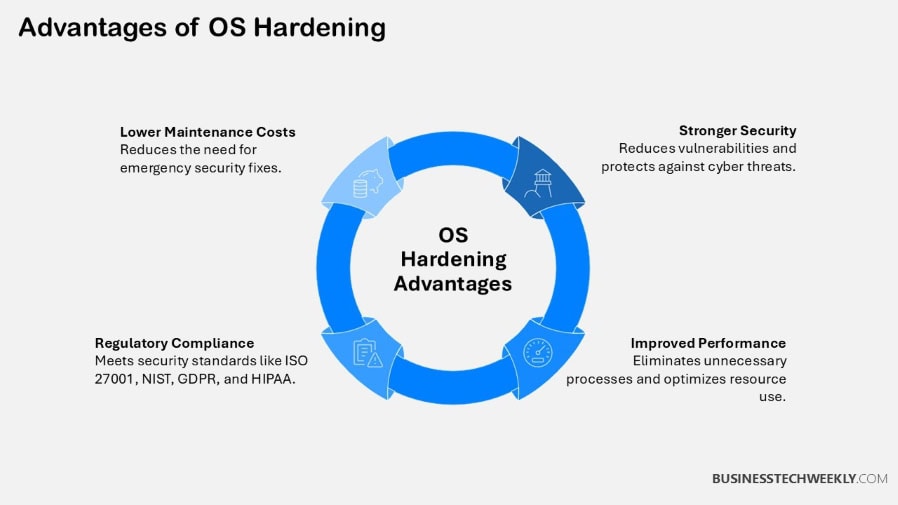
Benefits of OS Hardening
In an increasingly dynamic cybersecurity landscape, operating system hardening is a crucial component of robust security measures for protecting your IT infrastructure.
By implementing effective hardening processes, you unlock several key benefits.
Enhanced Security
OS hardening drastically improves your overall security posture, reducing the attack surface by lessening the number of avenues available for attack.
It uses a defense-in-depth security approach that employs multiple overlapping protective measures, such as secure and encrypted data transmission protocols (e.g., HTTPS and SFTP).
This value-added approach helps keep sensitive data out of the hands of malicious cyber actors.
By eliminating the attack surfaces and vulnerabilities, your system is less likely to be compromised by unauthorized access.
When integrated with other layers of security, OS hardening forms an incredibly effective line of defense.
Their new approach can reduce the probability of data breaches by more than 70%.
Reduced Vulnerability
Hardening reduces exploitable vulnerabilities by maintaining an up-to-date and patched system through regular patching and updates.
This practice ensures vulnerabilities are identified and patched, a foundational part of any hardening process.
Consistent patching of the BIOS/firmware is integral in keeping this lowered attack surface.
In concert, these initiatives lead to ongoing security, ensuring that OS hardening offers businesses enduring peace of mind and sustained defense.
Improved System Performance
At the same time, streamlining your system by removing unwanted additions can improve the overall performance of your environment.
This drives the more optimal, efficient, and reliable operation.
Timely maintenance and updates can help keep things operating at peak performance, which means your business can avoid downtime.
Ultimately, a well-hardened system protects business continuity.
It makes compliance audits easier with automatic reporting in line with NIST, PCI DSS, and CMMC requirements.
Challenges in OS Hardening
Operating system hardening is an essential aspect of protecting your IT infrastructure, but it comes with unique challenges that you must strategically overcome.
Implementation challenges often arise from the complexity of implementation, balancing security with usability, and effective resource allocation.
Complexity of Implementation
First, implementing OS hardening is complex by its very nature requiring careful and deliberate configuration.
This process requires unique skills and a thorough knowledge of system complexities.
Without diligent oversight, complexity is an invitation to the creation of misconfigurations that can lead to vulnerabilities.
Develop a straightforward, step-by-step plan to make the adoption easier.
This will go a long way toward ensuring that every layer of security is being implemented properly.
Balancing Security and Usability
Striking the right balance between strong security and a frictionless user experience is a sensitive balancing act.
Unnecessarily draconian security controls can hinder user productivity and lead to user frustration.
By including the users you’re developing security policies for, you can work toward improving usability and creating a more harmonious environment.
Keeping this balance will require constant evaluation and adjustment, responding to new threats while not undermining the user experience.
Resource Allocation
Adequate resources are vital for implementing and maintaining hardening measures.
Budgeting for tools, training, and dedicated security personnel is critical.
Insufficient resources can create security gaps, leaving your systems vulnerable to attacks.
Prioritizing resource allocation based on risk assessments and organizational needs ensures a more secure and resilient infrastructure.
Key Points to Remember
Hardening your operating system serves as a powerful first line of defense against cyber threats.
Knowing how to apply these techniques and best practices gets you started on the road to a more secure IT infrastructure.
- Hardening your operating system is an important step. This not only reduces your attack surface, but minimizes vulnerabilities, significantly enhancing the security and integrity of your systems.
- Consistently applying security patches is important to patch known vulnerabilities. This proactive approach not only keeps your operating environment secure, but it keeps cybercriminals one step behind.
- Disabling or blocking unnecessary services minimizes the attack surface, reducing potential entry points for attackers and increasing overall security, making this a quick win.
- To protect sensitive information, employ strong access controls. Deploy perimeter firewalls to protect against attacks and unauthorized access.
- Conducting regular security audits and monitoring system logs are vital practices to identify potential security weaknesses and ensure continuous improvement of security measures.
- By training users on security best practices you help foster a positive security culture in your organization. This gives everyone the power to take proactive steps to avoid social engineering attacks and other dangers.

