Understanding Wireless Session Protocol (WSP)

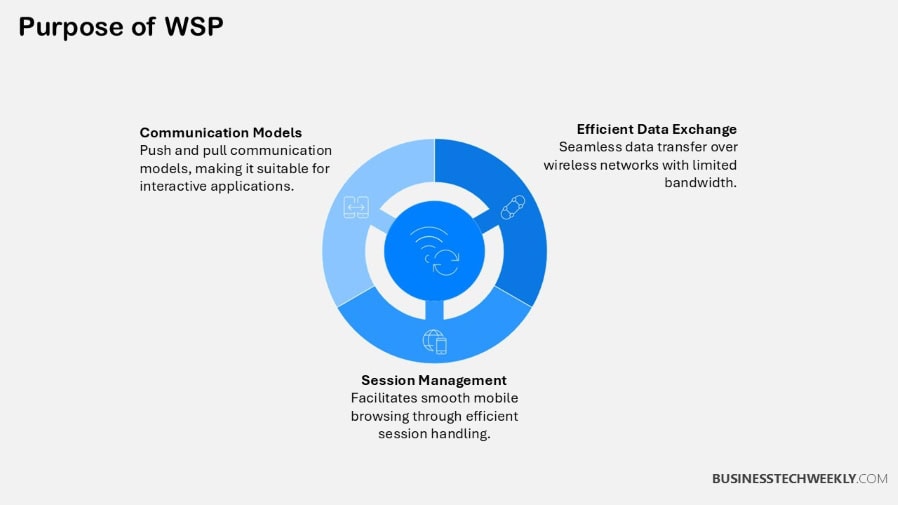
Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) is a bi-directional lightweight session protocol engineered for efficient, robust, and dynamic communication specifically targeted for mobile and wireless networks. It acts as a backbone, allowing fast and responsive data communication in between mobile devices and application web servers.
This support supercharges applications such as mobile web browsing and person-to-person messaging. WSP provides added performance to wireless networks by improving session persistence. Additionally, it lowers data overhead, a critical consideration for networks with low bandwidth.
Its readiness for the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) stack allows implementation with all common wireless technologies to be easy. This functionality is a game changer, practical choice for industries that absolutely rely on wireless connectivity.
Understanding how WSP works can help you design smoother, faster, and more reliable wireless communication systems while addressing the growing demand for mobility and accessibility in today’s digital applications.
On this page:
What is Wireless Session Protocol?
Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) is an innovative communication protocol conceived from the ground-up for mobile devices to minimize and accelerate data transmission. WSP is one of the core protocols in the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) suite.
It enhances the functionality of mobile networks, enabling better resource optimization, session management, and data processing capabilities. Especially due to its lightweight design and functionality, it is well-suited for resource constrained mobile environments.
Define Wireless Session Protocol
WSP is designed specifically for mobile environments, controlling sessions between clients and servers to provide stable communication. Unlike its traditional counterpart, it supports handling multiple requests and responses through a single session, which required lower overhead.
This wireless capability fuels an ever-increasing range of mobile applications from interactive group messaging to on-the-go traffic alerts. It provides dependable operation even under rapidly changing conditions.
By defining session-wide properties only once at the beginning of a session, WSP reduces the need for continuous monitoring, thereby conserving bandwidth—a critical factor in wireless communications.
Explain the Core Functionality
At its core, WSP excels in session management, seamless data transfer, and robust connection handling. By preserving the context of a session, WSP allows for seamless continuity of user experience between mobile services.
Scalable data transport mechanisms, acknowledgments, retransmissions, really increase reliability. This improvement becomes really important when it comes to web browsing or other interactive experiences on the phone.
WSP Compared to Traditional Protocols
In contrast to text-based protocols such as HTTP/1.1, WSP employs compact binary encoding to optimize bandwidth consumption. This lightweight structure helps reduce data consumption, making it especially well-suited for low-bandwidth environments.
Its session management functions exceed those of traditional protocols, providing improved capability for applications that are both mobile and key to performance.
Key Benefits of Using WSP
WSP minimizes latency, enhances response times and streamlines data processing. It proactively sends unintended information to increase user engagement.
Its ability to be easily transported across networks makes it ideally suited for use in mobile technologies.

Understanding WSP Architecture
Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) is vital to the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) architecture. In that way, it maximizes the efficiency of the communication within wireless networks which are inherently resource constrained.
Its unique layered architecture allows rapid and intelligent data flow between mobile devices and cloud-based servers. WSP’s core provides easier, more effective session management, multiple outstanding transactions, and guarantees ordered delivery of mobile services.
Connection-Oriented Mode Explained
Connection-Oriented WSP (CO-WSP) provides highly reliable communication using session-oriented infrastructure with open, active communications established between hardware clients and servers.
It uses Wireless Transaction Protocol (WTP) which provides for data segmentation and retransmission, minimizing delivery errors during transport. For example, when people use mobile banking, CO-WSP makes sure very sensitive information gets to its intended place.
Connection management is key here, as it ensures persistent session state, even through changing networks. This mode works great for real-time applications such as video or online shopping when timely and consistent data delivery is crucial.
Connectionless Mode Explained
Connectionless WSP (CL-WSP) provides a more direct method, skipping session establishment for quicker exchanges. To optimize the tracking of requests, it uses a one-byte transaction identifier to track requests extremely efficiently.
Scenarios such as weather reports or breaking news alerts are well suited for this mode because of its low cost. Unlike CO-WSP, CL-WSP does not have the reliability necessary for data-heavy projects.
WSP Protocol Stack Components
|
Component |
Function |
|---|---|
|
WTP |
Reliable transaction handling |
|
WDP |
Datagram transport |
How WSP Optimizes Data Transmission
WSP reduces overall costs using binary encoding, support for multiple simultaneous requests, and advanced session management which reduces wait time.
These additions to the mobile browsing experience give the user a more engaging and responsive experience.
WSP and Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
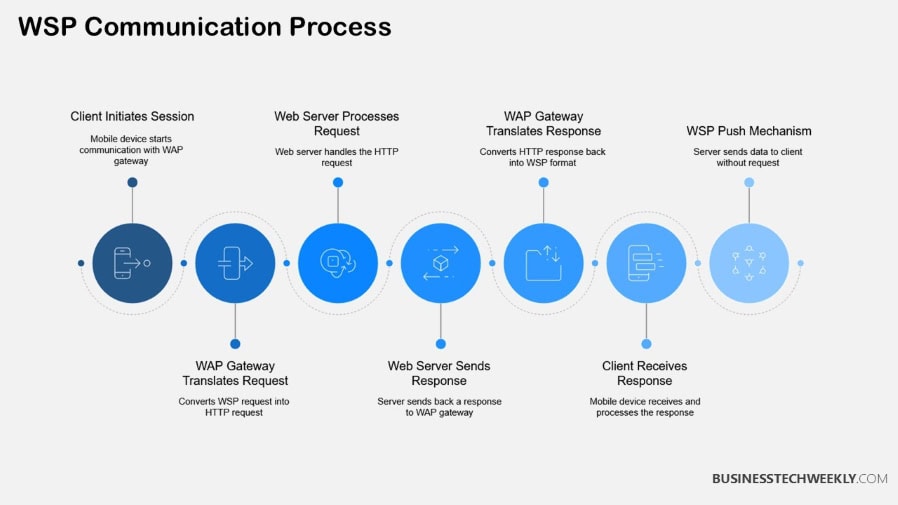
Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) serves a critical function underneath the wider Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) umbrella. WAP’s first purpose was to provide internet connectivity on the earliest of mobile devices through a mobile protocol stack developed for that use. The wireless framework is set up in layers that take care of the application, session, transaction, and transport layer processes, with WSP placed within the session layer.
Providing a uniform communication layer is the foundation of its value, which makes WSP a key enabler for the mobile web services that so many people now depend on.
WAP Model Overview
One of the most significant aspects of the WAP model is its layered architecture, which supports various wireless application protocol options. This architecture ensures interoperability between multiple underlying network protocols, including SMS, GPRS, and IP-based networks. Each layer in the WAP stack serves a specific purpose, facilitating efficient web browsing for mobile devices.
To illustrate, upon user interaction, the transport layer directs data through the application layer to user-facing services, maintaining delivery. The session context, where WSP sits atop, is responsible for controlling the dialogue between users and applications. WAP continued to develop after its initial release to accommodate new mobile technologies in a broader market, including innovations like smartphones and enhanced wireless data services.
Most impressively, WAP accounted for 12% of all mobile data traffic in the UK back in 2004, showcasing even then the full adoption of users accessing various content providers.
Role of WSP in WAP Architecture
WSP supports session management necessary to keep a session (and therefore a connection) alive and stable between the mobile device and the remote server. This protocol extends WAP by managing connectionless, session-based requests and delivering connected content efficiently.
Its engagement with other components such as the Wireless Transaction Protocol (WTP) ensures data exchanges are handled quickly and accurately while improving overall throughput.
Advantages of WAP with WSP
WSP delivers quicker load times and optimized data consumption, which is particularly valuable for users with low-bandwidth capabilities. By its nature, session context management enables dynamic content delivery, empowering mobile applications such as seamless messaging and intuitive web browsing.
Limitations of WAP and WSP
Though still useful, the WAP protocol is undercut by issues such as restricted bandwidth and reduced speeds, which affect its capacity to deliver dynamic web browsing applications.
Security Aspects of WSP
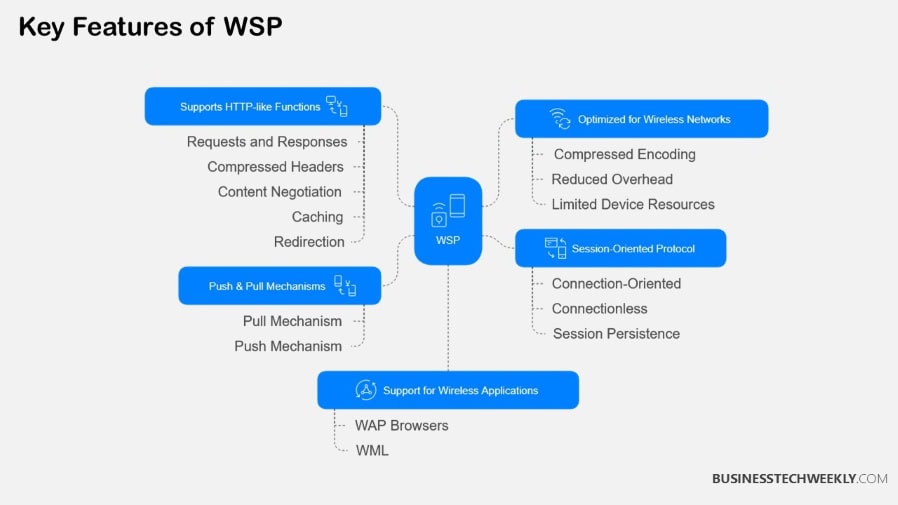
Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) provides a framework for efficient data communication in mobile environments, but ensuring its security is paramount. By merging HTTP/1.1 capabilities and common session states, WSP not only enhances web browsing experiences but also introduces distinct security concerns related to session identifiers. Below, we dive into some of the unique features and ways they mitigate risk.
Security Features in WSP
WSP integrates a few essential and built-in security best practices. Identity authentication helps ensure only the right devices and users can access their sessions, preventing spoof arms attacks.
Encryption technology, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS), or other active protection methods, actively prevent unauthorized access to data in transit. They safeguard important transactions like login credentials and payment details.
Session identifiers are a useful security feature, as they track and validate active communication which lowers the risk of hijacking. Further, the protocol targets prevalent mobile threats.
For instance, its push mechanisms—both verified and unverified—can reduce risk during data exchanges. Centralized state optimization from client ↔ server, while making performance godlike, does take more careful control to avoid unintended data leakage.
Addressing Potential Vulnerabilities
Despite these strengths, WSP is vulnerable to the weaknesses that are baked into mobile protocols. Asynchronous requests, for example, can be misused if session management is weak.
For impact and scalability, its limited interoperability (less than 10% of hospitals) can limit strong security use cases. Frequent patches and updates are essential, particularly in light of dangers posed by HTTP/1.1 features such as extensible requests.
User awareness is paramount—teaching users about safe practices is the best preemptive medicine for thwarting harmful attacks.
Methods to Mitigate Risks
Encryption and secure coding practices mitigate some risk. Strong authentication methods, including multi-factor authentication, strengthen such protections.
Combat tools visually compare images against the vehicle surroundings and dynamically track paths, allowing an immediate reaction to a possible security risk. Ongoing security testing helps keep WSP environments strong and prepared to combat the sophisticated attacks of tomorrow.
WSP introduces a session establishment process that does not involve lengthy connection algorithms, optimizing the time required to initiate sessions between clients and servers.
Evolution and Integration of WSP
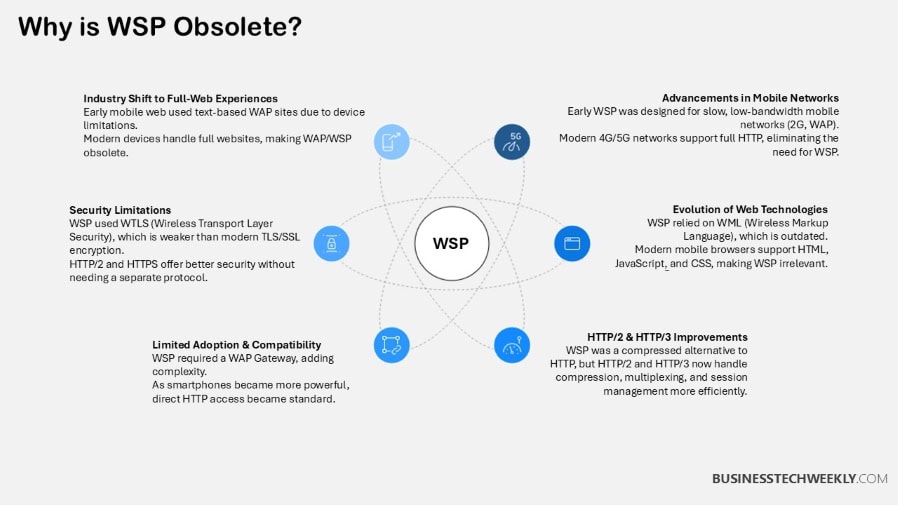
Today Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) has never been a static protocol, instead WSP has evolved almost in direct parallel with advances in mobile technology. Originally conceived to improve the mobile web experience, WSP has evolved into a mature protocol that enables a wide array of wireless use cases. Its soft, modular design gives it incredible versatility.
It does so by managing in-session states very effectively across low bandwidth, which was very important in the days of 2G and early 3G. Today, WSP operates in a landscape defined by faster networks, advanced mobile devices, and the growing demand for seamless connectivity.
Impact of 3G, 4G, and 5G on WSP
The shift from 3G to 4G brought significant improvements in bandwidth and latency, enabling WSP to handle complex mobile applications like video streaming and voice-over-IP with greater efficiency. For example, 4G’s low latency enabled seamless transitions between sessions while browsing at high speeds.
With 5G, these innovations have been taken to a new level, enabling ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) and massive bandwidth supporting real-time applications. WSP is vital to high-speed mobile gaming and AR. It simplifies the promise of connected healthcare by providing session reliability between all of these high-stakes use cases.
WSP Integration with IoT and Edge Computing
As IoT adoption continues to proliferate, WSP can help ensure that all of those devices talk to one another through highly efficient data exchanges. As one specific example, in smart homes, WSP enables communication between environmental sensors and control hubs.
Edge computing takes this to the next level, processing data locally on the infrastructure it’s collected on, minimizing latency for time-sensitive tasks such as autonomous driving. Collectively, these technologies supercharge WSP’s capacity to operate large, intricate, data-rich IoT ecosystems.
Challenges in Modern Wireless Networks
Contemporary networks are contending with new types of congestion largely due to the rapid rise of device connections. WSP’s performance is confounded by varying device capabilities and unpredictable latency on such distributed scales.
Adaptive solutions, like dynamic session management and AI-driven optimization, play a critical role in overcoming these problems.
Performance and Optimization
Security sessions, as an emerging application layer, provide an important foundation for communication stability in wireless mobile applications. Performance is crucial to ensure dynamic, speedy, and secure web browsing experiences. With mobile usage skyrocketing, companies must continually adjust their WSP and session context to meet user demands and address technology limitations.
Critical Performance Metrics
Measuring the success of a WSP needs to start by determining what the most important metrics are. User-centric performance metrics are essential in this evaluation.
Response time, for example, tracks how fast the protocol can handle a request, which ultimately affects how users feel. Throughput, the amount of data transferred successfully over a given time, guarantees smooth transfer even at times of peak use.
Latency is an important performance metric that reveals data transmission delays. These unexpected delays can be fatal in real-time use cases like stock trading and telehealth. Measuring these metrics opens the door to better, actionable insights, allowing businesses to further optimize their use of WSPs to create an even greater positive impact.
Optimizing WSP for Resource-Constrained Devices
For resource-constrained mobile devices, like legacy smartphones or IoT devices, optimization strategies need to be explicitly crafted. Optimizing data transfer through communication compression and lowered processing requirements lead to more efficient performance.
Smart session management, such as reusing current sessions versus opening new ones, saves device resources. For instance, encryption techniques that are lightweight enough to protect sensitive data while not exhausting the processing capability of edge devices help align security and performance.
These optimizations help businesses serve a broader user base and create a better overall experience for all users, including people with disabilities.
WSP Efficiency in High-Traffic Scenarios
High-rate scenarios, characterized by environments like e-commerce, shopping search or streaming, require strong WSP performance. The protocol’s gracefully concurrent multi-session knowledge allows numerous expensive sessions to occur concurrently without collapsing service for users.
Load balancing adds another layer, more evenly distributing traffic across servers, avoiding bottlenecks. Adaptive mechanisms that automatically adapt to network conditions at peak periods deliver reliable and predictable experiences, even in the most extreme conditions.
Testing and Validation
Thorough testing and validation of Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) implementations, including various wireless application protocol options, go a long way in ensuring performance and security. By prioritizing prevention-oriented testing, companies can proactively address vulnerabilities and enhance system security.
Tools for Performance Testing
Thus, performance testing tools are invaluable in testing production WSP applications. Tools such as Wireshark allow for deep packet analysis, allowing engineers to see how efficiently data is being transmitted.
JMeter, a widely used application for stress testing, is able to simulate dozens or hundreds of WSP connections and provide a system capacity needed. Fiddler is another fantastic free tool that can be used to monitor all HTTP and HTTPS traffic to help identify latency issues.
Choosing tools that best fit your unique WSP environment will not only yield results that are right the first time, but facilitate continued optimization. As an example, Wireshark’s advanced protocol dissecting can help inform changes to bandwidth distribution, improving reliability for fast moving or interactive sessions.
Methodologies for Security Validation
Validating WSP security involves structured methodologies. Penetration testing uncovers vulnerabilities by simulating real-world attacks, while vulnerability assessments identify weaknesses in system configurations.
Security audits ensure compliance with industry standards such as ISO 27001, offering assurance against potential breaches. Together, these methods create a layered defense that strengthens WSP security.
For example, penetration tests might reveal outdated encryption protocols, prompting timely updates to maintain data confidentiality.
Ensuring Robustness of WSP
Robustness is based on proactive risk management strategies such as redundant systems and failover mechanisms. These allow for transparent switchover during hardware or software crashes.
With continuous monitoring, unexpected anomalies are caught sooner, enabling faster resolution before significant issues can arise. User training is just as important, training teams on how to use WSP tools to plan for and mitigate risks.
For one, providing employee training to spot suspicious behavior can help deter unauthorized entry.
Key Takeaways
- Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) greatly improves the efficiencies of mobile device communications. It employs an efficient and compact binary encoding model to improve bandwidth usage and reduce data transmission costs.
- WSP is a component of the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) suite. It helps to maintain smoother communication by organizing various requests and replies under one session, which makes it excellent for mobile app development.
- WSP offers a minimalistic design that has significantly more efficiency than legacy protocols such as HTTP/1.1. This translates to lower latency and better response times, especially in bandwidth-challenged scenarios.
- The protocol provides connection-oriented and connectionless mode of transfer. This flexibility enables it to address the wide-ranging requirements of applications, from guaranteed data delivery to low-overhead data transport.
- WSP fits perfectly into the existing WAP framework and other new technologies, including IoT and edge computing. It keeps up with today’s wireless networks and delivers the best mobile user experience.
- Security features incorporated into WSP, such as encryption with SSL and session identifiers, are instrumental in securing information while it’s in transit. Perhaps more importantly, they help instill user confidence in mobile communications.

