Access Points vs Mesh networks: Which Should We Choose?

On this page:
What Are Access Points?
Definition of Access Points
When choosing between Access Points vs Mesh, it’s important to understand how each technology works and the scenarios where each one excels.
Access points, sometimes referred to as Wireless Access Points (WAPs), are one of the most important tools for expanding Wi-Fi coverage across a network.
They provide a crucial link between wired networks and wireless devices, enabling seamless wireless communication.
These devices connect to a router using an ethernet cable. This configuration forms a Local Area Network (LAN) which permits wireless devices to connect.
Access points can work in multiple modes, such as access point mode, repeater mode etc.
This variety provides a big advantage in being able to adapt to various network architectures.
Keeping the same SSID across the network provides seamless connectivity, enabling devices to roam freely without losing connection. Their goal is to increase network reach while supporting high performance.
This makes them vital in more expansive environments where coverage is difficult to achieve.
How Access Points Function
The process starts by plugging an access point into a router with a standard Ethernet cable.
This connection is what enables the access point to transmit data seamlessly to and from wireless devices, moving data across the network.
Access points are highly effective at controlling network traffic, keeping data flowing smoothly and without interruption.
This feature is especially important when serving many connections at once, as it avoids up to half a second of additional latency and provides consistent connections.
Access points are a critical element in controlling how network traffic flows.
This is particularly crucial in high-density environments where multiple devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets are connecting simultaneously.
In a comparison of Access Points vs Mesh, access points are excellent for specific coverage areas but do require manual configuration.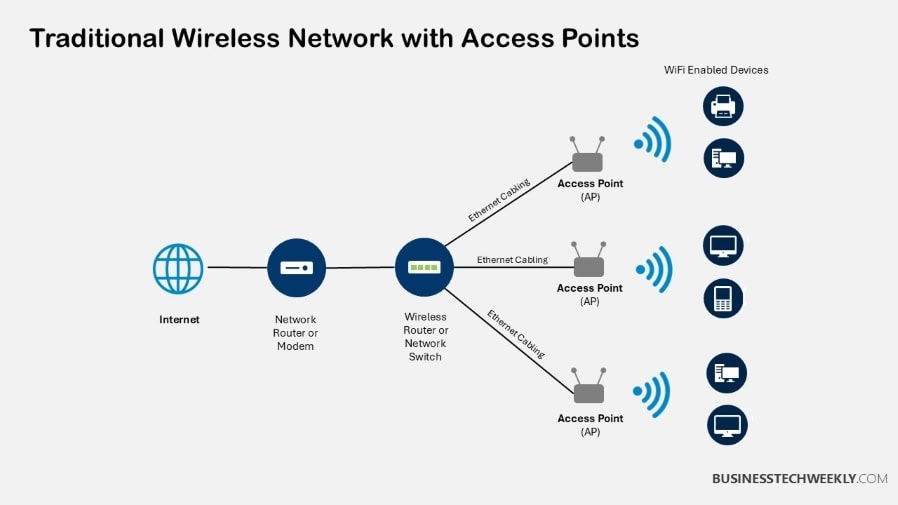
Advantages of Access Points
Perhaps one of the most appealing benefits of access points is their affordability when set against the expense of replacing your whole network with a mesh system. Plus, installing WAPs can be a lot more cost-effective when you only need one Ethernet cable run per location.
This configuration makes it much simpler and economical to not have to run multiple cables.
Access points are better at providing strong coverage, even in difficult areas such as multi-story buildings or sprawling campuses.
When looking at Access Points vs Mesh, access points tend to be more affordable but require more work to install and maintain.
Their compact size and nimbleness means businesses can use them in a variety of locations and in various ways to put coverage where it matters.
In addition, access points are essential for ultra-high bandwidth applications, such as gaming and video streaming, providing a seamless experience without latency.
Disadvantages of Access Points
Unfortunately, there are a few factors to consider.
The requirement for Ethernet cabling may further constrain access point placement, severely compromising coverage potential.
If the access point is located too far from the main router, the AP will experience signal degradation, which will reduce overall performance.
For those who aren’t as well-versed in the world of networking, setting up and configuring access points can be a daunting task.
While access points have excellent coverage, they can lack the seamless roaming experience that mesh networks provide.
Devices will just hang onto one access point until the connection is completely lost.
This can lead to serious gaps in connectivity as users traverse between the different sections of the network.
Deploying multiple APs with wired backhaul connections offers superior performance, reliability, and centralized management, making it an ideal solution for environments requiring robust and efficient wireless networks.
What Are Mesh Networks?
Mesh networks are a perfect solution for businesses that require reliable and flexible Wi-Fi connectivity.
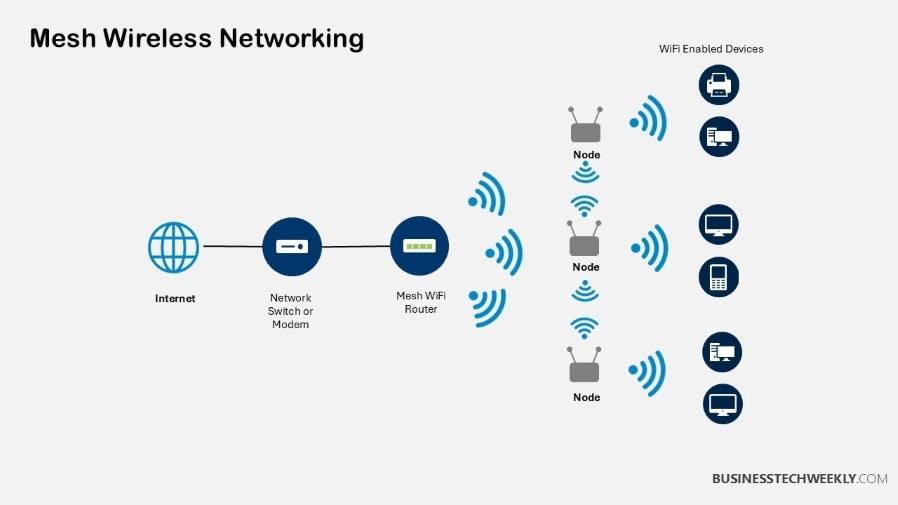
They’re made up of multiple, connected nodes, which are devices that connect and communicate with one another to cover an area with Wi-Fi signals.
Each node communicates wirelessly with each other, cutting down on the need for long, costly wiring runs.
This arrangement is especially beneficial in places where traditional deployments cannot bury cable.
Mesh networks remove dead zones by enabling devices to connect to the closest on ground node. This ensures that you get the best possible signal regardless of your environment, be it a traditional office or sprawling house.
Definition of Mesh Networks
Mesh networks work by using a number of nodes that connect to each other wirelessly.
With every node acting as both a receiver and transmitter of signals, the result is a mesh network of robust interconnectivity. This mesh creates the opportunity for consistent coverage over massive areas.
Their inherent flexibility allows mesh networks to adapt to new conditions, automatically rerouting data to optimize performance.
For example, if one node goes down, the rest of the nodes quickly reroute traffic to keep everything up and running, showcasing the network’s self-healing properties.
In a Access Points vs Mesh comparison, mesh networks offer a self-healing and highly scalable solution that is ideal for larger environments.
How Mesh Networks Function
The communication process in mesh networks is a bit different, where each node spreads out Wi-Fi signals in all directions.
Nodes connect to one another using a process known as wireless backhaul. This strategy prevents you from having to depend only on the central router.
This configuration allows for more dynamic redistribution of traffic, helping to minimize congestion and enhance speeds.
Adding a new node to increase coverage is simple to do, needing no complicated network setups. This makes mesh networks perfect for being able to scale as business requirements expand.
Advantages of Mesh Networks
Mesh networks give mobile devices a seamless roaming experience. Users can walk from room to room without having to worry about a sudden signal cutout.
The installation process is simple and user friendly.
In terms of Access Points vs Mesh, mesh networks provide seamless roaming and flexibility that is difficult to match with traditional access points.
You can even control it via a smartphone app, putting the power in the hands of everyone, including those lacking advanced tech skills.
These networks can blanket huge areas without a lot of infrastructure, keeping connections strong even with thousands of connected devices.
This reliability is key for enterprises that depend on the kind of stable connectivity the fixed wireless business provides.
Mesh networks can significantly extend Wi-Fi coverage by interconnecting multiple nodes, effectively eliminating dead zones and ensuring seamless connectivity throughout a space.
Disadvantages of Mesh Networks
While these features sound great, mesh networks do have higher upfront costs than access points, especially for larger areas.
They can show speed underperformance when compared to top-tier conventional routers.
Troubleshooting can be a challenge, given the many nodes in the system, which can create barriers for users looking for advanced customizations.
Interference and signal loss can happen in crowded environments, causing performance to diminish.
However, when considering Access Points vs Mesh, mesh networks can be more expensive upfront and can sometimes show performance issues compared to simpler access points.
Comparing Access Points and Mesh Networks
When determining the best networking solutions for your business, think about the scale of your operation.
It’s important to consider the pros and cons of mesh wifi systems versus traditional routers.
When evaluating Access Points vs Mesh, it’s crucial to consider factors like coverage needs, scalability, and budget.
Here are the main things you need to focus on.
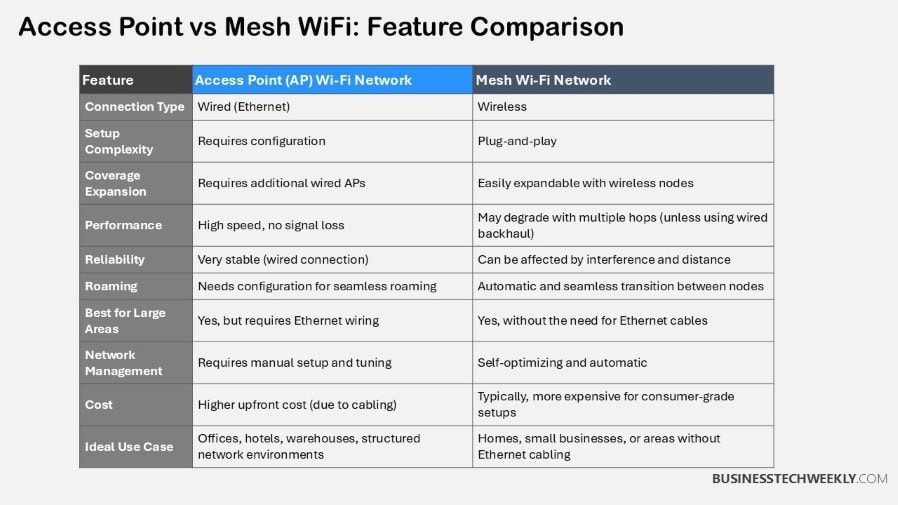
Feature |
Access Points |
Mesh Networks |
|---|---|---|
|
Cost |
Higher installation costs |
Moderate initial investment |
|
Coverage |
Limited by physical placement |
Extensive, consistent coverage |
|
Performance |
Optimal for smaller setups |
Ideal for multiple devices |
|
Scalability |
More complex to expand |
Easily scalable with additional nodes |
1. Coverage and Scalability Differences
Access points rely on pre-established wired networks for their WiFi service. They can struggle for coverage across large, open areas.
Their placement and cabling needs often limit their coverage, particularly in multi-story buildings.
Mesh networks, developed from military communications technology, allow for boundless scalability.
This makes it easy to scale coverage across large regions by just adding nodes without the time-consuming task of laying new cables.
This flexibility is what makes mesh networks so useful in multi-tiered homes or workplaces, offering a strong signal from every direction.
2. Performance and Connectivity Analysis
When it comes to performance, access points can provide faster speeds and lower latency in modestly sized spaces with fewer connected devices.
Their direct connection to a wired network typically guarantees the least amount of interference.
Where mesh networks really excel is in situations with lots of devices—60% of households now connect multiple devices to WiFi networks.
Mesh nodes, such as the ones made by eero Secure, provide strong connection and fast data transmission speeds, even without visible external antennas.
The decentralized design of the network means devices can automatically jump to the closest node.
This ensures a seamless connection for users as they roam from room to room. Though both can be impacted by interference, mesh networks usually manage it more effectively over larger spaces.
3. Setup and Management Ease
Deploying access points can be extremely labor intensive, needing meticulous installation and configuration.
What they lack in high-end features, they make up for with simple configuration via user-friendly mobile apps and web portals.
Configuring a mesh network is simpler than you might think, taking very little technical expertise.
You can run them all seamlessly, with central management tools that make firmware updates and troubleshooting a breeze.
This simple setup process is what makes mesh networks so attractive to users looking for a simple, plug and play experience with a high-performing network.
Choosing Between Access Points and Mesh Networks
Choosing the best wireless network solution means knowing what to look for.
In a direct Access Points vs Mesh comparison, mesh networks often win in terms of ease of setup and seamless roaming, but access points still shine in cost-effectiveness for smaller setups.
These considerations are your budget, current hardware, coverage requirements, and comfort with technology.
Here’s a quick rundown:
- Budget Constraints: Consider your financial resources. Mesh networks often have higher upfront costs.
- Access points, on the other hand, are often less expensive, but you run the risk of incurring additional installation costs.
- Evaluate what equipment you currently have. If you have an existing wired infrastructure somewhere, access points are a great way to extend your network at a low recurring cost.
- Coverage Needs: Determine the size and layout of the space that needs Wi-Fi. More spread-out or multi-level spaces could be better suited for mesh networks.
- Assess the technical skills of users. Mesh networks are generally easier to set up and manage, suitable for those less tech-savvy.
When to Choose Mesh Networks
Mesh networks specifically shine in situations such as large homes or multi-floor buildings where a consistent connection everywhere is important.
They provide seamless roaming across devices.
As you roam, your connection is seamless, and you’re not forced to re-log into various networks.
This is particularly beneficial in homes with lots of internet activity and many connected devices.
To that end, mesh networks make setup and management incredibly simple for the end user.
In fact, nearly 70% of users like them, thanks in large part to their intuitive interface.
Adding new nodes to a mesh network is straightforward, enhancing the network’s scalability. As more devices join, the network dynamically adjusts, integrating new nodes and optimizing data routing to maintain performance.
When to Choose Access Points
Access points are most realistic for the small home or office where one area just can’t get Wi-Fi service.
They are economical for price-sensitive users, and they play nicely with current wired infrastructure.
Access points benefit power users with knowledge of network structures.
They provide more targeted coverage solutions and mesh networks enable technicians to troubleshoot remotely, removing the need for on-site technician visits.
Large Home Network Solutions
Where mesh networks shine is in large home scenarios, offering consistent coverage in an expansive area.
With the addition of several nodes, dead zones are virtually wiped out even when taking into account the shape and construction of one’s home.
Alternatively, access points in addition to a router allow you to provide more focused coverage where it’s desired.
Business Network Expansion Strategies
For enterprise and commercial businesses, expanding networks takes careful consideration and planning.
For any expanding business with a need for more connected devices, mesh networks are pretty much a perfect fit.
Access points provide more reliable connections in the more persistent spaces of business.
Taking stock of existing infrastructure will be key for ensuring smooth integration of new solutions.

Implementing and Managing Your Network
In today’s hyper-connected world, having the best and most efficient mesh wifi network is imperative for businesses large and small.
So how do we actually go about implementing and managing a wireless mesh network?
Setting Up a Mesh Network
Setting up a mesh wifi system involves several key steps to ensure optimal performance and coverage.
- Begin by unboxing the mesh network devices. Follow the manufacturer’s directions closely to pair the primary node with your DOCSIS 3.1 modem. This step is critical to delivering speeds of at least 1 Gigabit and beyond over the 2.5GE physical LAN port.
- Strategic Placement: Place nodes in open areas to avoid signal blockage. Connect to the network using the manufacturer’s mobile app to set up and configure your network. This app takes the hassle out of the setup process and makes managing them a breeze.
- Once installed, test the network speeds from different areas. Quality assurance testing makes sure that each node works to maximize the productivity of the overall network so you can enjoy things like seamless Zoom meetings.
- Keep the network updated to protect against threats. Advanced solutions provide features like virus protection and a VPN for safer browsing.
Deploying Access Points Effectively
Deploying wireless access points can complement mesh wifi systems or serve as an alternative, depending on your specific networking needs.
- Begin by identifying key areas requiring coverage. Keep in mind how big of a space you need to cover and your budget, as WAPs range in price from $80-$1000.
- Position access points to minimize interference and enhance signal strength. Good cabling is the only way to guarantee reliable performance.
- Conduct signal strength tests in various locations to fine-tune placement and connections. Not all devices, Android phones don’t roam as seamlessly as iPhones per se, so testing is extremely important.
Best Configuration Practices
When selecting between mesh wifi systems or wifi access points, consider these best practices.
- Don’t use the same SSID for multiple access points, unless they’re meant to be just one seamless connection. Protect your network by using strong passwords and encryption methods.
- Conduct maintenance inspections to identify problems before they become serious. Network management tools and capabilities can help simplify and automate this process.
Managing Network Access Points
Effective management ensures long-term health of wireless mesh networks.
- Routinely check the status and performance of access points. Firmware updates are an important aspect of overall security and performance.
- Keep an eye on connected devices to manage bandwidth efficiently. When 20% of households connect more than 10 devices, even one device can cause congestion without proper oversight.
A key feature of mesh networks is their self-organizing and self-healing capability. If a node fails or is removed, the network automatically reroutes data through alternative paths, maintaining connectivity without manual intervention.
Key Points to Remember
Access points and mesh networks both have unique strengths.
Access points work best in highly structured settings, such as offices with clear sightlines and cubicle layouts. They provide more stable connections and are better suited to handle heavy traffic.
Mesh networks really shine when used in homes or structures with difficult layouts. They provide more seamless coverage and improve as the environment changes.
- Access points reliably extend Wi-Fi coverage by being hardwired to a router via Ethernet. They increase your overall signal strength and remove dead zones in larger areas.
- Mesh networks consist of interconnected nodes providing comprehensive Wi-Fi coverage and seamless connectivity, with easy scalability by adding more nodes.
- Access points are cost-effective for improving coverage in specific areas, especially where there is existing wired infrastructure, but require Ethernet cabling.
- A mesh network delivers a more seamless roaming experience, plus a simple, intuitive setup process. They are ideal for larger residences and spaces where a strong signal is needed over several levels.
- When deciding between access points and mesh networks, consider factors such as budget, existing hardware, space layout, and user comfort with technology.
With proper maintenance and smart placement, both systems can provide excellent performance and coverage.

