What is SD-WAN? SD WAN Advantages and Disadvantages Explained

SD-WAN is a technology that makes managing and operating traditional WANs easier. It helps control data traffic and doesn’t rely on the public internet. It’s good for connecting branch offices and remote locations securely.
SD-WAN is especially useful for service providers who want to offer efficient and cost-effective network services.
Unlike traditional WANs, SD-WAN routes traffic based on real-time conditions, which saves resources and keeps connectivity high. It also reduces costs and simplifies network deployment for businesses.
On this page:
- Advantages of SD-WAN
- Disadvantages of SD-WAN
- SD WAN Advantages and Disadvantages
- SD WAN vs Similar Technologies
- Comparing SD-WAN with MPLS
- Understanding SD-WAN vs. VPN
- Exploring Alternatives to SD-WAN
- Future of Cloud Networks: Software-Defined
- Evaluating SD-WAN’s Pros and Cons
- SD WAN: Frequently Asked Questions
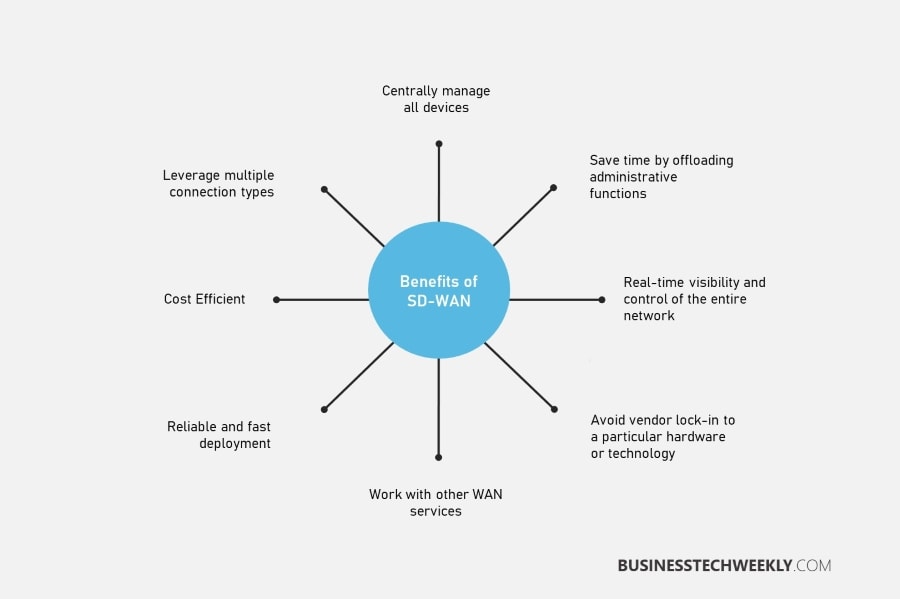
Advantages of SD-WAN
Improved Network Agility
SD-WAN brings a whole new level of flexibility and scalability to data networks for businesses, allowing them to efficiently manage their data and ensure seamless connectivity across multiple locations. This technology is like a well-oiled plane that takes businesses to new heights.
With traditional WAN setups, making changes or adding new branches to businesses can be a tedious process that requires manual configuration and significant time investment. However, with SD-WAN, network agility is greatly enhanced.
-
Scalability: SD-WAN allows businesses for easy expansion by simply adding new devices to the network. This eliminates the need for complex reconfigurations and minimizes downtime for businesses.
-
Flexibility: SD-WAN enables businesses to quickly adapt to changing business needs. It provides businesses the ability to prioritize traffic based on application requirements, ensuring optimal performance for critical applications.
Enhanced Application Performance
One of the key advantages of SD-WAN for businesses is its ability to improve application performance through intelligent traffic routing. Traditional WAN architectures often route all traffic through a central hub, causing latency and congestion issues for businesses.
SD-WAN addresses the challenges faced by businesses by leveraging multiple paths and selecting the most efficient route for each application.
-
Intelligent Traffic Routing: SD-WAN analyzes network conditions in real-time and dynamically selects the best path for each application’s traffic, benefiting businesses. This ensures that businesses’ critical applications receive priority treatment, resulting in improved user experience for businesses.
-
Optimal Bandwidth Utilization: SD-WAN optimizes bandwidth utilization for businesses by intelligently managing traffic flows. Businesses can prioritize mission-critical applications while allocating appropriate bandwidth for less important ones.
Cost Savings
Another significant advantage of implementing SD-WAN for businesses is the cost savings it provides.
Traditional WAN solutions for businesses often rely heavily on expensive MPLS connections, which can strain IT budgets.
On the other hand, SD-WAN leverages cheaper broadband links for businesses without compromising performance or security.
-
Replacement of MPLS Connections for businesses: By utilizing broadband links as an alternative to MPLS connections, businesses can achieve substantial cost savings without sacrificing reliability or speed.
-
Efficient Resource Utilization: With SD-WAN’s ability to load balance across multiple links, organizations can make better use of existing resources, avoiding the need for costly upgrades.
Better Security Features
Security is a top concern for any network infrastructure. SD-WAN offers advanced security features that help protect against cyber threats and ensure data privacy.
-
Encryption: SD-WAN solutions often include encryption capabilities, ensuring that data transmitted over the network remains secure and protected from unauthorized access.
-
Firewall Capabilities: Many SD-WAN solutions come with built-in firewall functionality, adding an extra layer of protection to the network. This helps prevent malicious attacks and unauthorized access attempts.
Disadvantages of SD-WAN
SD-WAN, despite its numerous advantages, also comes with its fair share of disadvantages. Let’s take a closer look at some of the challenges organizations may face when implementing SD-WAN solutions.
Initial setup costs can be high due to hardware and software investments
One of the main drawbacks of SD-WAN is the initial investment required for setting up the infrastructure.
Organizations need to invest in expensive equipment and software to deploy SD-WAN effectively. This can include routers, switches, firewalls, and other networking components. There may be licensing fees associated with specific SD-WAN solutions.
Organizations may face challenges in integrating existing legacy systems with SD-WAN solutions
Integrating existing legacy systems with SD-WAN can prove to be a complex task. Many organizations have established networks that rely on traditional WAN technologies such as MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching).
Adapting these legacy systems to work seamlessly with SD-WAN can pose compatibility issues and require additional configuration or upgrades.
Dependence on internet connectivity may result in potential downtime during outages or disruptions
While SD-WAN offers increased flexibility by utilizing multiple network connections, it also introduces a level of dependency on internet connectivity.
In case of an outage or disruption in the internet service provider’s network, organizations relying solely on SD-WAN may experience downtime until the connection is restored. This reliance on external networks can impact productivity and business operations.
Proper training and expertise are required for managing and troubleshooting complex SD-WAN deployments
Implementing and managing an efficient SD-WAN solution requires specialized knowledge and expertise. IT teams need to possess a deep understanding of networking concepts, security protocols, and advanced configurations specific to their chosen SD-WAN solution.
Without proper training and expertise, organizations may struggle with troubleshooting issues that arise during deployment or maintenance.
To navigate through these disadvantages effectively, organizations should consider several factors before implementing SD-WAN:
-
Cost-benefit analysis: Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to determine if the advantages of SD-WAN outweigh the initial setup costs and ongoing maintenance expenses.
-
Integration planning: Evaluate existing network infrastructure and assess compatibility with SD-WAN solutions. Consider consulting with experts or service providers who specialize in integrating legacy systems with modern networking technologies.
-
Redundancy measures: Implement redundancy measures to minimize potential downtime caused by internet outages or disruptions. This could involve utilizing multiple internet service providers or employing backup connectivity options such as 4G/LTE failover.
-
Training and skill development: Invest in training programs for IT teams to enhance their understanding of SD-WAN concepts, configuration, and troubleshooting techniques. This will enable them to effectively manage and maintain the SD-WAN deployment.
Despite these challenges, it’s important to note that many organizations have successfully implemented SD-WAN solutions and reaped the benefits they offer.
By carefully considering the disadvantages and taking appropriate steps to mitigate them, organizations can leverage SD-WAN technology to optimize their network performance, enhance security, and improve overall productivity.
SD WAN Advantages and Disadvantages
| Aspect | Advantages of SD-WAN | Disadvantages of SD-WAN |
| Cost Savings | Reduced MPLS costs | Initial setup costs |
| Better utilization of multiple WAN links | Subscription and licensing costs | |
| Centralized control for cost management | Ongoing maintenance expenses | |
| Network Efficiency | Dynamic traffic routing | Complex to set up for some organizations |
| Load balancing and optimization | Network complexity may increase | |
| Improved application performance | Quality of service (QoS) challenges | |
| Flexibility | Easy addition of new sites or connections | Requires compatible hardware or appliances |
| Supports hybrid or multi-cloud environments | Vendor lock-in potential | |
| Application-aware routing | Skillset required for management | |
| Security | Enhanced security policies and encryption | Security must be configured correctly |
| Centralized threat management | Single point of failure if not redundant | |
| Improved visibility and monitoring | Potential for misconfiguration | |
| Scalability | Scalable to accommodate network growth | Complex for small organizations or networks |
| Easily adapts to changing business needs | May require redesign for significant growth | |
| Supports branch consolidation | Dependency on WAN links’ bandwidth | |
| Management | Centralized management and policy control | Learning curve for administrators |
| Automation and orchestration capabilities | Potential for mismanagement | |
| Real-time monitoring and analytics | Monitoring tools may require additional cost | |
| Reliability | Improved uptime and redundancy | Dependence on internet connectivity |
| Application-based failover | Requires proper failover planning | |
| Load balancing for reliability | Potential for service provider issues |
SD WAN vs Similar Technologies
The choice between SD-WAN, MPLS, or traditional WAN depends on the specific requirements and priorities of an organization’s network.
Each technology has its strengths and weaknesses, and the ideal choice will vary based on factors such as cost, scalability, security, and performance needs.
| Feature | SD-WAN | MPLS | Traditional WAN |
| Network Architecture | Software-defined, virtualized, and dynamic | Hardware-based, static, and circuit-switched | Hardware-based, static, and circuit-switched |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced costs, flexible use of internet | Expensive due to dedicated lines | Expensive due to dedicated lines |
| Bandwidth Utilization | Efficient use of multiple links | Limited flexibility, fixed bandwidth | Limited flexibility, fixed bandwidth |
| Network Flexibility | Supports hybrid, multi-cloud environments | Less adaptable to changes in network needs | Less adaptable to changes in network needs |
| Quality of Service (QoS) | Application-aware routing and QoS control | Limited QoS options | Limited QoS options |
| Security | Enhanced security with encryption and threat management | Limited security features | Limited security features |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to accommodate growth | Scalability can be challenging | Scalability can be challenging |
| Management | Centralized management, automation, and analytics | Limited management capabilities | Limited management capabilities |
| Redundancy & Failover | Supports automatic failover and redundancy | Requires manual failover configurations | Requires manual failover configurations |
| Application Performance | Improved performance through optimization | Consistent performance, but less flexible | Consistent performance, but less flexible |
| Deployment Complexity | Can be complex during setup and integration | Usually simpler to set up | Usually simpler to set up |
| Vendor Lock-In | Potential for vendor lock-in | Less vendor lock-in | Less vendor lock-in |
| Monitoring & Analytics | Real-time monitoring and analytics tools | Limited monitoring and analytics | Limited monitoring and analytics |
| Uptime & Reliability | Improved reliability with load balancing | High reliability, but may have single points of failure | High reliability, but may have single points of failure |
| Maintenance | Ongoing maintenance may be required | Requires less ongoing maintenance | Requires less ongoing maintenance |
| Network Congestion | Dynamic routing to mitigate congestion | Susceptible to network congestion | Susceptible to network congestion |
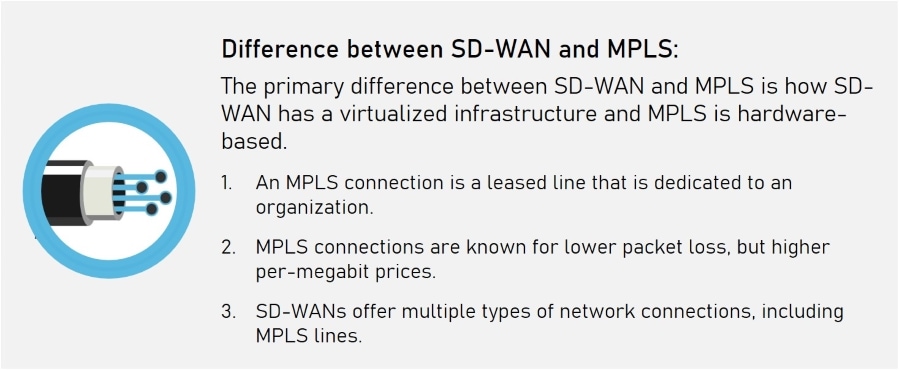
Comparing SD-WAN with MPLS
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) is a traditional networking technology used for connecting branch offices. It has been the go-to solution for many years, providing reliable connectivity. However,SD-WAN takes the lead.
Cost: SD-WAN vs. MPLS
One of the main advantages of SD-WAN over MPLS is its cost-effectiveness. While MPLS provides reliable connectivity, it tends to be more expensive compared to SD-WAN solutions. This is because MPLS requires dedicated physical infrastructure and specialized equipment, which can result in higher operational costs.
On the other hand, SD-WAN leverages virtualization techniques for network management.
This means that it can utilize existing infrastructure and leverage multiple transport options, including broadband internet connections. By utilizing these cost-effective alternatives, SD-WAN offers significant savings in terms of both upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
Flexibility: SD-WAN’s Edge
Flexibility is another area where SD-WAN shines when compared to MPLS. Unlike MPLS, which relies on a single connection type (typically T1 or E1 lines), SD-WAN allows organizations to take advantage of multiple transport options. This includes broadband internet connections from different providers.
By leveraging these diverse transport options, organizations can achieve greater network resilience and performance optimization.
SD-WAN intelligently routes traffic across different paths based on real-time conditions such as packet loss or latency. In contrast, MPLS typically relies on a single path between locations.
The ability to use multiple transport options also gives organizations the flexibility to choose the most suitable connection type for each location based on factors such as availability and cost-effectiveness.
Virtualization: The Power of Software
One key difference between MPLS and SD-WAN lies in their underlying technologies. As mentioned earlier, MPLS requires physical infrastructure and specialized equipment. SD-WAN, on the other hand, leverages virtualization techniques.
SD-WAN software can be deployed on commodity hardware or even in the cloud, eliminating the need for dedicated physical infrastructure. This makes it easier and more cost-effective to deploy and manage network connections across a wide range of locations.
The virtualized nature of SD-WAN also enables organizations to quickly scale their networks as needed. Adding new branch offices or remote locations becomes a simpler process compared to MPLS, which often requires additional physical infrastructure and configuration.
Understanding SD-WAN vs. VPN
In today’s interconnected world, where remote access and secure communication are paramount, two technologies stand out: SD-WAN and VPN.
While both provide secure connections over public networks like the internet, they differ in their focus and scope. Let’s dive into the details and understand the advantages and disadvantages of each.
VPN Creates Secure Connections for Remote Access
Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that enables users to establish secure connections over public networks.
It allows individuals to access private networks remotely while ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. VPNs use encryption protocols to protect data transmission from unauthorized access or interception.
However, it’s important to note that VPN primarily focuses on user-level access rather than broader network management aspects. It facilitates secure remote access between individual devices and private networks, making it an ideal choice for individuals working from home or accessing corporate resources while on the go.
SD-WAN Manages Multiple Sites Efficiently
Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN), on the other hand, covers broader network management aspects. It is a technology that simplifies the management of multiple sites spread across different locations by centralizing network control and providing intelligent routing capabilities.
With SD-WAN, organizations can efficiently manage their wide area networks, optimize bandwidth utilization, prioritize traffic flow based on application requirements, and enhance overall network performance.
It offers centralized visibility and control over network traffic, allowing organizations to monitor and manage their entire network infrastructure from a single interface.
While both technologies provide secure communication, there are distinct advantages and disadvantages associated with each:
Pros of VPN:
-
Provides secure remote access for individual devices.
-
Offers robust encryption protocols for data protection.
-
Can be easily set up on various devices such as laptops, smartphones, or tablets.
-
Allows users to bypass geographical restrictions by masking their IP addresses.
Cons of VPN:
-
Limited scalability when managing multiple sites or branches.
-
May result in slower network performance due to encryption overhead.
-
Requires additional configuration and management for each device.
Pros of SD-WAN:
-
Simplifies network management by centralizing control and visibility.
-
Optimizes bandwidth utilization through intelligent routing.
-
Enhances network performance and application experience.
-
Enables seamless integration with cloud services.
Cons of SD-WAN:
-
Security protocols used in VPNs are typically more robust than those used in SD-WAN solutions.
Exploring Alternatives to SD-WAN
SD-WAN is not the only option available.
Traditional WAN Technologies
One alternative to SD-WAN is leveraging traditional Wide Area Network (WAN) technologies such as Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) and leased lines.
These established methods have been used for years and offer reliable connectivity with guaranteed service levels. While MPLS and leased lines may provide consistent performance, they often come at a higher cost compared to newer solutions like SD-WAN.
Pros:
-
Reliable connectivity with guaranteed service levels.
-
Consistent performance.
Cons:
-
Higher cost compared to newer solutions.
Cloud-Based Networking Solutions
Another alternative approach for organizations is adopting cloud-based networking solutions, such as Direct Internet Access (DIA).
DIA allows businesses to connect directly to the internet without relying on a traditional WAN infrastructure. This approach offers flexibility and scalability while reducing costs associated with dedicated connections.
Pros:
-
Flexibility and scalability.
-
Cost reduction by eliminating the need for dedicated connections.
Cons:
-
Reliability may be dependent on internet service providers.
-
Security concerns as direct access to the internet bypasses traditional security measures in place within a WAN.
Hybrid WAN Architectures
Hybrid WAN architectures combine multiple networking technologies, including SD-WAN, to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness. This approach allows organizations to leverage different connection types based on specific requirements.
For example, critical applications can be routed through MPLS or leased lines for reliability, while non-critical traffic can utilize lower-cost broadband connections.
Pros:
-
Optimized performance by leveraging different connection types.
-
Cost savings by utilizing lower-cost broadband connections for non-critical traffic.
Cons:
-
Complexity in managing multiple connections and routing policies.
-
Potential challenges in ensuring consistent performance across different connection types.
Future of Cloud Networks: Software-Defined
The future of cloud networks is rapidly evolving, and one approach that is gaining significant traction is software-defined networking (SDN), particularly in the form of SD-WAN.
As organizations increasingly rely on cloud-based applications and services, the need for agile and scalable networks becomes crucial. SDN offers a solution to these challenges by enabling dynamic provisioning, automation, and enhanced security in cloud environments.
Agile and Scalable Networks for Cloud-Based Applications
With traditional network infrastructure, managing network resources can be complex and time-consuming.
However, with SDN, network management becomes more streamlined and efficient. SD-WAN allows organizations to centrally manage their entire network infrastructure through a single interface, making it easier to scale up or down based on changing business needs.
Dynamic Provisioning and Automation
SD-WAN provides the ability to dynamically provision network resources based on application requirements. This means that critical applications can be given priority over less important ones, ensuring optimal performance and user experience.
Automation plays a significant role in reducing manual intervention in network configuration tasks. With SD-WAN, organizations can automate the deployment of new sites or services, saving time and effort.
Enhanced Security in Cloud Environments
Security is a top concern. SD-WAN offers enhanced security features that help protect sensitive data transmitted over the network.
By using encryption protocols such as IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), organizations can ensure secure communication between different locations or branches connected through SD-WAN. This added layer of security helps safeguard against potential cyber threats.
Managing Network Traffic Efficiently with Edge Computing and IoT Devices
As edge computing continues to gain prominence and IoT devices become more prevalent, managing network traffic efficiently becomes paramount. Traditional WAN architectures may struggle to handle the increased volume of data generated by these devices at the network edge.
However, with SD-WAN’s centralized control plane and distributed data plane, organizations can effectively manage network traffic, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing latency.
Leveraging Public Internet for Cost-Effective Solutions
One of the significant advantages of SD-WAN is its ability to leverage the public internet as a transport mechanism. This allows organizations to reduce costs associated with dedicated private circuits while still maintaining secure and reliable connectivity.
By intelligently routing traffic over multiple paths, SD-WAN ensures that applications receive the necessary bandwidth and quality of service they require.
Simplified Deployment and Management
Deploying traditional WAN solutions can be complex and time-consuming. However, SD-WAN simplifies deployment by providing a centralized management platform that allows administrators to configure and monitor network resources from a single location.
This streamlined approach reduces the need for manual configuration at each site, making it easier to scale the network as needed.
Evaluating SD-WAN’s Pros and Cons
The future of cloud networks was also touched upon to give you a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
As we conclude this discussion on SD-WAN, it is important to note that while it offers numerous benefits such as increased network agility, cost savings, and improved application performance, there are also potential downsides to consider.
It is crucial for organizations to carefully evaluate their specific requirements and weigh the pros and cons before implementing SD-WAN solutions.
To make an informed decision about adopting SD-WAN technology for your organization, consider factors such as network infrastructure, security needs, budget constraints, and scalability requirements. Consulting with industry experts or trusted service providers can provide valuable insights tailored to your unique business needs.

SD WAN: Frequently Asked Questions
Is SD-WAN suitable for small businesses?
SD-WAN can be beneficial for small businesses as it offers cost-effective alternatives to traditional networking solutions like MPLS. It provides increased flexibility in managing network traffic and optimizing application performance.
However, it is essential for small businesses to assess their specific requirements and consult with experts to determine if SD-WAN aligns with their objectives.
Can SD-WAN improve network security?
SD-WAN can enhance network security by providing features like encryption protocols, secure tunnels between sites, centralized policy management, and integrated firewall capabilities.
However, organizations should still implement additional security measures such as next-generation firewalls or intrusion detection systems to ensure comprehensive protection against evolving threats.
What are the key considerations when choosing an SD-WAN vendor?
When selecting an SD-WAN vendor, factors like reliability of the solution, scalability options offered by the vendor’s platform or architecture design flexibility should be considered.
It is also important to evaluate the vendor’s support services, integration capabilities with existing infrastructure, and their track record in delivering successful deployments.
Can SD-WAN be integrated with existing network infrastructure?
Yes, SD-WAN solutions are designed to integrate with existing network infrastructure. They can work alongside traditional MPLS networks or other connectivity options like broadband internet or LTE.
This flexibility allows organizations to adopt SD-WAN gradually without completely replacing their current setup.
What is the cost implication of implementing SD-WAN?
The cost of implementing SD-WAN can vary depending on factors such as the size of the organization, the complexity of the network architecture, and the specific requirements.
While SD-WAN can potentially reduce costs by leveraging cheaper connectivity options, organizations should consider upfront investments in hardware or software licenses, ongoing maintenance expenses, and any additional security measures required.
A thorough cost-benefit analysis should be conducted to determine the overall financial impact before making a decision.
These FAQs aim to address common questions that may arise when considering SD-WAN adoption. Remember to assess your unique business needs and consult with experts for personalized guidance on implementing SD-WAN effectively.

