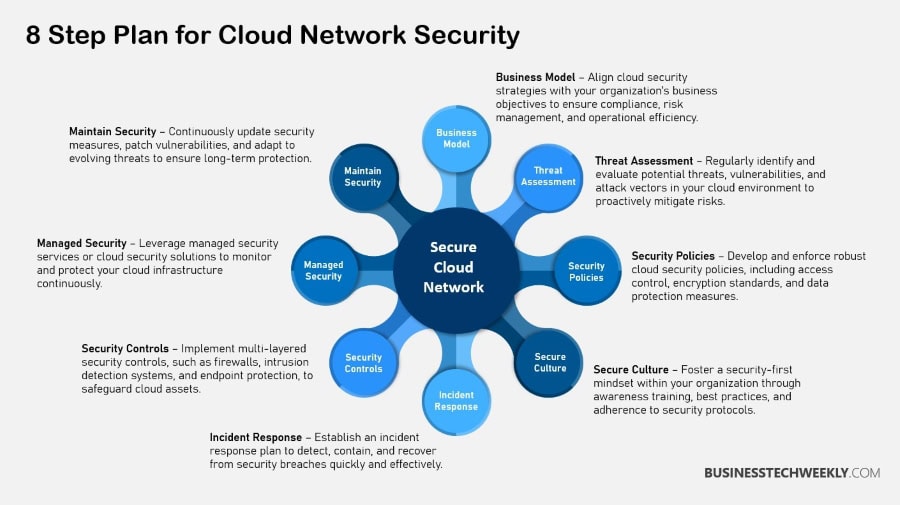
Cloud Network Security: An 8-Step Plan

On this page:
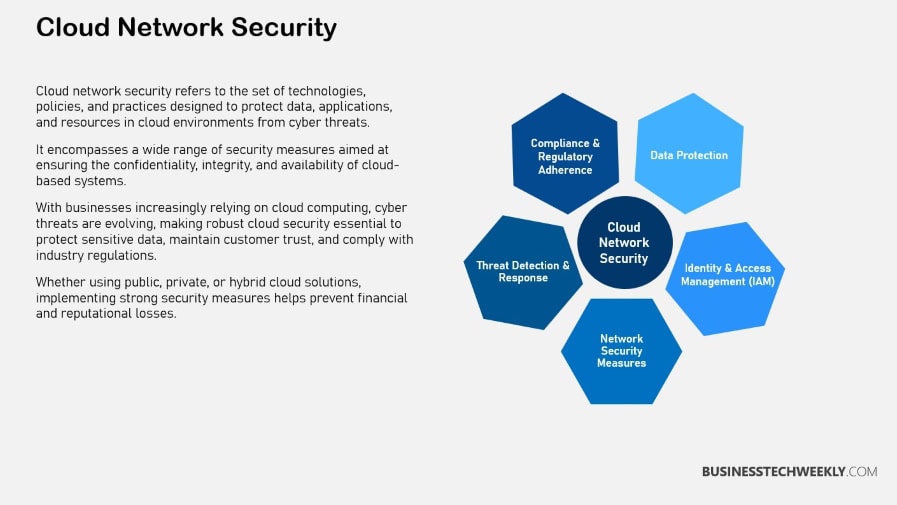
What is Cloud Network Security
Definition of Cloud Network Security
Cloud network security helps keep sensitive data and resources safe inside cloud environments, just as it does on-prem.
It is the backbone of modern computing.
It’s a broad approach that uses a variety of strategies and technologies tailored for the unique cloud environment to protect cloud assets.
Cloud network security is used to safeguard the integrity of cloud-based services and applications.
This means your data is always in sync, protected, and available. We provide this protection through a combination of preventative measures such as firewalls and encryption.
Along with that, we have incident response strategies in order to quickly respond to any possible breaches.
Multi-factor authentication and intrusion detection systems are powerful deterrents to anyone trying to gain unauthorized access.
They do a great job of reinforcing the security perimeter of cloud networks.
RELATED: Creating a Network Security Strategy: Best Practices for Protecting Your Business
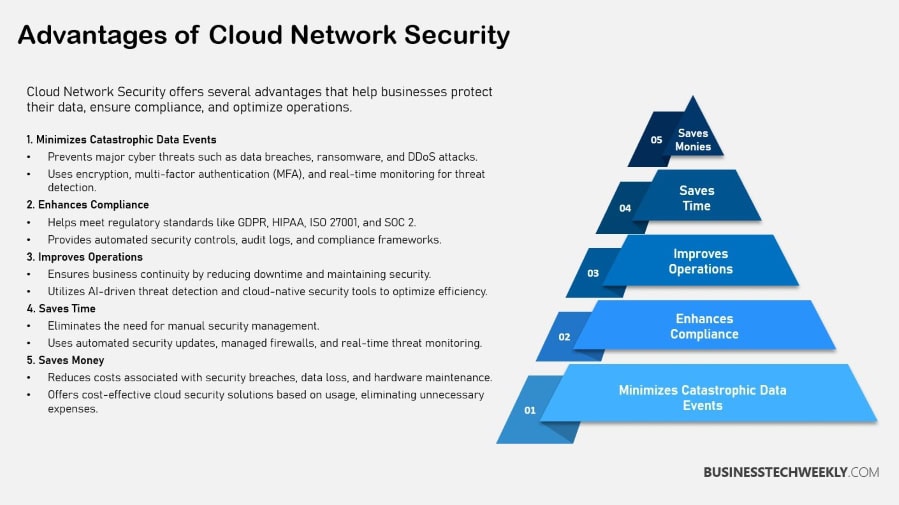
Importance of Cloud Network Security
Organizations are increasingly trusting cloud services with a growing amount of their sensitive data.
Robust security practices protect this information from cyber attacks.
This type of protection allows businesses to explore and adopt new technologies confidently without compromising data integrity or security.
With nearly all organizations using some form of cloud services, strong security frameworks are more important than ever.
These measures allow enterprises to conduct their business with confidence in a rapidly evolving digital environment.
By prioritizing effective security measures, organizations can grow and innovate with confidence.
They and their customers can sleep soundly, knowing their data is secure from future dangers.
Key Components of Cloud Network Security
![]() Security Component Overview
Security Component Overview
|
Security Component |
Risk Mitigated |
Effectiveness Level |
|---|---|---|
|
Firewalls |
Unauthorized Access, DDoS Attacks |
High |
|
Intrusion Detection |
Suspicious Activity, Breaches |
Moderate |
|
Encryption |
Data Breaches, Data Interception |
High |
|
Identity Management |
Unauthorized Access, Insider Threats |
High |
|
Zero Trust Architecture |
Internal Threats, Unauthorized Network Access |
Very High |
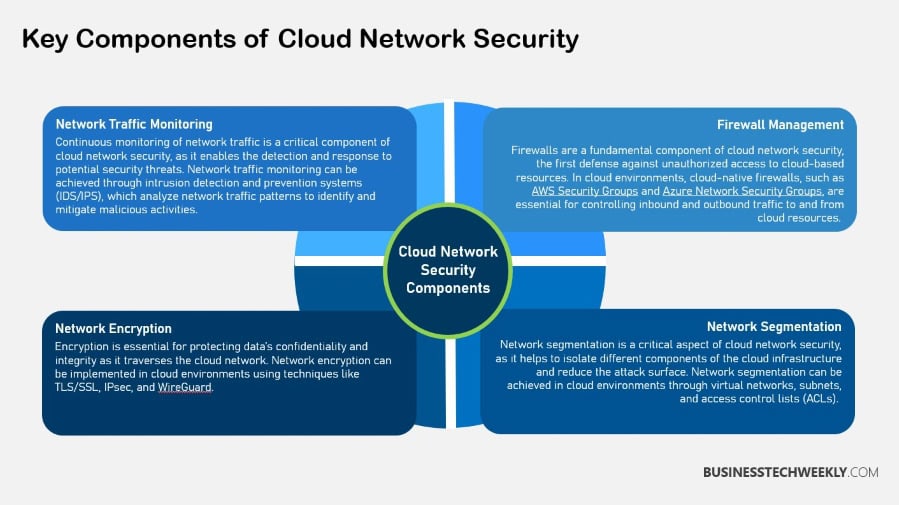
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection
Firewalls play a vital role in maintaining cloud network security posture, acting as a crucial line of defense by controlling inbound and outbound traffic to and from cloud networks.
They serve as a virtual protective barrier, effectively screening out malicious traffic while allowing only legitimate data to pass through.
For instance, configuring firewall rules to allow or deny traffic based on IP address or protocol can significantly enhance overall network security.
Additionally, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) provide an essential layer of security by ensuring constant visibility into network activity.
These systems continuously monitor cloud environments for any signs of anomalous activity or potential security risks, alerting administrators to take quick action to mitigate threats.
When a properly configured firewall is combined with a robust IDS, organizations can establish a comprehensive cloud network security strategy, creating a formidable barrier against unauthorized access and attacks.
RELATED: Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): What is an IDS, and how does it protect Businesses?
Encryption and Data Protection
Encryption serves as one of the bedrock elements of data security, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access while at rest and in transit.
Techniques like end-to-end encryption and secure socket layers (SSL) prevent sensitive data from being caught in transit. Meeting regulatory standards adds to the need for strong data protection.
As an illustration, using encryption at rest and in transit is now an industry best practice that helps protect against data breaches.
With the growing usage of cloud services, keeping data secure is crucial, making encryption all the more essential to the cloud network security.
Identity and Access Management
IAM is at the core of securing who can access what in your cloud environment.
It outlines roles and permissions, making sure users only have the access they need to do their jobs.
When you implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Single Sign-On (SSO), security gets an extra boost with multiple layers of verification.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) policies increase security by continuously and definitively verifying and authorizing all traffic.
This complex process makes it exceedingly difficult to gain unauthorized access.
Better IAM practices, like Just-In-Time access and context-aware policies, can severely limit lateral movement.
RELATED: Zero-Trust Network Access: Designing a Zero Trust Network
Even when one of the security layers is compromised, these practices show how IAM plays a vital role in cloud network security.
Technologies in Cloud Network Security
Cloud network security is not a simple matter either; it requires a robust cloud network security strategy that leverages core technologies like Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to enhance the protection of data and applications.
Virtual Private Networks
VPNs implement encrypted tunnels through the internet, protecting the data that flows between users and their cloud resources.
This encryption helps ensure sensitive information cannot be stolen as it is moved from point A to point B.
VPNs play a crucial role in remote access, offering secure tunnels that ensure data integrity and confidentiality across public networks.
VPNs establish a private tunnel, allowing employees to securely access cloud resources from any location.
This ensures that sensitive organizational data doesn’t fall in the wrong hands.
Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA goes a step further than just using passwords and provides another layer of security by demanding multiple forms of verification.
By integrating something you know (a password), something you have (a phone), and something you are (biometrics), MFA significantly reduces unauthorized access risk.
Require MFA for all cloud accounts. In this manner, should one credential become compromised, you can prevent unauthorized access before it starts.
RELATED: Why MFA Cloud Security is Critical for Your Business Data Protection
Security Information and Event Management
SIEM tools are at the heart of any organization’s ability to monitor and analyze security events.
SIEM solutions provide organizations with real-time threat detection and response capabilities powered by advanced analytics and machine learning to collect and correlate data from multiple sources.
This integration with other technologies, especially next-gen firewalls, provides more complete monitoring and visibility and improves overall security posture.
Best Practices for Cloud Network Security
1. Implement Strong Access Controls
Implementing strong access controls is a foundational practice to securing a cloud network.
They limit user permissions, so that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data. By restricting access, we mitigate insider threats and deter unauthorized access.
Regularly reviewing and updating access policies ensures that security measures adapt to changes within the organization.
For instance, if one of your colleagues transfers to another department, their access should be decreased to reflect their new role and keep security in check.
2. Regularly Update Security Protocols
Maintaining up-to-date security protocols is key in helping to combat new and emerging threats.
Patch management and timely software updates remove vulnerabilities that hackers can easily exploit.
By consistently iterating on these protocols, you can maintain a strong security posture.
Consider implementing a routine schedule for updates, ensuring no critical patches are overlooked, thus safeguarding your cloud infrastructure against potential breaches.
3. Conduct Frequent Security Audits
Security audits are important in a regular maintenance cycle that can highlight system vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with organizational security policies.
These audits are truly priceless, providing transparency into current protections and what needs to be bolstered.
Focusing on the results from audits improves the security landscape as a whole.
For instance, if an audit finds that the encryption protocols are outdated, patching those vulnerabilities as soon as possible can prevent future harm.
4. Use Automated Threat Detection
Automated threat detection tools are proving extremely useful in quickly identifying security incidents and other threats.
Such tools dramatically improve response times and decrease the likelihood of human error while helping to automate security processes into larger, enterprise-wide security postures.
Automation enables 24/7 monitoring, providing reassurance that if a new threat is detected, it can be acted on quickly.
5. Train Employees on Security Awareness
Training employees helps create a culture where security is prioritized—essential for avoiding incidents.
Frequent sessions get all staff tuned in and attuned to threats, supporting awareness initiatives to reduce opportunities for security breaches.
By learning about typical phishing techniques, such as how to spot a phishing email, employees can be the first line of defense against cyber threats.
Challenges in Cloud Network Security
Cloud network security is a complex landscape, frequently exposing organizations to pervasive challenges they need to address with greater agility.
One of the biggest challenges is understanding where the responsibility lies between your organization and the cloud service provider (CSP).
Most organizations find it hard to draw a clear line in the sand on whose security responsibility ends and the other’s begins, leading to security gaps.
One example is the threat of cyber attacks, which necessitate organizations to proactively defend themselves.
The risks are further compounded by zero-day exploits that target unpatched vulnerabilities, emphasizing the importance of strong defense mechanisms.
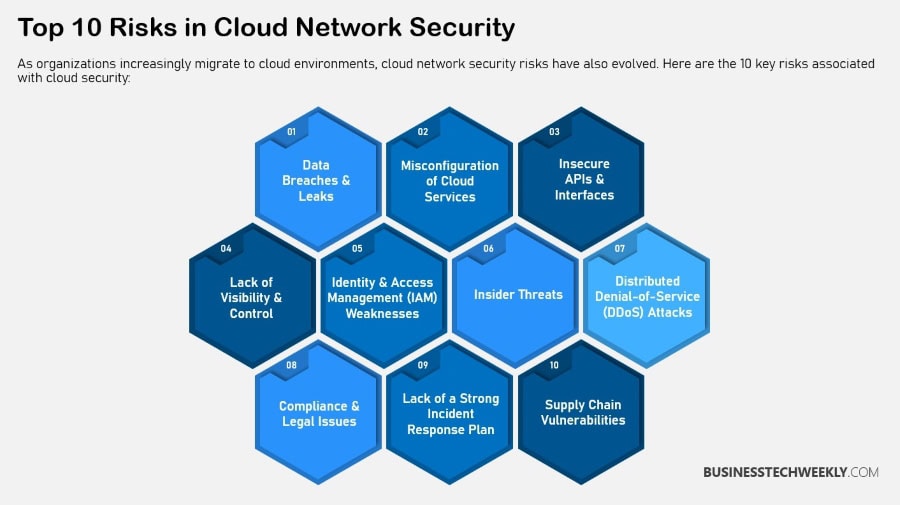
Data Breaches and Cyber Attacks
With data breaches and cyber attacks rapidly evolving from a nuisance into a dire threat, organizations must understand the impact on reputation, financial stability, and customer trust.
The integration of DevOps with security only complicates the issue, given the effort of orchestrating roles and permissions across dozens of team members.
Proactive measures, like creating a multifaceted response plan in advance, can help reduce these risks.
To avoid the next breach, organizations need to make the auto-remediation of cloud misconfigurations a top priority.
Knowing the value of a clear-cut approach to security threats goes a long way toward mitigating the damage of any future attack.
RELATED: 5-step Data Breach Response Plan for modern business
Compliance and Regulatory Issues
Ensuring compliance in cloud environments is tricky, yet critical to security.
Aligning cloud security practices with industry regulations ensures compliance with the law. It further builds confidence with customers and stakeholders.
For businesses, compliance is usually the make-or-break element in proving trustworthiness.
As Gartner predicts, by 2025, human error will be the cause of 99% of cloud security failures.
This serves as a call to action for improved compliance protocols.
Mitigating security risk can be difficult when the software we use has so many moving parts. Which is why knowing the industry-specific regulatory landscape is key.
Future Trends in Cloud Network Security
Lessons learned Businesses in 2025 will face far greater difficulties in securing their cloud environments from a host of emerging threats.
We project more than 40 billion IoT devices, fully connected, by 2030.
This otherworldly expansion will add to the security challenge, further increasing the imperative for new technologies and innovation to enhance security defenses.
Cloud-native application protection platforms (CNAPP) are becoming key tools to help organizations tackle these challenges.
These days, secure access service edge (SASE) is the other trend making waves here. Additionally, AI-driven tools will be key for real-time discovery and monitoring, ensuring IoT and OT devices are secure.
Artificial Intelligence in Security
AI will play a crucial role in cloud network security, providing advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
We will explore how AI can quickly sift through all that big data in seconds, recognizing security threats that would have otherwise been missed.
This capability provides an effective solution for a more proactive approach to threat management.
When AI can take care of other security processes, efficiency increases, allowing security teams to act much faster on possible threats.
For example, AI-driven security systems can keep an eye on IoT devices in real time, delivering essential security against more and more complex cyberattacks.
Zero Trust Security Models
The zero trust security model has gained significant traction.
It runs on the core tenet of never trust, always verify, which requires constant validation and upholds least privilege access.
This zero trust model means users and devices never should be trusted, even after logging in once during a session, to access any resource.
Implementing zero trust principles from the start is essential to protecting the cloud.
This is particularly pressing considering 66% of transportation agencies have been targeted by ransomware and 77% of public sector organizations are challenged by poor IoT device discovery.
Such an approach improves the collective protection from new or unknown threats, resulting in a strong security posture.
Key Points to Remember
- Cloud network security is a key component in protecting sensitive data and resources in the cloud. Cloud network security involves strategies and technologies that safeguard cloud assets in a cost-effective manner. Understanding its significance is key to ensuring the security and reliability of services and applications that depend on it. It defends against threats such as unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Firewalls, encryption, and identity management are all important elements of cloud network security. Each one plays a crucial part in protecting cloud environments. Just by implementing these simple measures, organizations can dramatically shrink the threat landscape.
- Technologies such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) increase security by building encrypted tunnels. At the same time, multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security by mandating multiple forms of verification. When implemented in tandem, these technologies have proven to provide strong protection against unauthorized access.
- For security purposes, enforcing strict identity and access controls are critical. Regular updates to security protocols and frequent audits have shown to boost a proactive security posture. Organizations need to adopt these practices to create a more robust security paradigm.
- Consistent employee education and training on security awareness is key in creating a culture of security Guardians. When organizations empower their staff to understand how to identify and properly respond to threats, they can significantly reduce the possibility of security breaches.
- Keeping up with what’s next—like the increasing role of artificial intelligence and the adoption of zero trust security models—is imperative. These new technologies offer deeper threat intelligence, detection, response and prevention. They empower organizations to ensure they stay one step ahead of evolving security challenges and harden their defenses.

