What is the Difference Between AI and ML?

On this page:
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence is the complex discipline focused on creating systems that replicate human intelligence.
At its most foundational level, AI is about recreating human thinking processes in machines so that they can carry out tasks that we typically associate with human intelligence.
These systems run the gamut of technologies, from virtual assistants like Amazon’s Alexa to fully autonomous vehicles.
Instead, they are purposefully designed and built to accomplish tasks with human-level competency and sometimes exceed that capability.
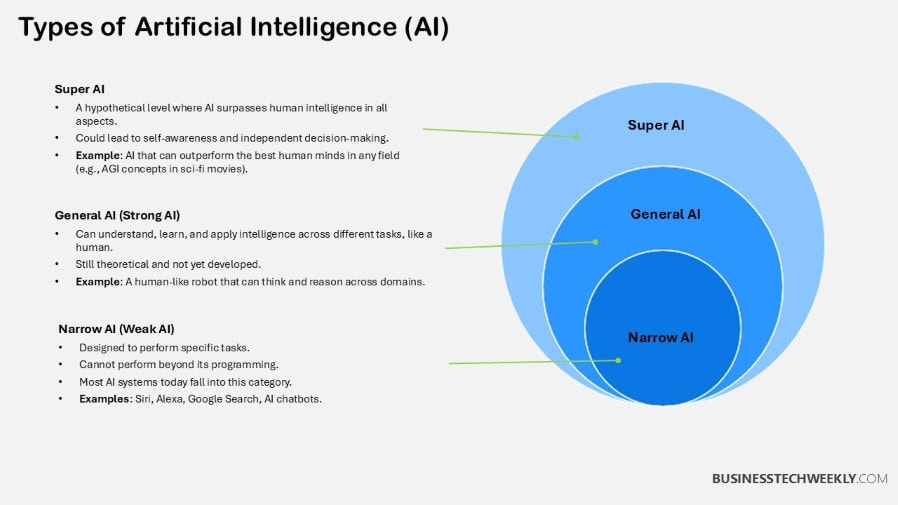
Definition of AI
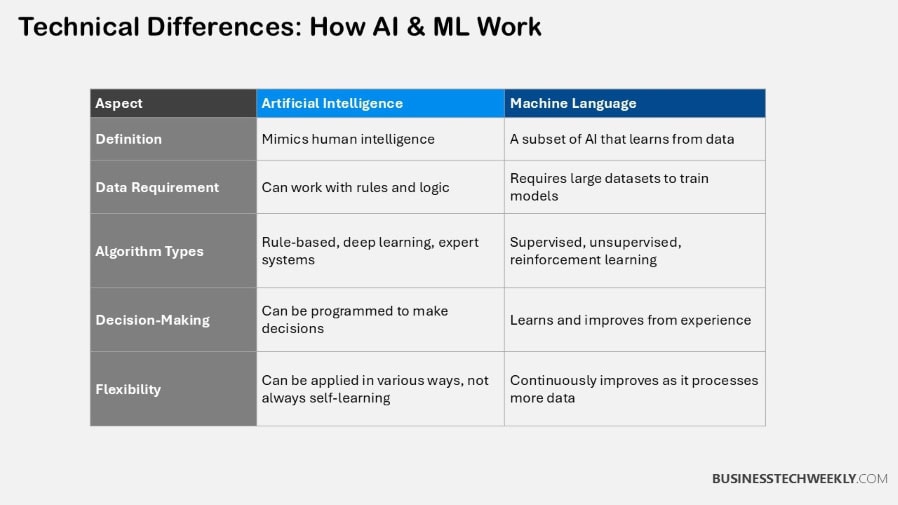
AI introduces human-like intelligence to machines through the use of complex algorithms. These algorithms, sometimes called AI, train machines to perform tasks that require human-like intelligence such as learning, reasoning, and problem-solving.
AI systems benefit from data-driven iterative approaches.
Unlike previous hard-coded programming layers, these systems are constantly learning and refining themselves, making them more efficient and effective in their operations.
Objectives of AI
AI seeks to increase machines’ ability to reason and solve problems.
It aims for the highest level of efficiency possible through continual learning and self-correction.
AI seeks to enable machines to undertake complicated tasks independently.
It delivers timely, relevant, and reliable data that empowers better decision-making and drives innovation in the public and private sectors.
Methods Used in AI
AI uses a wide variety of approaches including but not limited to rule-based systems, neural networks, and genetic algorithms.
These techniques allow AI to leverage advanced machine learning and data analysis, improving performance over time as the system learns and adapts.
Continual learning is important for all AI systems. This enables them to stay ahead of emerging challenges and take advantage of new opportunities, ensuring that they are as useful and impactful as possible.
What is Machine Learning?
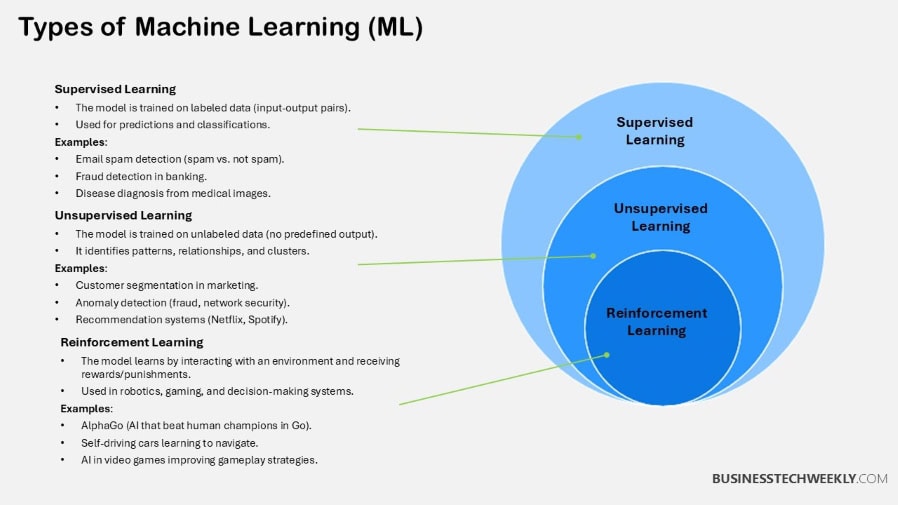
Definition of ML
Machine learning, the heart of artificial intelligence, is all about allowing computers to learn from data. It employs algorithms that detect patterns in this data, building models to perform complicated tasks.
Unlike traditional programming, where rules are hard-coded, machine learning is based on learning from data.
This key distinction places machine learning – at the very least – as a technical foundation of these smart systems.
Objectives of ML
The overarching goal of any machine learning application is to make these systems better able to learn from experience, and ultimately make predictions with greater accuracy.
The more data machines analyze, the better they become at predicting the best outcome.
This process is intended to increase accuracy but to automate tasks, increasing overall operational efficiency.
Methods Used in ML
Machine learning uses techniques such as supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.
These data driven approaches are about using these massive datasets to look for trends and patterns. Your training data is incredibly important to creating effective machine learning models.
It enhances their precision by offering varied and rich data.
How Do AI and ML Connect?
Interaction Between AI and ML
Artificial intelligence and machine learning compliment each other to develop systems that can think and act smartly.
AI systems use ML algorithms to make them more effective so they can analyze data and learn from it.
This relationship is well demonstrated in AI applications like virtual assistants. They leverage AI and machine learning to understand the intent of user searches and deliver more relevant results.
AI and ML complement each other’s strengths to tackle the most challenging issues.
For instance, ML enables autonomous driving cars to make decisions in real-time by processing data collected from other vehicles and their surroundings.
Similarities Between AI and ML
At their core, both artificial intelligence and machine learning are about working more efficiently and increasing automation.
Both of these technologies are data-driven, but the reliance on data for machine learning is far more extreme.
It focuses on teaching machines from data to inform better decisions. In both fields, algorithms are the stars of the show.
They power the development of smart systems that automate complex business processes, enhance customer interactions, and accelerate potential new sources of revenue.
Key Differences Between AI and ML
1. Scope and Functionality
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, is a wide-ranging set of technologies and applications that mimic human-like intelligence.
It encompasses natural language processing, machine learning and AI-enhanced decision-making, and robotics.
Machine Learning (ML) is the most prominent and powerful subset of AI. It’s all about using data to learn and improve performance over time.
AI is a broader concept that focuses on all intelligent behavior, whereas ML is a data-specific subset that focuses on specific tasks such as image or speech recognition.
Aspect |
Artificial Intelligence |
Machine Learning |
|---|---|---|
|
Scope |
Broad, various intelligent behaviors |
Focused on learning from data |
|
Functionality |
Diverse, including NLP, automation |
Data-driven applications |
2. Learning Process
AI focuses on rule-based learning, where predetermined rules dictate how tasks are performed.
ML, on the other hand, learns purely from data, needing training datasets to make its performance more accurate.
ML’s learning isn’t stagnant—far from it. It learns, evolves and improves itself with real-time data, as opposed to AI’s rigid approaches that aren’t always data-driven or progressive.
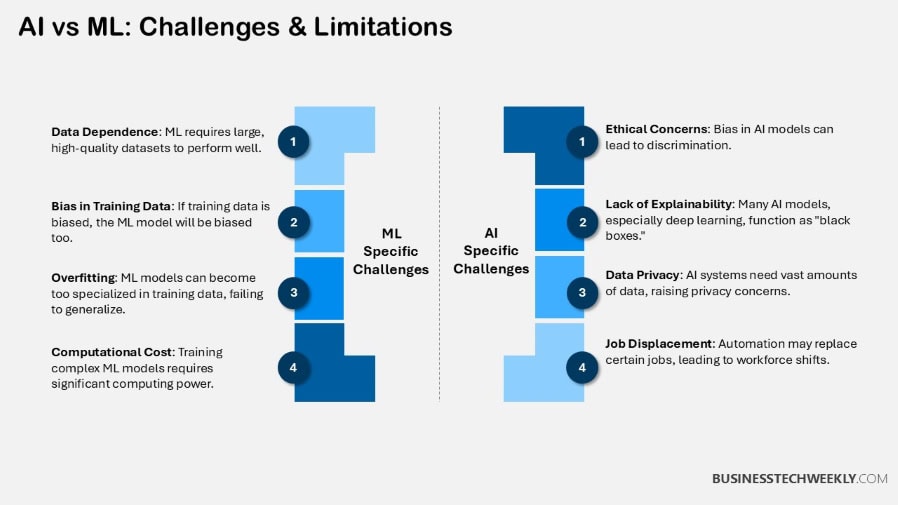
3. Data Dependency
ML is very much dependent on robust and clean structured datasets to iteratively train and hone models.
AI, on the other hand, can operate with more unstructured data, providing more operational flexibility.
Here’s a list of data types used:
- ML: Structured data, labeled datasets
- AI: Unstructured data, real-time inputs
4. Implementation Techniques
AI implementation typically includes expert systems and often relies on expensive computational power and data. ML uses neural networks which help easily deploy models.
Typical solutions include AI tools like APIs for AI integration and ML tools like TensorFlow, showing the varying level of complexity in their solutions.
Benefits of Combining Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Enhanced Decision-Making
The combination of artificial intelligence and machine learning provides you with the ability to make truly data-driven decisions.
Combined, artificial intelligence and machine learning make sense of all that data and produce smart insights that give you the strategic advantage you need.
This is where predictive analytics really come into play, helping you predict trends and outcomes more accurately than ever before.
This powerful combination of AI and ML makes data analysis a powerful tool for creating successful business strategies.
AI and ML have revolutionized countless industries. Organizations can use deeper data analysis to make more strategic decisions that better match their organizational priorities.
Automation of Processes
Combined, AI and ML help organizations increase efficiency by reducing the burden of manual tasks and increasing productivity.
Automation increases both the speed and accuracy of execution, greatly decreasing the chance of error.
Take systems like driverless cars or facial recognition software. These innovations deploy AI and ML to take on work with minimal or no human intervention.
These are just a few examples of how AI and ML-driven automation can help you work more efficiently and reliably to do more with less.
Improved Efficiency Across Industries
When AI and ML combine, they release massive efficiency gains throughout the economy.
AI and ML will transform the speed and effectiveness of early disease diagnosis, like melanoma, while enhancing remote patient monitoring. Industries such as finance and education are similarly improving their overall operational performance thanks to AI and ML.
These technologies drive the innovation all around us and empower everyday applications such as Siri and Alexa.
They show the transformative potential of AI and ML, delivering tangible benefits to your industry.
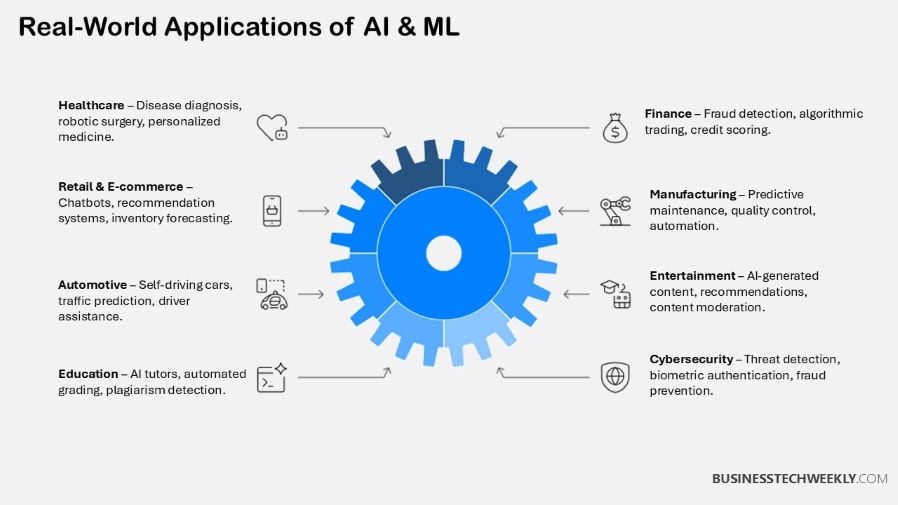
Applications of AI and ML
AI and machine learning work are revolutionizing many sectors with creative, practical solutions.
Equipped with adaptability, these intelligent systems address unique industry challenges, boosting both profitability and customer satisfaction across sectors like retail, finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Usage in Healthcare and Life Sciences
AI and ML tools improve patient diagnosis and treatment plans, applying predictive analytics to deliver more effective care.
In medical imaging, AI detects anomalies, helping doctors offer more accurate diagnoses.
For example, AI algorithms in imaging help detect tumors at earlier stages where patients have more treatment options and higher survival rates.
Usage in Manufacturing
Ultimately, AI revolutionizes production and predictive maintenance, enhancing operational efficiency and driving down costs. Automation in smart factories accelerates and optimizes automation.
For instance, AI-powered robots are taking over assembly lines, boosting efficiency, and minimizing the potential for human error.
Usage in Ecommerce and Retail
AI improves customer experiences with targeted product or content recommendations.
Predictive analytics help to avoid over and under stocking items by better aligning inventory with demand.
Retailers are taking advantage of AI-powered marketing campaigns, increasing revenue with targeted advertisements and promotions.
Usage in Financial Services
AI identifies fraud and evaluates risks, improving their security. Predictive modeling helps narrow down which investment strategies are most worthwhile, providing a deeper understanding of customers.
AI chatbots boost customer service, offering immediate help and support, which increases user engagement and satisfaction.
Requirements for Starting with AI and ML
Essential Tools and Technologies
Regardless of context, to take your first steps with AI and ML, you’ll need the right tools.
Among these, Python and R stand out as popular programming languages, with TensorFlow and PyTorch offering powerful frameworks for development.
Cloud computing provides the flexibility and scalability required to handle massive data sets.
Cloud platforms such as AWS and Google Cloud enable this. Technologies like Hadoop are big data enablers and they will help us manage and process all that data.
APIs and prebuilt models have the ability to drastically accelerate development by providing out-of-the-box solutions for complex tasks.
Skills and Expertise Needed
In short, navigating this AI and ML landscape requires a confusing mix of soft and hard skills.
Understanding data science fundamentals is critical as is fluency in programming languages such as Python.
Ongoing education is essential as technologies change at a staggering pace.
While there is tremendous demand for senior software engineers, AI researchers and data scientists, the likes of Codingscape provide much faster routes.
Getting familiar with the differences between AI and ML can inform your strategic perspective.
Key Points to Remember
AI introduces a wide range of new capabilities. It’s something that automates processes and improves decision-making.
ML, a narrower field than AI as a whole, is about learning from data in order to predict and classify.
Together, these two technologies complement each other to open up a world of new possibilities.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are closely related but different areas of study. AI is a much wider concept than ML, which is a subfield of AI that is about learning from data.
- AI aims to emulate human intelligence and perform tasks autonomously. At the same time, ML strengthens these systems by allowing them to automatically learn from new data, increasing both predictive accuracy and operational efficiency.
- AI is based on algorithms and heuristics to guide decision making. Machine learning uses methods like supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning to identify patterns and trends in data.
- Both artificial intelligence and machine learning are about automating processes and increasing productivity. They are only as good as the data and algorithms they are built on, which is where the problems start.
- Combining AI and ML enhances decision-making capabilities, streamlines operations, and provides actionable insights, leading to increased productivity and efficiency across various industries.
- To do artificial intelligence and machine learning successfully, you require a robust data infrastructure and significant computing power. Additionally, advanced expertise in programming and data science are critical, reinforcing the need for learning and agile adaptation.

