What is Cyber Security Monitoring?

On this page:
- What is Cyber Security Monitoring?
- Key Components of Cyber Security Monitoring
- Types of Cyber Security Monitoring
- Implementing Cyber Security Monitoring
- Techniques and Tools for Monitoring
- Best Practices for Effective Monitoring
- Challenges in Cyber Security Monitoring
- Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity Monitoring
- Key Points to Consider
What is Cyber Security Monitoring?
Cybersecurity monitoring is the watchful mechanism for identifying and responding to security events in the enterprise environment. Consider it a security camera that monitors your most sensitive data 24/7.
This proactive procedure is a crucial step in stopping possible threats before they become major violations.
With the help of ongoing monitoring, organizations can foster a safer community, shielding vital information from malicious attacks.
The three-stage process, which includes detection, analysis, and response, is essential in preventing threats such as ransomware in real-time.
Definition and Purpose
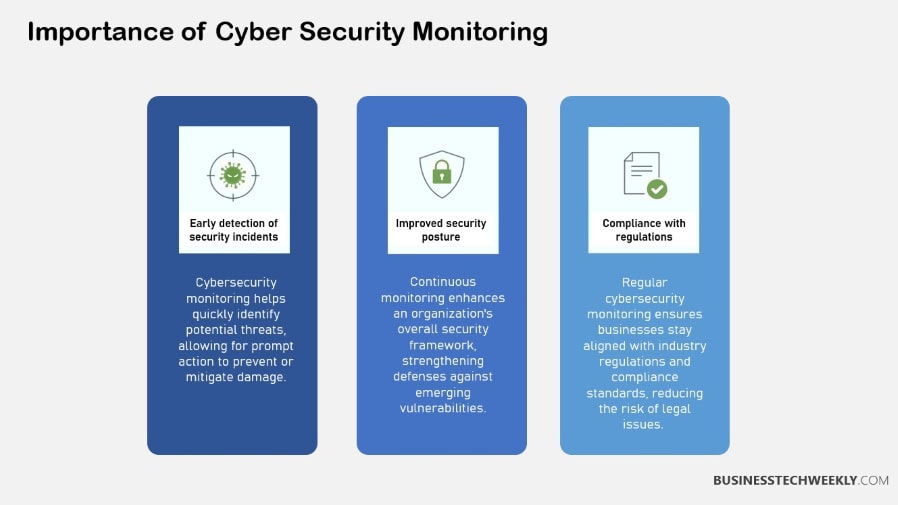
In fact, at its core, the main focus of cybersecurity monitoring should be protecting sensitive information. Through streamlined monitoring, businesses get faster incident response times, reducing any potential harm.
Monitoring is wide-ranging and comprehensive, and it’s key to maintaining compliance with security regulations and standards.
Today, it is an absolute necessity for today’s organizations.
Importance in Modern Organizations
With the increase in cybercrime comes the increased need for cyber security monitoring. The average cost of a data breach in 2024 is a whopping $4.22 million.
In short, continuous monitoring can assist organizations in keeping user data and intellectual property safe, making it the first line of defense.
By identifying these incidents sooner, businesses can steer clear of expensive penalties, such as the $700 million JPMorgan Chase settlement in 2014.
88% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error.
Key Components of Cyber Security Monitoring
Cyber security monitoring involves a comprehensive approach, divided into three essential stages: detection, analysis, and response.
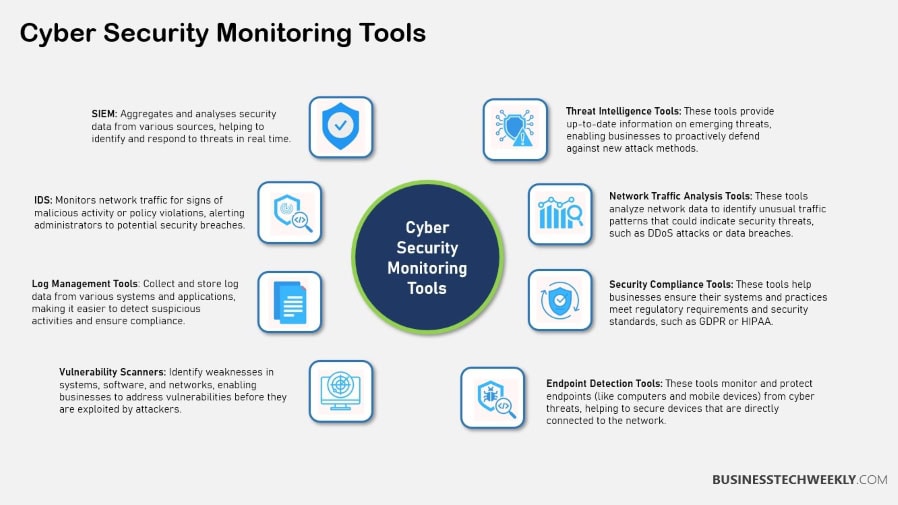
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS), and proper log management are all key factors in this process.
These tools complement each other to improve security posture and create operational efficiencies.
When combined, these components form a comprehensive security framework, essential for protecting sensitive data from breaches.
Security Information and Event Management
SIEM systems are key components of cyber security monitoring, aggregating and analyzing security data from a wide variety of sources.
They deliver real-time visibility into security threats and occurrences, a key component for fast-actionable decision-making.
Through the automation of alerts, SIEM solutions improve incident response capabilities, enabling organizations to take quick action in reducing and remediating threats.
This tool serves as a single pane of glass, providing security teams with a complete picture of their IT landscape.
RELATED: What is SIEM? Understanding Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM)
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
IDS and IPS are essential to monitoring network traffic for unusual, threatening activities.
Where IDS is primarily concerned with detecting potential threats, IPS goes further by actively preventing them as well.
These systems combine signature-based and anomaly-based detection methods to deliver near-real-time alerts that are critical to preventing breaches.
In short, they serve as your ever-watchful sentinels, always on the lookout for unauthorized access.
RELATED: Intrusion Detection Systems versus Intrusion Prevention Systems
Effective Log Management
Centralized collection and analysis of logs is critical for detection of anomalies and root cause analysis of security incidents.
Following log retention and management best practices will keep you compliant and allow for more effective forensic investigation.
Key log types to monitor include:
- System logs
- Application logs
- Security logs
This practice highlights the value of having a historical timeline of activities, which is essential for long-term and continuous security monitoring.
Types of Cyber Security Monitoring
In the increasingly dynamic world of cyber security, a comprehensive, multi-layered approach is essential to safeguard an organization’s most valuable digital assets.
Cyber security monitoring comes in many forms, each with their own focus on protecting specific security requirements in an enterprise.
These four types of cyber security monitoring are network surveillance, endpoint protection, application monitoring, and cloud environment monitoring.
Learning about these categories can help us better protect ourselves from cyber threats.
1. Network Surveillance
Network-based monitoring entails monitoring incoming and outgoing network traffic to identify any nefarious behavior.
Its purpose is to identify threats like external or internal shady access and data exfiltration.
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) serve as great examples here. They provide for the real-time analysis of cyber threats and help organizations respond quickly to threats.
The significance of network surveillance is underscored by the fact that threats can bypass traditional defenses, necessitating vigilant monitoring to protect critical infrastructure.
RELATED: Network Monitoring: Recognizing the need for Monitoring your Network for Cybersecurity
The average time to identify a breach is 194 days.
2. Endpoint Protection
The goal of endpoint protection is to protect every device that connects to the network, from desktops and laptops to tablets and smartphones.
Antivirus and anti-malware solutions are key components, protecting your endpoints against a wide range of digital threats.
Frequent updating and patching is just as crucial, closing off vulnerabilities that cybercriminals could take advantage of.
As of 2023, there are 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity jobs. Endpoint protection makes sure these crucial touchpoints are always protected, reducing attack vectors.
RELATED: EPP vs EDR: Which Solution Should You Choose?
3. Application Oversight
Application oversight focuses on software applications and their code, allowing organizations to scan for security vulnerabilities.
Secure coding practices are key in preventing application-level attacks, which can lead to damaging risks like data breaches.
Common vulnerabilities to monitor include:
- SQL injection
- Cross-site scripting
- Buffer overflow
These threats to our nation underscore the necessity of stringent application oversight, protecting the quality and trustworthiness of the software we use.
4. Cloud Environment Monitoring
Monitoring cloud environments poses challenges that differ from on-premise IT infrastructures, especially considering the ephemeral nature of cloud resources.
Tools such as CyberScope allow security teams to easily validate edge network configurations.
Strategies that focus on holistic visibility into cloud resources are key to effective threat detection and regulatory compliance.
Cybercrime is predicted to reach $10.5 trillion per year by 2025. In order to thrive, organizations need to ensure that cloud security is a top priority.
Implementing Cyber Security Monitoring
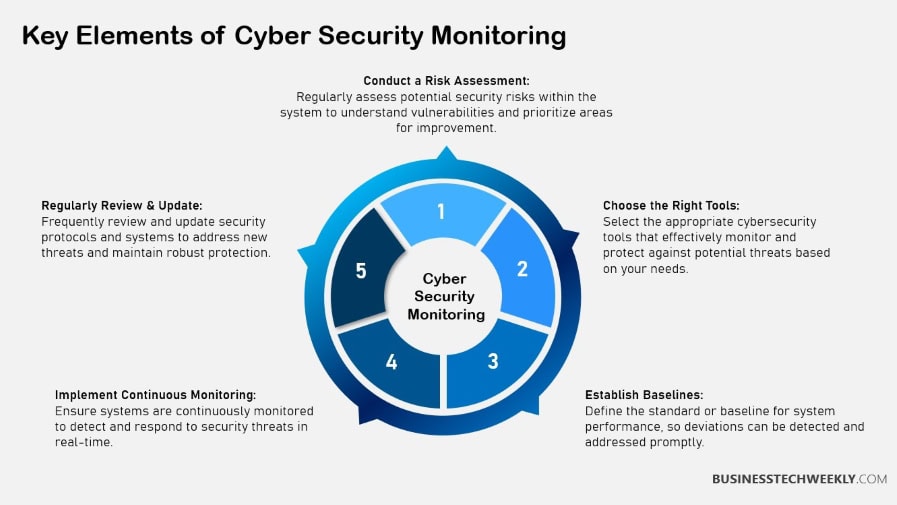
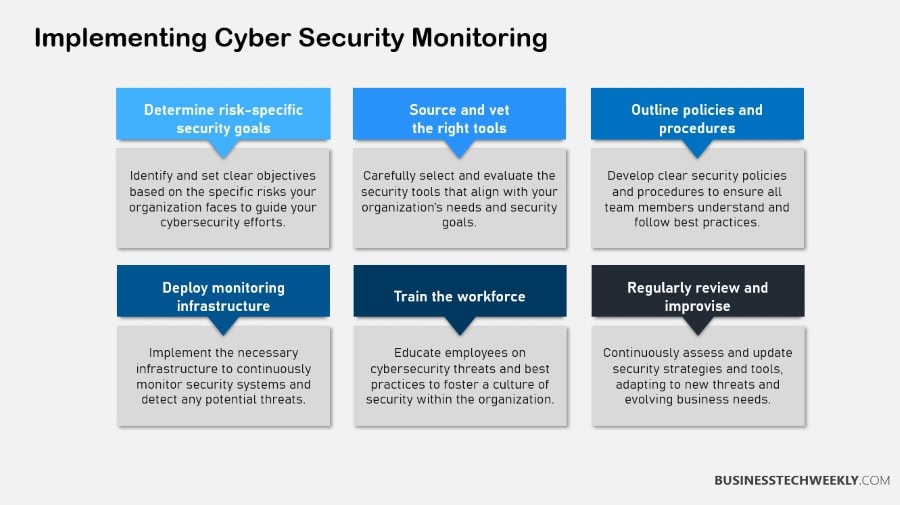
Implementing cybersecurity monitoring within an organization requires a structured approach, starting with a thorough risk analysis.
This involves identifying and assessing potential security threats to prioritize monitoring efforts effectively. Understanding organizational vulnerabilities is crucial for determining where to focus resources.
Conducting risk assessments can involve vulnerability scans, threat modeling, and penetration testing, which help pinpoint weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
1. Conduct Risk Analysis
Risk analysis is the foundation of any security strategy. It involves identifying potential threats and assessing their impact on an organization.
By understanding vulnerabilities, organizations can prioritize monitoring efforts and allocate resources efficiently.
Effective risk assessments might include methods like vulnerability scans, threat modeling, and penetration testing.
These techniques provide a comprehensive view of potential risks, enabling proactive measures to mitigate them.
2. Define Security Goals
Setting concrete security objectives is vital for ensuring that cybersecurity initiatives serve the broader purpose of furthering business goals.
Clearly defined goals should inform the selection of monitoring tools and strategies.
These multifaceted tools and strategies need to match the organization’s larger goals.
Measurable outcomes are key, and will help determine the overall success of security monitoring initiatives. For example, incident response time or frequency of data breaches are concrete metrics that can be used.
3. Choose Suitable Security Tools
Choosing the best cybersecurity monitoring tools means looking for a solution that has scalability, integration, and is easy to use. A single security monitoring platform brings together data from all of these sources.
This offers you the most holistic view of your organization’s security posture and brings with it many benefits. Immediate threat identification is one of the cornerstones of most cybersecurity monitoring platforms.
It enables organizations to detect and respond to security threats faster and prioritize the most critical security issues, increasing their overall threat response capabilities.
Global cyber attacks increased by 30% in Q2 2024, reaching 1,636 weekly attacks per organization.
4. Formulate Security Policies
Security policies are the backbone of your cyber security monitoring practices. Creating and continuously updating these policies are key to protecting against ever-changing threats and advancements in technology.
It’s incredibly important to ensure staff development and adherence to security practices and policies.
After all, human error is the number one cause of security breaches.
Transparent, easily-understandable security policies build a culture of security throughout the organization.
5. Educate Employees on Practices
As with any other area of cyber defense, employee training is key to improving the efficacy of cybersecurity monitoring.
In-person or virtual training sessions must include information about phishing awareness, secure password practices, and how to recognize suspicious activities.
There are many approaches that can be used, from in-person workshops to web-based courses to immersive simulations. In doing so, organizations can significantly lessen their susceptibility to cyberattacks.
They accomplish this by arming employees with the skills to recognize and address threats.
- Interactive sessions to engage employees in hands-on learning.
- Flexible learning options for remote and diverse teams.
- Real-world scenarios to test employee responses to threats.
RELATED: Establishing a Cybersecurity Culture at your company
6. Review and Adapt Strategies
Regular reviews and adjustments to your monitoring strategy are critical to keeping pace with evolving threats. Building the practice of taking lessons learned from security incidents or vulnerabilities into strategy updates promotes a culture of continuous improvement.
This ongoing, iterative process helps ensure that security measures stay effective and responsive to new challenges, keeping a strong security posture.
Techniques and Tools for Monitoring
Similarly, in cybersecurity monitoring, a mix of techniques and tools is key to detecting all types of threats. Using a variety of tactics gives us the best chance to spot, track, and react to emerging threats quickly.
Here’s a closer look at some prevalent monitoring techniques:
- Signature-Based Detection: Recognizes threats using predefined signatures.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifies unusual behavior suggesting security threats.
- Protocol Analysis: Examines network protocols for malicious activity.
- Machine Learning: Bolsters monitoring by recognizing complex attack patterns.
Signature-Based Detection Methods
This approach detects established threats using predefined signatures. It’s great at detecting known threats quickly, but can overlook anything new or emerging.
When integrated with other detection techniques, it strengthens overall security.
Anomaly Detection Approaches
Anomaly detection detects odd behavior that could be a sign of a risk. These machine learning algorithms continue to refine its accuracy.
Creating a baseline of what normal behavior looks like is the key to effective anomaly detection.
Protocol Analysis Techniques
Protocol analysis examines network protocols and traffic for indications of malicious activity. Security tools such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems are key here, offering real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware.
Having a solid understanding of normal protocol behavior is critical to be able to spot deviations.
Machine Learning Applications
Machine learning improves monitoring efforts, allowing for better detection and response to threats. AI-driven solutions shine at recognizing multifaceted attack patterns, providing organizations with more flexible and adaptive security defenses.
Today’s SIEM solutions are powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate and accelerate threat detection and response.
By integrating Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems into your platform, you can increase the effectiveness of your monitoring strategies.
Implementing IDS and IPS systems complement your security measures. Deployed behind agency firewalls, Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) monitor traffic coming and going across an agency’s perimeter, alerting on threats that may breach the network.
Best Practices for Effective Monitoring
There are best practices for effective monitoring that, when established, will help your organization achieve the ideal state of strong security.
First, ongoing surveillance is key to identifying threats in real time.
For one, it enables organizations to take immediate action against violations, a process that can greatly improve organizational security.
Embedding this into the security posture changes the game to how those threats are detected and provides a greater sense of security.
Emphasize Continuous Surveillance
Continuous monitoring, especially through advanced threat detection capabilities, allows you to spot threats in real-time.
For example, the use of 24/7 cyber security monitoring tools boosts security by identifying unusual behavior before it leads to disaster, becoming a critical piece of a holistic security strategy.
Perform Regular Audits and Reviews
Regular audits evaluate the effectiveness of cyber security monitoring tools, identifying security gaps and providing insights into vulnerabilities.
Documenting these findings is vital for reference and future cybersecurity strategy planning.
Leverage Automated Solutions
Automation plays a key role in cybersecurity monitoring by lightening the overall load on security teams.
Tools such as Sprinto automate the process of threat detection, allowing you to quickly establish an incident response process.
That’s why automation is crucial to ensuring your security is always a step ahead.
Prepare Incident Response Plans
Incident response plans are foundational blueprints for navigating security incidents. In addition, they provide detailed plans for responding to all types of threats, keeping staff – and students – prepared.
It’s regular testing and updating that makes these plans so effective, allowing them to adapt to new and changing risks.
Cybersecurity monitoring comprises four phases: identification, preparation, execution, and review. It’s vital to assess risk tolerance and tailor strategies based on fundamental risks.
Tools selected must align with organizational needs, budget, and integration capabilities.
The focus shifts from reactive to proactive strategies, emphasizing risk assessment first.
With visibility challenges in cloud and remote networks, cyber risk monitoring provides insights into vulnerabilities.
Testing current security infrastructure ensures tools function correctly, forming the basis of a continuous monitoring plan.
RELATED: Incident Response Plan Testing: The Ultimate Guide
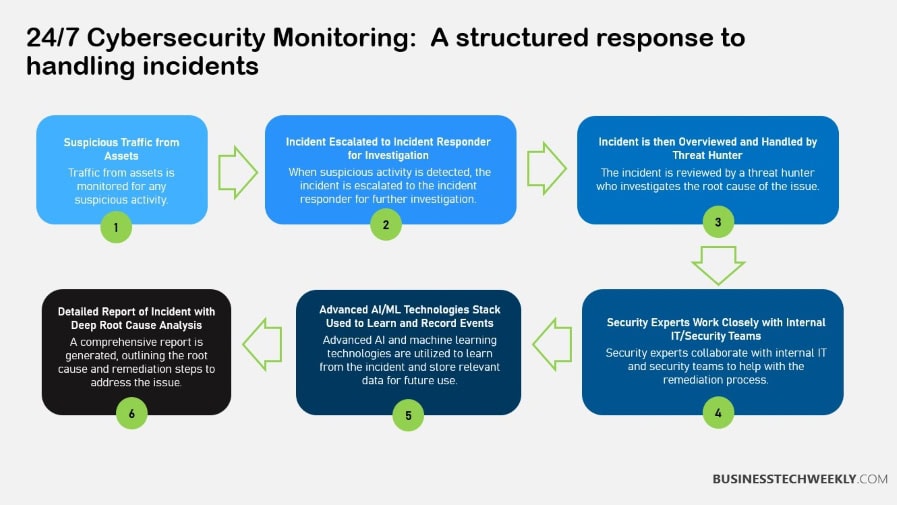
Challenges in Cyber Security Monitoring
Managing Large Data Volumes
Dealing with large volumes of security data is an enormous challenge for organizations. Monitoring tools produce a HUGE amount of data which creates a challenge for IT security teams to sift through it all to be most effective.
This data tsunami ultimately results in alert fatigue, wherein even the most critical alerts are completely overlooked.
Even a newly hired SOC analyst could be overwhelmed by hundreds of alerts per day, leading to burnout.
To combat this, efficient, scalable solutions are key.
These solutions are key to efficiently analyzing and processing incredibly large data sets so that the most critical alerts are always addressed first.
Prioritization – deciding what to monitor – is key. This prevents needless data tidal waves and lets you focus on real threats.
Addressing False Alerts
False alerts, often caused by benign activities, can inundate security teams with alerts. This concern distracts from actual threats, complicating the ability to respond to an incident. Retooling detection systems across the board to avoid generating false positives is essential.
By honing in on these systems, security teams can prioritize the true threats and make their security efforts more effective.
Tackling Workforce Skill Gaps
Another challenge is the lack of skilled cybersecurity professionals. Now, with 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity job vacancies in 2023, organizations struggle to create well-informed security teams.
Training and development programs are some of the best long-term strategies to fill these skill gaps.
By prioritizing investment in these programs, organizations can better prepare their teams’ skills, creating a stronger cybersecurity landscape.
Navigating Compliance and Privacy
Ensuring compliance with various regulations and privacy laws adds complexity to cybersecurity monitoring. Integrating compliance requirements into monitoring strategies is vital.
Regular assessments help maintain compliance, safeguarding organizations from potential legal issues.
By embedding these requirements within monitoring processes, organizations can effectively manage compliance challenges, ensuring their security practices align with legal standards.
Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity Monitoring
In today’s dynamic digital landscape, cyber security monitoring is rapidly adapting to address emerging threats.
With the evolving cyber threat landscape advancing with greater sophistication, organizations are compelled to reconsider their approaches to security by leveraging advanced monitoring and appropriate cybersecurity tools to provide stronger cyber defenses.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Additionally, AI and machine learning are changing the game when it comes to cybersecurity monitoring. These technologies improve threat detection efforts by analyzing mountains of data rapidly and with precision.
For example, AI can help spot irregularities that could indicate a cyber attack, helping security teams respond faster and reduce potential impact.
By continuously learning from emerging threats, AI-driven solutions are incredibly effective in today’s dynamic, evolving threat landscape.
Adopting Zero-Trust Models
The zero-trust model requires that you verify any request to access before you grant it. This model improves security because it assumes that no user or device is trusted.
This approach protects organizations by ensuring that the risk of unauthorized access is kept to a minimum. Ongoing verification and monitoring are key, making sure that each movement on the network is being closely monitored.
RELATED: Zero-Trust Network Access: Designing a Zero Trust Network
Sharing Threat Intelligence Information
Collaboration, communication, and community. Sharing threat intelligence – both offensive and defensive – among organizations helps strengthen the overall security of the community.
Platforms such as Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs) streamline this information sharing, allowing for faster detection and response to new and evolving threats.
Collaborative efforts are the best way to increase our collective ability to predict, prevent, and protect against emerging risks.
Implementing Automated Incident Responses
Automated incident responses include pre-defined actions that automatically occur when a particular security event is detected.
Automation helps to cut down on human error and response time, allowing responders to get to the breach faster.
Regular updates to these protocols are imperative, not only to keep them fresh but to keep them effective against emerging threats.
Key Points to Consider
Cyber security monitoring is the first line of defense in the cyber landscape. Putting these practices in place can make a significant difference in your security posture.
- Cybersecurity monitoring is critical to an organization’s ability to detect and respond to security incidents. With the right cyber security monitoring in place, organizations can benefit from faster incident response times and compliance with security regulations and standards.
- Key components of cybersecurity monitoring are Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS). Plus, comprehensive log management is key to strengthening security posture. These components in tandem create a powerful framework for threat detection and incident response.
- Using a mix of monitoring methods, including signature-based and anomaly detection, is an additional security layer that enhances security infrastructure.
- To deploy effective cybersecurity monitoring, you require a clearly defined process. Begin with thorough risk analysis, articulate security objectives, choose appropriate technology, develop policy, and train your staff. Frequent examination and adjustment of tactics and techniques will keep the program strong and ready to face new or changed threats.
- Continuously educating teams on new trends, such as integrating AI, adopting zero-trust models, and enabling automated incident responses, better equips organizations to respond. This understanding allows them to augment their monitoring capabilities and improve their overall security posture in an ever-changing threat landscape.

