IT General Controls (ITGC): Your Guide to Security & Compliance

On this page:
- What Are IT General Controls
- Key Components of IT General Controls
- Implementing Effective IT General Controls
- Frameworks for IT General Controls Compliance
- Addressing Security Risks in IT General Controls
- Benefits of Implementing IT General Controls
- Best Practices for Maintaining IT General Controls
- Key Points to Note
What Are IT General Controls
Definition of IT General Controls
IT General Controls (ITGC) are the foundation of IT operations. Their scope encompasses a wide range of activities aimed at implementing and maintaining strong IT security and management practices.
These controls control how business systems operate. In addition, they harden endpoints like laptops, kiosks, and mobile devices to remove weaknesses in commonly used apps.
When implemented effectively, ITGCs are critical in protecting critical organizational data from suspicious insider and external actors.
These controls protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information, which is critical to protecting the public’s trust and the continuity of operations.
Putting IAM best practices into place and training your employees to recognize the signs of a cyberattack improves cyber security. As such, ITGCs are fundamental to protecting your organization’s most precious data assets.

Significance in Security and Compliance
The role of ITGCs in making sure organizations are secure and compliant is paramount.
They serve as your first line of defense against data breaches and operational failure.
This protection is particularly important for sectors such as financial services and healthcare that are subject to highly prescriptive regulations such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX.
Weak ITGCs can create opportunities for non-compliance, potentially exposing the organization to the risk of fraud and reputational harm.
As 80% of organizations use ITGCs, their reach goes beyond the realm of vendor management to impact the accuracy of financial reporting as well. They lay the groundwork by making sure that all new applications and procurement processes adhere to set standards.
This increases the overall reliability of financial data while reducing the opportunity for fraud.
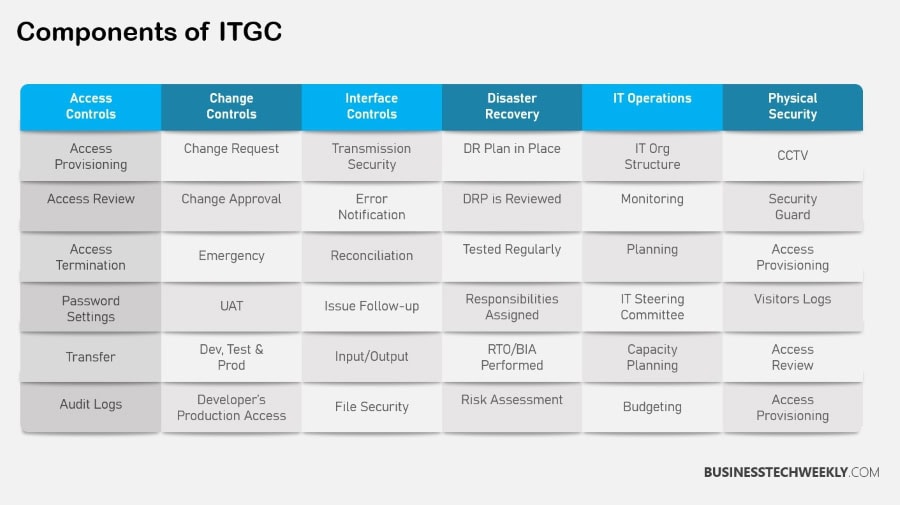
Key Components of IT General Controls
In the IT General Controls (ITGCs) world, a proven, methodical strategy makes all the difference.
It protects sensitive information and increases the efficiency of operations.
This is why these controls form the backbone of IT security architecture, covering multiple aspects of organizational security requirements.
Here’s a breakdown of essential ITGC components:
- Access Control Measures
- Change Management Procedures
- Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
- Security Management Practices
- IT Operations Controls
1. Access Control Measures
Access control is a major component in protecting against unauthorized access to confidential data.
By implementing proper user account management, organizations can dictate who has access to what data.
Implement stringent controls on how user accounts are created and deleted.
Use segregation of duties and implement strong password policies to protect your organization. These safeguards prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive data.
2. Change Management Procedures
Rigorous change management is required to ensure only authorized changes are made to sensitive IT systems.
This includes defined processes for creation requests, approvals, testing and documentation that together greatly reduce the chance of breaking something.
Proper change management protects the integrity of the system, allowing for smooth transitions any time the system is updated or changed.
3. Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
Data backup is critical for any organization’s business continuity.
Regular backups and testing recovery procedures are important elements that organizations need to prioritize.
Implementing preventive strategies to maintain data integrity during backup processes protects against data loss and allows for quick and effective recovery when necessary.
4. Security Management Practices
Technical and physical security management practices are important components to strong ITGCs.
Continuous monitoring and robust incident response protocols are key to detecting and responding to threats in real-time.
Conduct security awareness training for all employees.
Educating employees about security threats reduces risks by helping create a vigilant culture within the organization.
RELATED: Ten tips to improve Cyber Security Awareness amongst your employees
5. IT Operations Controls
These controls ensure that systems operate as intended. By concentrating on ITGCs related to job scheduling, backup and recovery processes, and incident response, the organization can ensure system availability and reliability.
Operational controls are central to maintaining effective day-to-day IT operations.
Implementing Effective IT General Controls
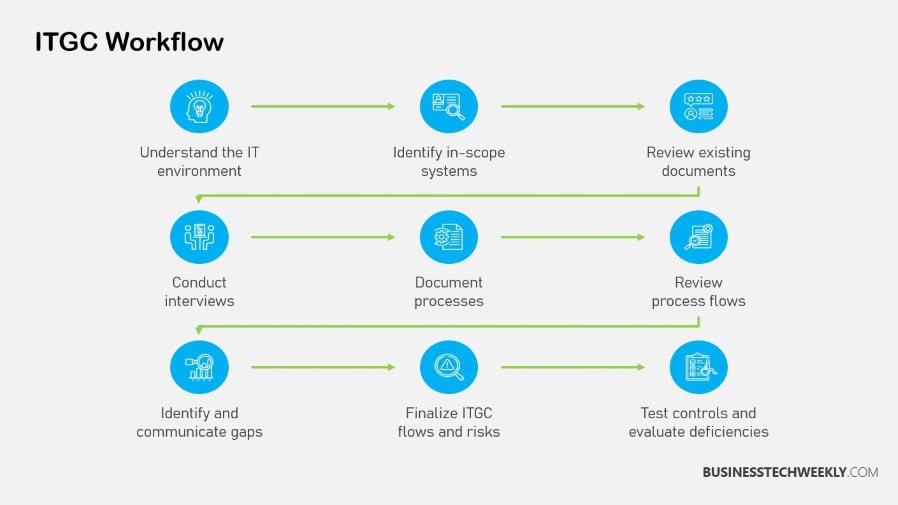
Organizations that want to improve their IT governance need to develop a repeatable, systematic process for implementing IT General Controls (ITGC).
This approach is key to increasing efficiency and reliability.
ITGC is a multi-step process that helps organizations ensure that the systems they use are reliable and secure.
They affect the gamut from Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) to project management tools, even affecting vendor management.
Planning and Scoping Steps
You need to begin with an understanding of scope.
Define ITGC objectives that align with organizational goals and compliance requirements, ensuring all stakeholders from IT staff to senior management are engaged.
This guarantees an in-depth grasp and application of essential information security controls that support business goals.
Conducting Risk Assessments
Risk assessments are pivotal in identifying threats to your information technology systems.
By evaluating and prioritizing these risks, you allocate resources effectively, shaping your ITGC strategies to ensure strong ITGC that mitigate insider and external threats, including those from endpoints like laptops.
Designing and Implementing Controls
Designing effective ITGCs means implementing them in a way that benefits your organization.
Documentation is key, providing evidence that controls are aligned with industry frameworks such as COSO and COBIT.
They need to be reasonable and implementable, while honing in on core IAM principles, encryption, etc., to better protect sensitive data.
Testing Control Effectiveness
Testing provides confirmation or assurance of ITGC effectiveness.
Consistent testing exposes vulnerabilities in information technology general controls, allowing for strengthened security controls. Continuous feedback sharpens these measures, ensuring they meet compliance objectives.
Ongoing Monitoring Techniques
A process of continuous monitoring for information security controls helps maintain their effectiveness over time.
Using real-time tools and conducting frequent ITGC audits adjusts strategies to changing threats, keeping defenses strong and proactive.

Frameworks for IT General Controls Compliance
When it comes to IT General Controls (ITGCs), several frameworks are involved and extremely important.
They support organizations in the establishment of robust and pragmatic control frameworks.
Other frameworks are COSO, COBIT, ISO Standards, and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
Each one has its own set of features and benefits designed to help you better achieve a variety of compliance and security requirements.
Below is a comparative table that outlines the key features of each framework:
|
Framework |
Key Focus |
Compliance & Security Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
COSO |
Internal control and risk management |
Enhances governance, reduces legal exposure |
|
COBIT |
Aligning IT with business goals |
Improves accountability, transparency |
|
ISO Standards |
Information security and IT governance |
Promotes best practices, supports international compliance |
|
NIST Cybersecurity |
Cybersecurity risk management |
Strengthens ITGCs, focuses on risk response |
Overview of COSO Framework
The COSO framework focuses on internal controls and risk management, which are fundamental principles of ITGCs.
It works on five key principles that include control environments, that help maintain industry standards, and provide protection from litigation.
By embracing COSO, organizations are not only making strides toward compliance, but better governance.
This is what makes COSO an obvious choice for organizations wanting to improve their security posture.
Overview of COBIT Framework
COBIT takes a strong focus on aligning IT efforts with overall business objectives and has introduced a detailed framework of components that help to ensure effective ITGC are implemented.
The IT Governance Institute created COBIT to help increase accountability and transparency.
Most importantly, it ensures that IT processes flow directly from and contribute to overall business strategy.
Overview of ISO Standards
Relevant ISO standards, including ISO 27001, aim directly at ITGCs and security of information.
Following these widely accepted international standards is an important step toward developing and sustaining compliance while establishing leading practices in IT governance.
ISO standards are ideal frameworks for establishing, implementing, and continually improving IT security compliance.
Overview of NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is designed to manage cybersecurity risks through its core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
Organizations that adopt this framework can make meaningful improvements to their ITGCs.
They fight both insider and external threats with robust monitoring, effective IAM practices, encryption, and comprehensive employee education.
Addressing Security Risks in IT General Controls
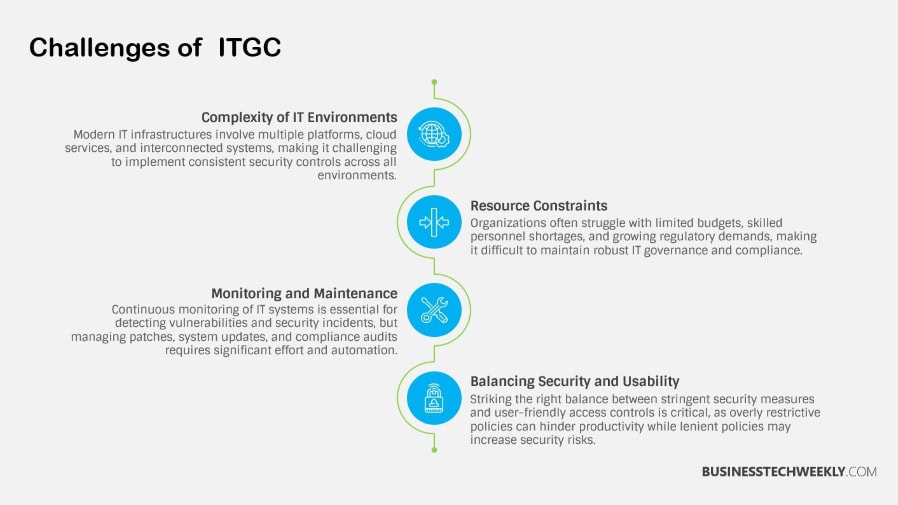
Navigating the ITGC maze isn’t easy—especially without recognizing the security risks that could derail your organization’s operations.
These risks are data breaches, unauthorized access, and system vulnerabilities. By not only knowing these threats, but identifying them, you lay the groundwork for bolstering your security practices.
A comprehensive ITGC framework secures all endpoints, removes vulnerabilities, and upholds IAM best practices.
This process by design makes it more difficult for insiders and outside actors to pose a threat and limits opportunity for fraud.
Frequent inventory audits, either on a quarterly or yearly basis, assist in identifying valuable data that all control systems can continuously improve upon.
RELATED: IT Risk – Managing Common IT Security Risks
Managing Insider Threats
Insider threats happen when people inside your organization abuse their access, whether on purpose or by mistake, to negatively impact your organization’s security.
To detect these threats, it is critical to analyze deviations in user behavior and access history.
Mitigating them positively takes a combination of employee education and frequent oversight.
Prevention through training ensures employees know how to recognize and avoid risks.
Monitoring allows you to identify suspicious activity as it occurs.
This preventative strategy goes a long way toward protecting your most sensitive data and the trust of your organization.
Countering External Threats
Additionally, external threats like cyberattacks and data breaches pose ever-looming threats to IT systems.
Proactive measures such as implementing firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems are essential.
Having a strong incident response plan to begin with is key.
Most importantly, it puts your organization in a better position to respond quickly, reducing the potential for devastating downtime and financial loss.
ITGC audits guarantee these measures are being taken, testing their effectiveness to protect against today’s cyber threats and zero-day attacks.
RELATED: Incident Response Plan Testing: The Ultimate Guide
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Whether you’re a government agency or a private company, compliance with government regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA is essential.
ITGCs are fundamental principles that support these initiatives, making sure systems are developed and deployed in compliance with required standards.
Failure to comply can result in heavy fines and harm your brand’s reputation.
ITGC processes cover all IT aspects, from the implementation of software to how data is processed and stored. They fit perfectly into your organization’s needs because IT and business systems are integrated.
Benefits of Implementing IT General Controls
Implementing strong IT General Controls (ITGCs) enhances operational efficiency and security, providing organizations with significant benefits in information security controls and compliance frameworks.
- Enhanced security
- Improved risk management
- Increased compliance
- Strengthened business continuity
Enhancing Security Measures
ITGCs support the security posture of an organization by embedding security into daily processes.
They prevent unauthorized access by locking down endpoints such as laptops and mobile devices, mitigating insider and external threats.
Continuous improvement should be a cornerstone of your security posture.
Tools such as encryption and antimalware are actively defending our data.
Improving Risk Management Practices
When ITGCs are effective, organizations can achieve better risk management outcomes by offsetting risk with appropriate controls based on the organization’s risk appetite.
Ongoing evaluation sharpens approaches, making sure the systems are able to detect and prevent vulnerabilities.
This reduces the likelihood of a data breach, thereby increasing the reliability of financial reporting and reducing the risk of fraud.
Increasing Regulatory Compliance
Robust ITGCs make it easier to comply with ever-changing regulations, protecting organizations from legal liability by as much as 90%.
Organizations ward off the next regulatory amendment by continuously improving themselves.
They implement industry-standard frameworks such as COSO and ISO 27001 to avoid fines and litigation.
Supporting Business Continuity Plans
ITGCs, or information technology general controls, play an essential role in business continuity by reducing the impact of potential disruptions through strong ITGC implementation.
Routine testing and updates keep compliance frameworks relevant, protecting the long-term success of operations.
Best Practices for Maintaining IT General Controls
Conducting Regular Audits
Continuous audits remain a key factor in the ongoing upkeep of IT General Controls (ITGCs).
Audits are incredibly important as they assist in identifying areas of weakness that could be overlooked. By consistently reviewing systems and processes, organizations can identify areas that need to be strengthened.
Independent audits add the benefit of objectivity, delivering a neutral evaluation that is free of the bias an internal review could include.
This external perspective is crucial for transparency. In addition, it allows us to focus on making our controls effective and efficient.
RELATED: Vulnerability Assessments: 4 Crucial Steps for Identifying Vulnerabilities in your Business
Training Employees on Responsibilities
Educating employees on their roles in ITGCs ensures that an organization becomes a security-minded place.
Employees armed with information on how they can help keep IT secure play a major role in risk mitigation.
Regular security awareness campaigns ensure that the entire workforce understands where the newest threats are lurking, and the most up-to-date security practices.
When employees understand just how important their actions are, they form the bedrock of a robust security culture.
They don’t just react—they proactively defend their organization’s assets.
Developing Control Strategies and Processes
In order to create those best-fit control strategies and processes, it’s vital that they are matched up with the organization’s unique business requirements.
This alignment helps to ensure that controls are relevant, applicable, and provide value.
Ongoing discussion and training about these tactics and approaches go a long way to keeping them fresh and effective against new threats that continue to emerge.
By continuously improving these processes, organizations will be able to stay one step ahead in their ITGC maintenance and support endeavors.
Key Points to Note
- ITGCs are a collection of critical policies, procedures, and technical controls. They ensure proper and secure operation of IT systems. Their critical role is in protecting sensitive data, while ensuring operational integrity across the public and private sectors.
- Implementing robust ITGCs is crucial for regulatory compliance, particularly with standards such as SOX and GDPR, and is instrumental in ensuring the accuracy of financial reporting and preventing fraud.
- ITGCs are only effective if they are built on strong foundations including access control mechanisms and change management processes. Moreover, they include data backup and recovery strategies, security management practices and IT operations controls. Each component plays a vital role in an organization’s security posture.
- To make ITGC a reality, organizations need to take a more structured approach. This involves proactive designs, threat modeling, tailored controls, and ongoing penetration testing to meet the ever-changing threats head on.
- Widely adopted frameworks such as COSO, COBIT, ISO Standards, and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework provide a foundation for organizations to build strong ITGCs. These frameworks improve security and help organizations stay compliant with industry standards.
- Regular audits and ongoing employee education are common practices that help support strong ITGCs. By creating these adaptive control strategies organizations can take a proactive approach with risk management and maintain business continuity.

