What is the Difference Between Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery?

On this page:
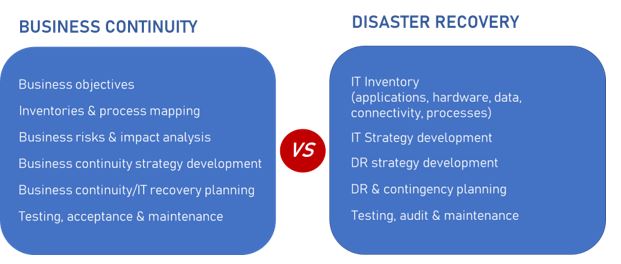
What is Business Continuity?
Business continuity is the comprehensive strategy that ensures the continuance of operations both during and after disaster.
It’s about making sure your business can still operate efficiently even in the face of adversity.
This methodology calls for comprehensive contingency plans that emphasize the continuity of essential business operations, protecting the organization from potential interruptions.
A complete business continuity plan (BCP) addresses all the possible issues you may face—from natural disasters to cyber-attacks.
Unlike many other response plans, it truly engages critical stakeholders during its creation and execution. These stakeholders are key in developing strategies that address the unique needs of the business.
Purpose of Business Continuity
The ultimate goal of business continuity is to reduce the amount of time operations are down in times of crisis. By safeguarding essential business activities and procedures, continuity plans help to make organizations more resilient to unexpected incidents.
This resilience is paramount for the safety of employees during disasters.
It fosters open communication, which is key to ensuring that everyone stays informed and on the same page.
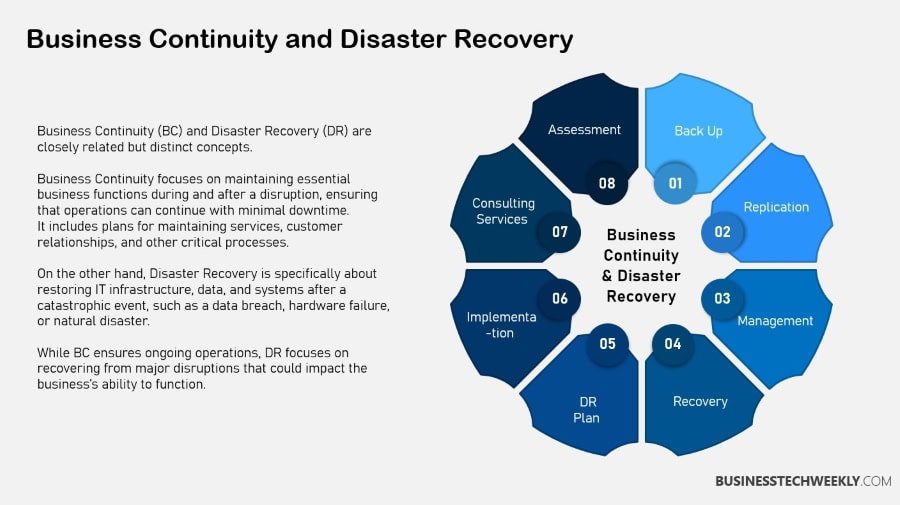
Components of Business Continuity
Essential components of business continuity include risk assessments, business impact analysis, and recovery strategies.
A robust communications plan keeps stakeholders informed throughout any crisis. Regular training and drills prepare employees for emergencies.
Technology and data management support continuity efforts, ensuring that operations can continue without significant disruptions.
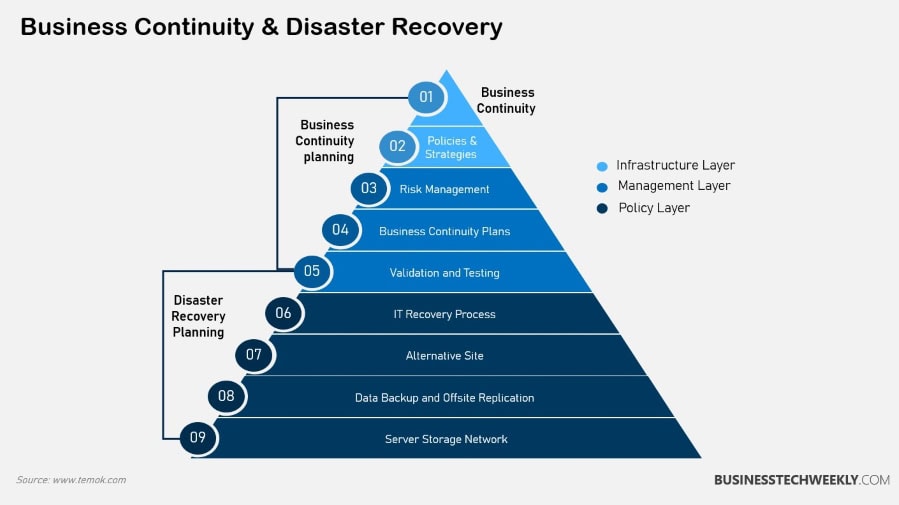
Planning for Business Continuity
- Conduct risk analysis
- Engage stakeholders
- Document procedures and responsibilities
Regular reviews and updates to the business continuity plan (BCP) are essential, as changing circumstances will require the plan to be adaptable and responsive to remain effective.
Collaboration across departments encourages a comprehensive approach to disaster recovery planning, bringing together a variety of perspectives and expertise.
What is Disaster Recovery?
Disaster recovery is an essential component of business continuity. It focuses on rapidly recovering IT systems and having access to critical data once a disruption has taken place.
This laser-focused, strategic approach is more important than ever to minimize the effects of major occurrences, whether they be cyberattacks or the next natural disaster.
Disaster recovery plans (DRPs) are critical to protecting against disasters such as large-scale outages, ransomware, and malware attacks.
In 2023, the average cost of a data breach increased to USD 4.45 million.
Having a sound disaster recovery plan (DRP) in place will save you from expensive data loss and minimize your downtime.
Purpose of Disaster Recovery
The main goal of disaster recovery is to get everything back to normal as quickly as possible after a disaster. Well-crafted plans guard against loss of critical data and IT infrastructure, keeping disruptions as short and manageable as possible.
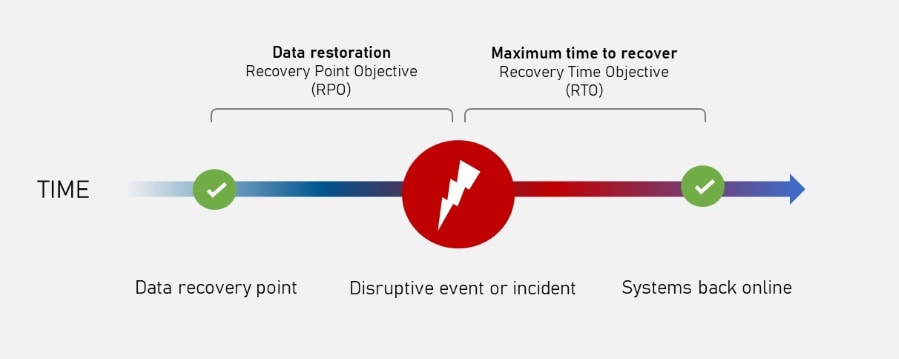
Having clearly predefined recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) is essential to accomplishing this.
RTO is the amount of time a business can afford to be down, and RPO is the amount of acceptable data loss.
Together, they help create business resilience and operational stability.
Components of Disaster Recovery
A major key to successful DRPs lies in the data backups, recovery solutions and testing protocols. A committed staff drives recovery strategies, bolstered by a clear paper trail of processes and roles.
Technology and software are critical to enhancing recovery’s capabilities and capacities, and being fully prepared for all threats.
Planning for Disaster Recovery
- Conduct risk assessments and allocate resources
- Regularly test and update plans for effectiveness
- Involve IT and business leaders in planning
- Establish clear communication channels for recovery scenarios
RELATED: Business continuity and crisis management
Key Differences Between the Two
1. Scope and Focus
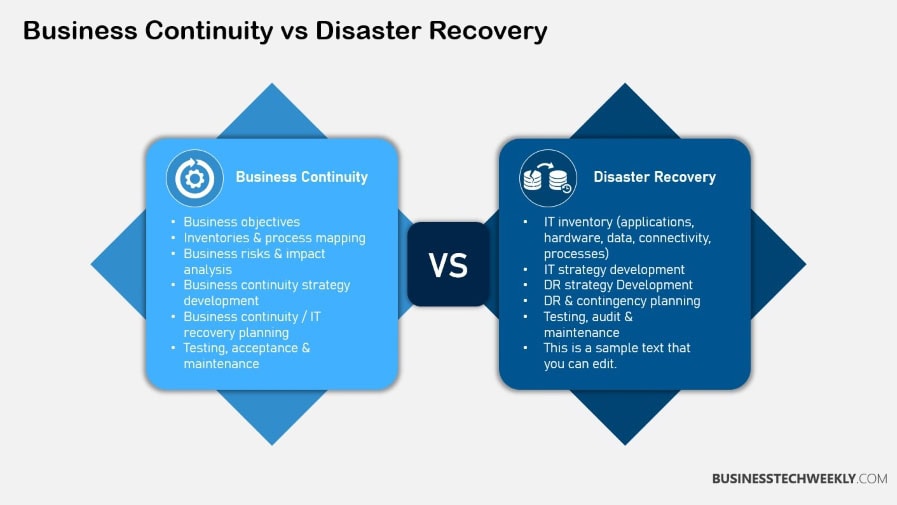
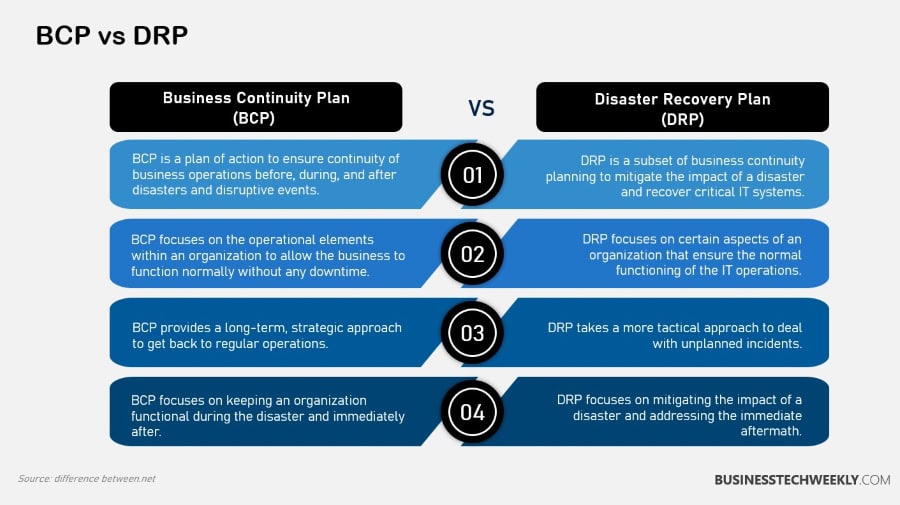
Business continuity and disaster recovery are related but different strategies that fall under the umbrella of organizational resilience.
Business continuity is concerned with keeping the enterprise going during and after the disaster, addressing every aspect, including employees and physical plants.
This strategy allows the organization to keep operating with minimal interruptions, even under difficult circumstances.
Conversely, disaster recovery narrows your focus to how you restore IT systems and access to data after a disaster or disruptive event.
Its scope is much narrower, focusing on the technology and data management required to get those critical systems back up and running as quickly as possible.
Together, these strategies provide a complete roadmap. While business continuity encompasses the whole organization, disaster recovery is focused on offering technical solutions for tech-related disruptions.
2. Timeframe and Objectives
The objectives and timelines of business continuity vs. Disaster recovery are very different.
Business continuity goes beyond emergency response to operational resilience, with an emphasis on long-term preparedness and adaptability.
It aims to reduce any disruption to day-to-day operations, making sure the business can survive through any potential threat. In contrast, disaster recovery is the opposite—it’s immediate recovery.
It focuses on short-term post-disaster response, including defined RTOs (recovery time objectives) to get IT systems back up and running in a timely manner.
Both strategies require varying timelines, with business continuity merging more into everyday practices while disaster recovery focuses on the need for quick action when necessary.
3. Strategies and Approaches
- Redundancy, cross-training, regular drills, and an all-inclusive communication plan.
- Operational readiness Data backups, cloud-based solutions, incident response plans, and regular system testing.
These disaster recovery strategies should be customized to mitigate specific organizational risks, creating a robust business continuity plan that provides the deepest level of preparedness.
Importance of Organizational Resilience
Organizational resilience is the ability of an organization to adapt to, withstand, and recover from all disruptions.
It is essential for long-term stability and success in today’s rapidly evolving business environment.
According to ISO 22316:2017, resilience enables an organization to absorb and adapt to changes, allowing it to deliver objectives, survive, and thrive.
Business continuity and disaster recovery are key parts of this resilience. They position organizations to absorb rather than incur the shock of disruptions, reducing the impact with financial losses and accelerating recovery.
Strong leadership is crucial to creating a culture of resilience in any organization.
By demonstrating a commitment to resilience, leaders can help their teams better grasp the value of preparedness and adaptability.
Besides the immediate goal of protecting critical assets, this proactive approach helps ensure stakeholder trust is preserved during crises.
RELATED: Maximizing Business Resilience: The Importance of Risk Assessment in Business Continuity Planning
Benefits of Business Continuity
Business continuity can provide four important benefits. It reduces the risk of downtime, builds employee trust in the organization, and creates better experiences for customers.
Sound business continuity planning improves overall risk management and preparedness, which can give your organization an edge over competitors.
Proactive planning maintains stakeholder trust during crises, ensuring the organization remains dependable even when faced with challenges.
Approximately 51% of companies globally do not have a business continuity plan in place.
Benefits of Disaster Recovery
With disaster recovery, there are benefits of quick data restoration, a decrease in overall financial impact and the ability to safeguard valuable assets.
By protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance, it improves overall business performance.
Disaster recovery is an important part of protecting your brand’s reputation in a crisis, and if your organization is not prepared, business will be disrupted.
Combined Impact on Resilience
Bringing business continuity and disaster recovery together improves organizational resilience.
The joint value add is more timely emergency response, enterprise-wide risk management, and meeting broader organizational objectives.
Monitoring, evaluation, and willingness to change these strategies as environments change are all key to resiliency.
- Improved response times
- Comprehensive risk management
- Alignment with organizational goals
Implementing Both Strategies
Here’s a guide to get you started on developing a robust disaster recovery plan.
- Identify potential threats and evaluate their impact on operations.
- Get buy-in and support from high-level executives and relevant departments.
- Be explicit about roles, responsibilities, and procedures in your preparedness and response plans.
- Create education efforts to involve agency employees to help them buy in and make them aware of their part.
- Hold periodic drills to test your readiness and improve logistics.
Steps to Develop a Plan
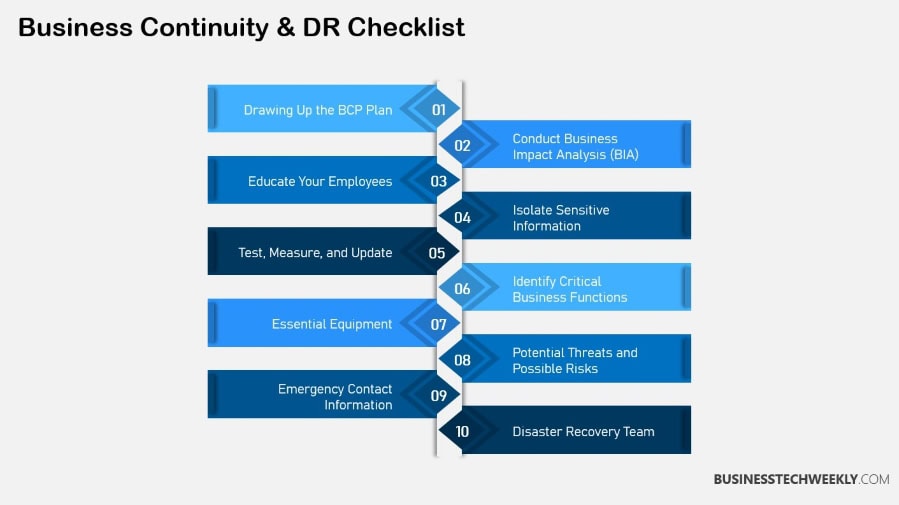
Developing a comprehensive plan requires thorough risk assessments and active stakeholder involvement. Documenting processes and responsibilities in detail is crucial.
Regular reviews and updates keep these plans relevant.
Collaboration across departments ensures a cohesive approach, enhancing overall effectiveness.
For example, companies should identify essential third parties for support during recovery.
Only 50% of businesses test their disaster recovery strategy at least annually, indicating a need for more regular testing to ensure effectiveness.
Monitoring and Updating Plans
Continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential to keeping successful strategies on track.
Continuously measure results with leading indicators like decreased downtime and lagging indicators like cost savings. Engage employees and other stakeholders early to get their input and ideas to help shape plans.
Continuously adapt strategy based on changes to the business environment and new, developing risks.
As businesses—large and small—prepare to spend USD 219 billion just on cybersecurity solutions, implementing these lessons can go a long way to better prepare organizations.
Key Points to Remember
By knowing the key differences between business continuity and disaster recovery, you can better establish solid strategies to protect your organization.
- Business continuity is a proactive strategy. It ensures smooth operations during and after a crisis, allowing organizations to maintain continuity while protecting their most critical processes. It is therefore critical to achieving operational resilience and reducing downtime during unexpected events.
- Disaster recovery focuses on getting those IT systems back up and data restored after a disaster has already occurred. It helps you get back up quickly, preventing data loss and lessening downtime. It acts as an extension of business continuity, focusing more narrowly on IT-related challenges.
- The main difference between business continuity and disaster recovery is in their purpose and breadth. Business continuity is much more holistic, addressing every organizational function, whereas disaster recovery focuses on technology and data restoration.
- Together, both strategies are key to establishing organizational resilience. While business continuity focuses on maintaining efficient operations, disaster recovery hones in on rapidly restoring IT systems after a crisis. Together, they allow companies to protect themselves from financial losses and preserve stakeholder trust.
- Successful integration of business continuity and disaster recovery comes from thorough planning, frequent revisiting of plans, and cross-departmental collaboration. By involving critical stakeholders and running regular and rigorous tabletop drills, we can improve our preparedness and response times.
- Ongoing evaluation and adjustment of these strategies is critical to respond to evolving risks and to maintain alignment with organizational priorities. This would help provide a comprehensive foundation for resilience to all types of disruptions.

