What You Need to Know About Data in Motion

On this page:
What is Data in Motion
Data in motion is data actively moving from one place to another, and it’s become a critical aspect of today’s enterprise data architectures. This is an important concept for most business use cases, with 80% of enterprises using data in motion to make business-critical decisions.
In contrast to static data, data in motion is dynamic, traversing networks like when someone uploads a file to a cloud-based storage service. This dynamic nature sets it apart from data at rest, which remains stored, and data in use, which is currently processed.
More practical applications are illustrated through examples such as emails and real-time analytics.
Definition of Data in Motion
Data in motion encompasses any data that is currently being transmitted, from data in an email to data during real-time analytics. This is distinct from static data types, in that it is a continuous transfer and possible modification.
For example, streaming video and audio content illustrate the dynamic nature of data in motion, providing real-time availability and engagement.
Importance in Modern Data Management
Securing data in motion is critical if organizations hope to avoid catastrophic financial loss and damage to brand and public reputation. Adhering to regulation standards helps keep sensitive information safe while in motion.
When done right, effective data management earns customer confidence while strengthening business performance. Data in motion plays a key role in enabling real-time analytics and IoT applications.
Integrating data in motion from various sources allows organizations to build personalization in real-time, enhancing consumer engagement across industries such as retail, hospitality, manufacturing, and financial services.
Examples of Data in Motion
- Email communications
- File transfers to cloud services
- Streaming video and audio content
- Real-time data analytics in applications
Understanding Data Encryption
Encryption of data protects sensitive information by converting it into unreadable code, preventing unauthorized users from accessing it. It’s similar to putting your data in a vault, only accessible with the right key. When you send sensitive information through the internet—like online banking information or personal messages—encryption protects that information.
Most importantly, it keeps your data private and secure.
What is Data Encryption
Data encryption is simply the process of making your data unintelligible to dissuade unauthorized access. Think about confusing a message so that only the person who knows the right code can understand it. That’s where encryption keys enter the picture—they’re key to reverting the scrambled data back to its readable format.
Encryption matters in everyday scenarios: online shopping, emailing confidential info, or even chatting securely.
RELATED: Data Privacy vs Data Security: Which Should You Prioritize?
Types of Data Encryption
|
Type |
Description |
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Asymmetric |
Uses two keys: public for encrypting, private for decrypting |
Secure key exchange, used in RSA, ECC |
Slower than symmetric |
|
Symmetric |
Same key for both encryption and decryption |
Fast and efficient |
Key distribution can be tricky |
|
Transport Layer Security (TLS) |
Ensures secure data transfer over networks, like HTTPS |
Widely used, prevents eavesdropping |
Can be complex to implement |
|
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) |
Encrypts data at the network layer |
Protects data in motion, flexible |
Requires proper configuration |
Importance of Encryption for Security
Encryption is our first line of defense in protecting sensitive data from cyber criminals. It’s a requirement to stay in compliance with regulations and protect sensitive customer information.
In addition to securing sensitive data, encryption protects the integrity of data, ensuring that the information isn’t altered as it moves between systems.
States of Data
Getting a grasp on these three states of data—data at rest, data in use, data in motion—is key to the future of data management. Each state is analogous to a different phase in the data lifecycle – creation, storage, transfer, or destruction – with distinct characteristics and security requirements.
Understanding the differences between these states allows you to develop strong security practices that are specifically designed to safeguard data in each state.
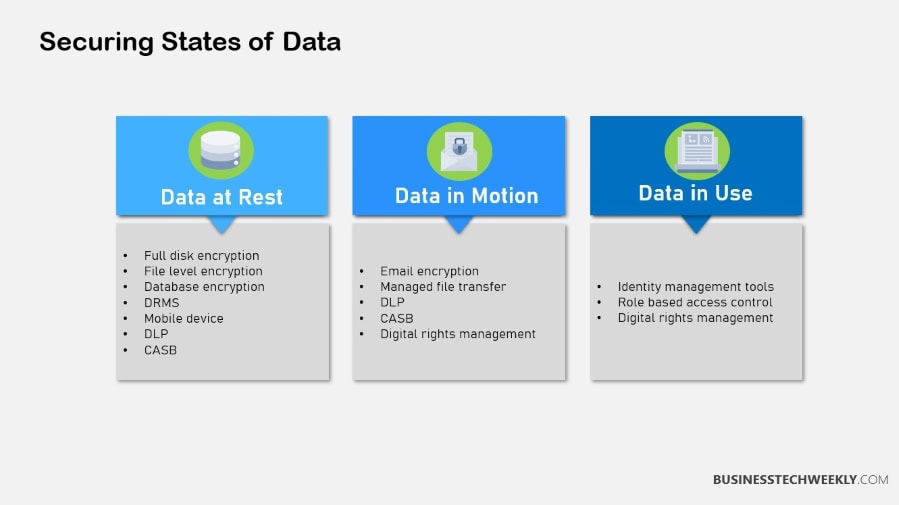
What is Data at Rest
Data at rest is information stored on devices or databases, not actively being transferred. This state may be files, databases, or number of widgets on hand as of the last day of each month.
Security challenges for data at rest include unauthorized access or data breaches, which is why encryption is extremely important. Encrypting data at rest protects sensitive information from unauthorized access due to loss or theft, ensuring confidentiality and integrity of data.
What is Data in Use
Data in use includes any personal information currently being processed or accessed, for example when conducting an analysis or while your app is running. As the most critical data state, it is particularly at risk such as being exposed to unauthorized users while the data is in processing.
In addition, protecting data in use is sometimes a matter of avoiding the loss of sensitive information and meeting regulatory requirements. This state is one where information is accessed and manipulated in real-time.
Differences Between Data States
|
Data State |
Characteristics |
Security Requirements |
Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Data at Rest |
Stored, inactive |
Encryption, access control |
Inventory numbers, archived files |
|
Data in Use |
Actively processed |
Real-time protection, user authentication |
Data analysis, application operations |
|
Data in Motion |
Transmitting between locations |
Advanced encryption, monitoring |
Cloud transfer, document folder movement |
Data in motion refers to sending digital information from one point to another, putting it at risk of attacks or accidental deletion. Business practices are built around these data.
In fact, protecting it is at least ten times more expensive than protecting data at rest. Sophisticated encryption algorithms are needed to protect it, wherever it goes — whether in transit on a local network or between different cloud infrastructures.

Protecting Data in Motion
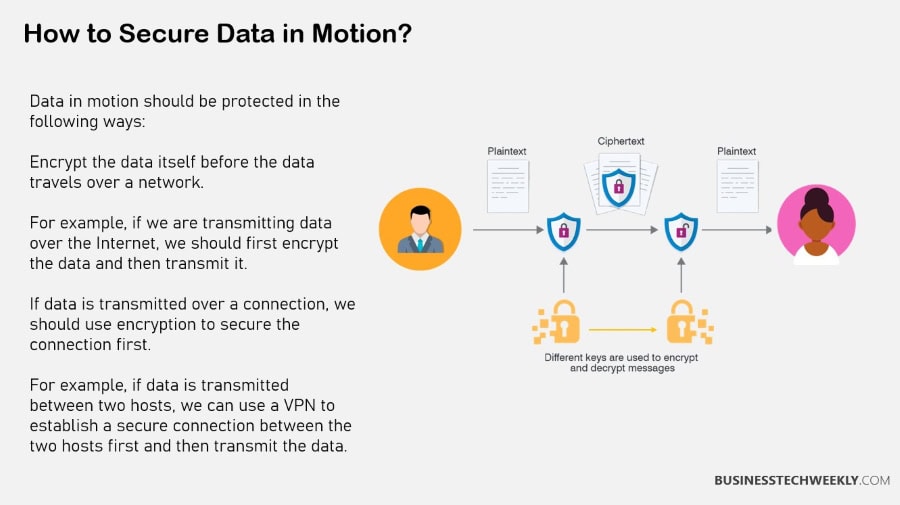
Protecting data in motion is crucial because it’s the most at-risk to threats. Putting strong security measures in place is the best way to protect this data. Encryption, access control, and monitoring all are key to protecting data in motion.
Strong encryption protocols such as AES 256 make hacking practically impossible. AES 256, an evolution of AES 128-bit, has never been hacked and would take centuries to crack. This is why encryption is critical for protecting data. As threats continue to change and evolve, so must our security practices and our continuous improvement of security practices.
1. Best Practices for Security
- Implement strong encryption protocols.
- Regularly update security policies.
- Conduct employee training on data security.
- Utilize secure communication channels.
2. Methods for Encrypting Data
Encryption methods such as TLS and IPSec are examples of how we can protect data in motion. Selecting the best approach to suit specific organizational goals is key.
Seamless integration of encryption into current data transfer processes boosts security. This is to ensure that all information transmitted is safe and secure.
RELATED: Understanding the Data Encryption Standard (DES)
3. Security Measures for Data Transfer
It’s not just about secure file transfer protocols, access controls, and monitoring. Conducting regular audits not only promotes compliance but can help spot suspicious activity.
Automated policies do the rest by preventing exposure and encrypting everything by default in transit.
4. Protecting Data During Exchange
Protecting data in motion is fundamental to avoiding unwanted breaches. Encryption and secure protocols protect data in motion.
Ongoing monitoring, auditing and active management help maintain compliance and security.
Seamless Integration and Security Measures
Seamless integration means integrating multiple applications and systems smoothly, so data can effortlessly flow between them. Imagine a rideshare app that could automatically integrate with your calendar to recommend rides to your next meeting. This type of integration saves time and increases overall interoperability.
Businesses win too, as they gain improved access to data, helping to foster collaboration. Customers feel the benefit as well, with more timely and relevant information available to them at their fingertips.
Importance of Seamless Integration
With the help of seamless integration, businesses experience a variety of advantages including better data access and enhanced collaboration. For example, e-commerce platforms can instantly pull from inventory, making sure that products are in stock and ready to ship when consumers order them.
This further improves customer experience by providing information that’s timely, relevant and useful. Security does matter. As integrated systems become more prevalent, it is crucial to safeguard them from potential vulnerabilities to maintain data security.
Security Measures in Applications
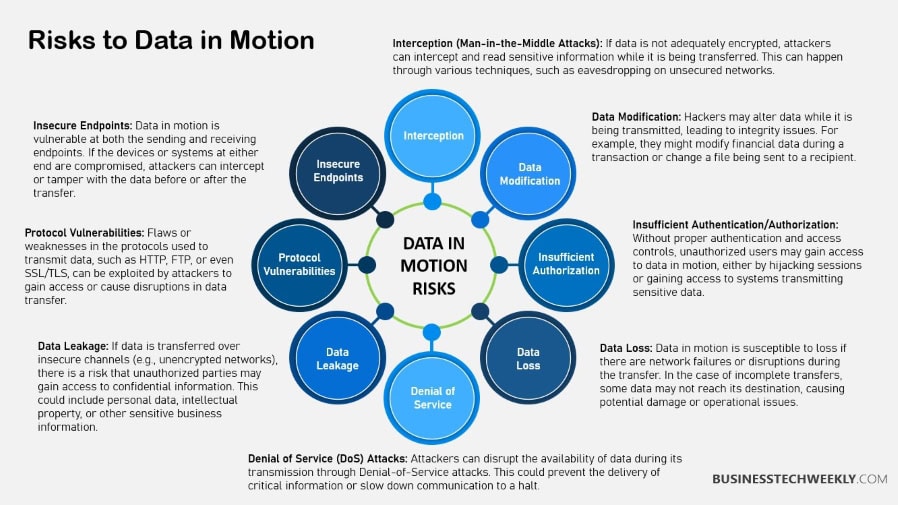
To protect data in motion, applications should implement key security measures for data exchange.
- Regular software updates
- Strong authentication protocols
- Data encryption during transmission
- Continuous monitoring for anomalies
According to the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO), incidents where data is emailed to the wrong recipient are the most common type of data breach reported.
hayesconnor.co.uk
Implications for Various Applications
Data in motion security has significant implications for data exchange and interoperability.
- Rideshare apps managing location data
- E-commerce platforms handling payment info
- Healthcare applications protecting patient data
- Communication tools ensuring secure messaging
Key Points to Remember
- Having a handle on data in motion is fundamental to a robust and secure modern data stack. It underscores major distinctions from data at rest and data in use, demonstrating its value for low-latency use cases such as messaging and streaming.
- Data in motion refers to information that is in transit. This sensitive data must be treated in an agile manner while being subjected to enterprise-level security controls to protect it while in motion.
- Encryption is an important technology to protect data in motion. It encrypts the sensitive data, keeping it out of malicious actor’s reach and ensuring data confidentiality while in transit across the network.
- Asymmetric and symmetric encryption both serve important purposes. Those are just a few of the things you need to think about when creating your data protection strategy.
- In order to protect data in motion from the growing, sophisticated wave of cyber attacks, you need fortified security solutions. This means deploying encryption, access control, and continuous monitoring to meet compliance and regulatory requirements.
- Seamless integration of systems enhances operational efficiencies and user experiences, necessitating the incorporation of security measures to protect data in motion and maintain system integrity.

