Centralized vs Decentralized vs Distributed Networking Explained

With the emergence of Blockchain and cloud technology, decentralized and distributed networks have become a major trend in today’s commercial contexts. These are far from the centralized networks that existed five to ten years ago. But, what are the differences betweern centralized vs decentralized vs distributed networking? Here we explain the fundamental distinctions between these networks and the primary benefits and drawbacks of each.
On this page:
What is a Centralized Network?
A centralized network design is centred on a single server that performs all the heavy lifting. Workstations connect to the server and send their requests to the central server for processing, rather than doing them directly. Processing can include programmes, data storage, and utilities.
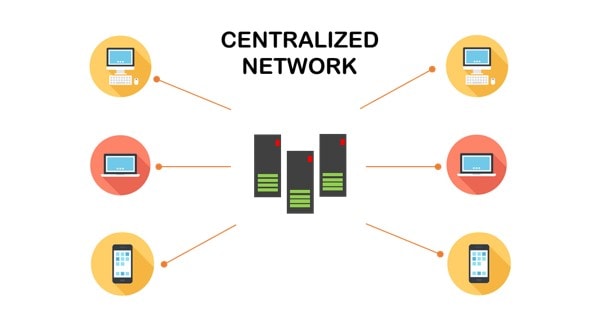
Centralized Networks: What are the Advantages and Disadvantages?
Comparing centralized vs decentralized vs distributed networking , consistency, efficiency, and affordability are just a few of the benefits of centralized network administration. Because network managers are under pressure to maintain equipment patched and current, having a single central server administer the whole network reduces IT administration time and staffing. Additionally, because all data on a centralized network must pass via a single point, tracking and gathering data across the network is highly straightforward. Centralized networks do have drawbacks. For example, a single point of failure might risk businesses. If the central—or master—server fails, the associated “client” workstations cannot handle user requests. The impact of this failure will be determined by the amount of data processed by the server. If client computers are tasked with nothing more than submitting requests, system availability can be ultimately jeopardized. Additionally, they have limited scalability. Because all applications and processing power are housed on a single server, the only method to expand your network is to increase the server’s storage, I/O bandwidth, or computing power. This may not prove to be the most cost-effective choice over time. Finally, a scarcity of bandwidth might constitute a hindrance. If your organization has peaks and valleys of inactivity, a single server may quickly become a bottleneck since it becomes impossible to keep up with the inflow of concurrent user requests—and the number of requests the system can handle. Related: What is a Wide Area Network? Understanding WANs
Why are Centralized Networks becoming unpopular?
To understand why decentralized and distributed networks are gaining popularity year after year, we need to understand what is wrong with centralized networks. First, a critical difficulty that many recognize is that centralized networks rely on a lead server that can simultaneously aggregate and handle all network data. This renders centralized networks susceptible to hacks and failures, as it only takes one server to be compromised or shut down for the entire network to collapse. Nonetheless, centralized networks continue to be the most often utilized network form today. One may argue that this is due to corporations’ desire for complete control of their networks. However, this might result in significant challenges for large enterprises. Have you ever experienced the loss of one of your favourite social networking websites? A centralized network presumably connects them. The master server has been compromised by an external force or is experiencing technical difficulties. As a result, centralized networks may undoubtedly benefit from an update. This is where decentralized and distributed networks come into play.
What is a Decentralized Network?
Comparing centralized vs decentralized vs distributed networking, through the popularity of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, decentralized networks have come to the forefront. These networks feature many positive attributes, which contributes to their growing popularity. See also: Blockchain Principles: Understanding Blockchain Technology Decentralized networks do not rely on a central server. Decentralized networks make use of a range of distinct connecting points or nodes. At no point in time is a single node capable of harnessing all of the network’s information, which means that no node is ever in control or in charge. Each node can have independent decision-making and information processing, enabling the network’s power to be distributed evenly. Both Bitcoin and Ethereum operate on decentralized networks, and there are many reasons why enterprises today prefer decentralization to centralization. Decentralized networks are far more difficult to attack than centralized networks. This is because an attack of a single node does not result in complete control of the network. Additionally, because the functionality is distributed across the network, this network architecture prevents total system failures or breakdowns. Scaling a decentralized network is easy, as you can add nodes or servers. Due to their decentralized nature, they provide greater user control and privacy.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Decentralized Networks?
A decentralized network has several advantages over a centralized network. These include greater system dependability, scalability, and privacy. A significant advantage is the absence of a single point of failure because individual users’ devices are not dependent on a single central server to administer all operations. Additionally, decentralized networks are considerably easier to grow, as additional computers may be added to the network to increase computational capacity. Decentralized network design provides greater anonymity. Data does not transit via a single point but through several points, which significantly complicates network tracking. While many would argue that decentralized networks are the natural progression from centralized networks, this emerging technology does have significant drawbacks. To begin, given the complexity of a decentralized network’s structure, it might be complicated to create. Additionally, it is challenging to administer a decentralized network, considering the multiple devices that require regular checks and maintenance. This implies increased maintenance and the possibility of faults, which puts extra strain on your IT resources.
What is a Distributed Network?
While distributed and decentralized networks have several characteristics, they are not synonymous. Additionally, a distributed network does not rely on a single central server. Data and decision-making are divided equitably among all servers – which is not the case with decentralized networks. In essence, each server receives the same amount of power. The distinguishing characteristic of distributed networks over decentralized networks is their reliance on equally powerful connecting hubs. However, unlike completely decentralized networks, distributed networks may become centralized. This can be advantageous under some circumstances, such as when quick system administration is required from a single server. Certain individuals favor decentralized networks since they lack this option. Distributed networks can also refer to physically and geographically dispersed networks with a top-down node power scheme, distinct from the first type of distributed network outlined above.
What are the downsides of Distributed Networks?
Distributed networks are far more orderly than decentralized networks. In part due to how equitably data and decision-making authority are spread across the network. Additionally, they are incredibly secure, far more so than centralized networks (though this is also the case for decentralized networks). Additionally, distributed networks are very transparent, as the authorities or persons managing each node or connection point are known. As a result, system failures, incursions, and crashes may frequently be traced back to specific servers, making it easier to pinpoint the source of the problem. They, like decentralized networks, are easily scalable by the addition of more servers. However, decentralized networks are not without flaws. They, like decentralized networks, may be costly to build and maintain. Another significant drawback of decentralized and distributed networks is a central authority overseeing and controlling the whole network. This may have a detrimental influence on decision-making speed and the general structure or coordination of the network.
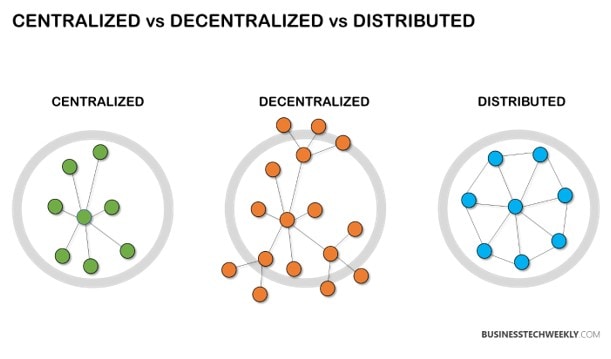
Are Decentralized and Distributed Networks the future?
With the growing popularity of decentralized and distributed networks, one can only anticipate that a rising number of businesses would migrate away from centralized networks in favor of these more secure and scalable alternatives. While construction and upkeep remain a concern, this does not mean they will always be.

