Understanding GRC: Governance, Risk, and Compliance

Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) assists organizations to harmoniously drive towards their set objectives within the bounds of regulatory expectations and risk management.
It helps you maintain compliance across your business processes, reducing your organization’s risk surface and building resilience into your operations.
By unifying governance, risk management, and compliance efforts, GRC improves decision-making and increases efficiency across processes.
For organizations operating in highly regulated industries or seeking to better protect customer data, implementing GRC frameworks offers visibility and oversight.
We invite you to learn more about how GRC can help your organization to thrive.
On this page:
What is GRC?
Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) is an integrated framework that helps organizations align their policies, manage risks effectively, and meet regulatory requirements.
Having come into clearer focus as a defined concept in 2007, GRC’s importance has only increased amid today’s dynamic and dangerous business landscapes.
This process allows organizations to identify and address the relationships between governance, risk, and compliance.
It helps save money, streamlines workflows, and encourages transparency and integrity. GRC is more than risk management.
It increases transparency, builds stakeholder trust, and gets all departments pulling in the same direction toward common goals, reducing duplication of effort.
Defining Governance
At its heart, governance offers a structure for transparent decision-making, allowing an organization to drive the trajectory of their work towards their desired outcomes.
Implementation components, including board oversight, internal controls, and performance monitoring, determine how well decisions are set and followed through on.
Strong governance ensures continued accountability and transparency, which is critical for keeping public faith with employees, investors, and others that the corporation serves.
A company that truly excels in governance will transparently demonstrate that its actions are in line with society’s expectations.
This approach serves to strengthen its credibility and ethical stature.
In the end, good governance serves the best interests of the organization and its long-term mission, allaying potential reputational risks.
Among businesses currently utilizing GRC technology, 61% plan to increase their spending on GRC platforms in the next three years.
Understanding Risk Management
Risk management involves systematically identifying, assessing, and addressing potential threats that could disrupt organizational operations.
Proactive risk assessment is critical for safeguarding financial stability and operational continuity.
For example, recognizing a cybersecurity gap early allows businesses to implement measures that prevent costly breaches.
A robust risk management strategy encompasses various risks—financial, operational, and reputational—and provides actionable steps to mitigate them.
Continuous monitoring and adaptation are vital, as risks evolve with changing markets and technologies.
Tools powered by artificial intelligence, such as predictive analytics, now enable organizations to anticipate risks more accurately and respond swiftly.
Define Compliance
Compliance is the foundation that provides the blueprint for businesses to comply with all laws, regulations, and internal policies that structure their business.
It encourages ethical behavior and legal compliance undercutting the risk of fines or reputational harm.
Compliance management systems help centralize policies and procedures, track regulatory updates, and foster an overall culture of integrity.
For example, compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR doesn’t just help you dodge hefty penalties — it enhances customer trust as well.
The role of automation in compliance management tools helps streamline manual processes, putting organizations a step ahead of rapidly changing regulations.
GRC Relationship Explained
Governance, risk management, and compliance have always been three sides of the same coin.
Smart governance empowers risk management and compliance initiatives alike by establishing strong policies and lines of accountability.
Just as the individual GRC principles segmented departments help, a global GRC strategy improves organizational performance by removing silos and aligning efforts organization-wide.
For instance, developing a data governance policy can both mitigate cybersecurity risks and ensure compliance with regulations, demonstrating GRC’s holistic approach.
Aligning these three components allows for businesses to not only pursue strategic goals, but to cultivate resilience and adaptability.
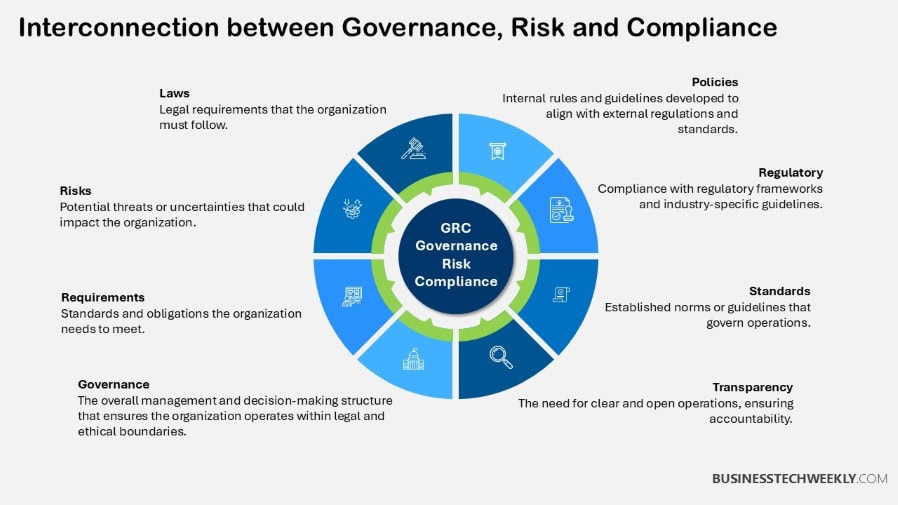
Why GRC Matters
Governance, Risk Management and Compliance (GRC) isn’t just a corporate requirement.
This is what makes it the true strategic compass for organizations sailing the turbulent seas of today’s complex and constantly changing business environments.
By bringing together governance policies, risk management strategies, and compliance efforts, GRC helps make sure companies stay agile, principled, and strong.
Its true importance is in enabling smarter decisions, promoting accountability, and strengthening our overall cybersecurity posture.
Data-Informed Decision Making
Organizations are using data analytics more than ever to help inform their mission-critical decisions and strategies.
Through a GRC framework, using data analytics can move organizations toward more proactive and rational decision-making, supporting that each action is based on the right information.
This is why real-time data visibility is so important, allowing businesses to see risks sooner and mitigate them before they happen.
For example, tracking financial transactions as they happen could allow businesses to identify trends in fraud activity before they develop into major financial losses.
Automated tools are able to quickly analyze millions of regulatory changes and flag areas at risk for non-compliance, all while minimizing human error.
For instance, organizations that are compliant with GDPR can leverage data analytics to track and report on data protection efforts.
Using data management tools and applications such as data governance platforms simplifies these processes. This results in a unified system that reduces risks and simplifies compliance.
Accountable Business Practices
Creating accountability mechanisms in GRC frameworks is important for fostering an environment of ethical business behavior.
Having defined roles and responsibilities helps guarantee that each person knows what they are accountable for and how they fit into larger governance objectives.
For instance, designating a chief compliance officer creates accountability, helping guarantee compliance with internal procedures.
Good accountability practices improve stakeholder trust and corporate reputation, too.
Stakeholder engagement and transparent reporting on governance activities such as environmental and social best practices improve public trust.
It’s a true reflection of the organization’s deep commitment to ethical practices.
Auditing and performance measurement on a routine basis builds faith by proving adherence to governance best practices.
While challenging, this collaborative process ultimately fosters an environment of integrity and accountability.
Enhanced Cybersecurity Posture
A robust GRC framework is foundational to effective cybersecurity.
Risk management practices help organizations identify vulnerabilities and implement measures to address them efficiently.
For instance, periodic risk assessments can uncover gaps in access controls, enabling timely remediation.
Successfully navigating the cybersecurity landscape—completing regulations like ISO 27001—keeps these types of businesses protecting industry standards, therefore lowering your exposure to huge penalties.
Employee training programs help shore up defenses by creating a culture of awareness about dangers such as phishing or malware.
With GRC, organizations get comprehensive visibility into their risks—giving them the power to protect their infrastructure and ensure continuity of operations.
Only 18% of organizations have automated processes for reporting and IT risk data collection, despite automation being proven as an effective way to mitigate risk.
Drivers Behind GRC Adoption
Governance, Risk Management and Compliance (GRC) frameworks are increasingly becoming the backbone of organizations on a global scale.
So what’s driving GRC adoption?
The adoption of GRC is driven by regulatory demands, stakeholder expectations, and operational and technological needs.
Together, each driver deeply influences how agencies and corporations move forward with governing and complying to the needed level of resilience, resiliency, and sustainability for long-term viability.
Regulatory Pressures
As the regulations we must adhere to become more and more complicated, compliance as an organizational priority is on the rise.
Industries including financial services, healthcare, and technology face complex and restrictive policies including GDPR, HIPAA, and international trade agreements.
The stakes of getting it wrong are high, with heavy fines, legal liability, and reputational risk looming large over organizations that fail to comply.
Since GDPR came into force, fines have reached up to 4% of annual global revenue.
Proactive compliance strategies, such as developing GRC frameworks, enable organizations to get ahead.
With compliance embedded into their operations, companies are able to track changes in regulations in real time and pivot quickly and collaboratively.
Tools that centralize compliance efforts allow organizations to save on manual effort and maintain compliance with emerging and changing standards.
This last approach is particularly important for multinational organizations that must navigate different regulations in different jurisdictions.
Stakeholder Expectations
In an age of heightened stakeholder awareness, there’s increased calls for transparency and ethics.
Accountability is the new currency. Investors, customers, employees, and regulators are increasingly expecting organizations to be accountable in their governance and compliance activities.
As an example, data privacy is becoming a prevalent concern among consumers, such that having strong data practices, such as cybersecurity and ethical AI, are now table stakes for establishing trust.
Building stakeholder engagement into GRC strategies not only solidifies relationships, but helps ensure that GRC efforts align with the broader organizational mission.
Whether through releasing regular compliance reports or through stakeholder meetings and discussions, keeping the lines of communication open demonstrates a desire for transparency.
Successfully meeting these expectations not only bolsters credibility but creates loyalty and enduring partnerships.
Operational Efficiency Needs
Efficient operations are a key driver for GRC adoption.
Integrated GRC frameworks streamline processes across departments, reducing redundancies and improving decision-making.
For example, automating risk assessments with AI-driven tools can save time and eliminate manual errors, enabling teams to focus on strategic priorities.
With the advantage of real-time data and built-in analytics, GRC platforms deliver actionable insights that empower businesses to mitigate risks and ensure compliance more efficiently.
These solutions further break down complex information into formats that enhance decision making among all stakeholders.
Continuous improvement initiatives further optimize operations, ensuring GRC frameworks remain adaptable to changing needs.
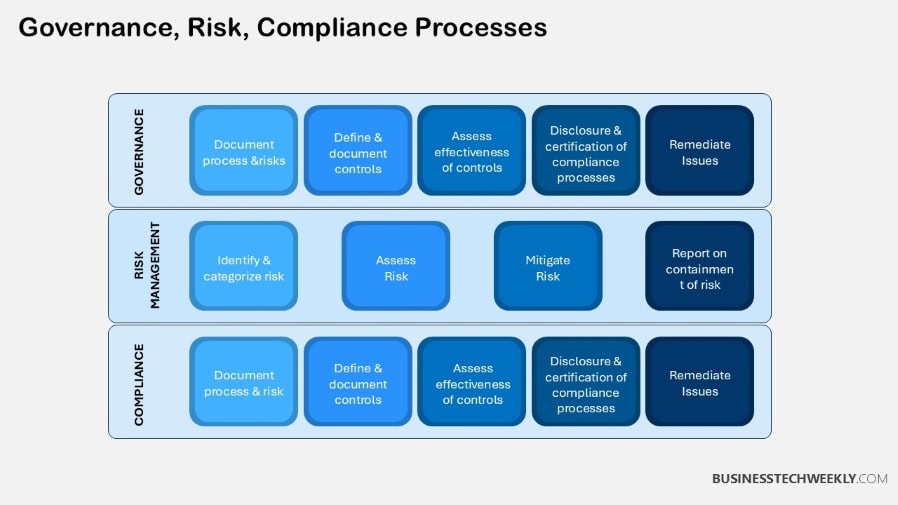
How Does GRC Function?
Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) together create an integrated framework.
It’s a holistic approach that harmonizes policies, processes, and technologies to create a unified framework for managing risks and driving compliance across the entire organization.
Effective progress requires organized partnership and careful execution.
With the power of these new tools, we can increase the efficiency of our operations while better serving the business purpose.
Key Individuals Involved
Successful GRC management requires the collaborative efforts of diverse roles, with clear and distinct, yet overlapping responsibilities.
The Chief Risk Officer (CRO) focuses on identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks, while the Chief Compliance Officer (CCO) ensures adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
GRC governance boards govern these efforts, holding them accountable to the organization’s mission and values.
Cross-functional teams, which include IT, legal, and operations, are crucial in executing GRC strategies.
Their collaboration guarantees the most holistic approach, addressing risks from all angles.
Transparent and ongoing communication between these stakeholders is essential, allowing for efficient adaptation and prompt decision-making.
The IT team is proactive about flagging any cybersecurity risk.
Simultaneously, the legal team ensures data practices are compliant with key regional laws such as GDPR.
GRC Framework Explained
A well-formed GRC framework is the foundation to effectively and efficiently govern, risk, and compliance.
It usually consists of policies, controls and automated tools meant to mitigate individual risks and regulatory obligations.
Ensuring this framework aligns with organizational goals makes sure that it feeds into higher-level business priorities and doesn’t exist separately.
Some best practices for implementing GRC frameworks are engaging stakeholders from the beginning, establishing clear roles, and using integrated GRC software.
These tools essentially centralize policies, procedures, and risks, allowing stakeholders to quickly and easily access information necessary to make critical decisions.
Conducting regular reviews and updates should be a priority, making certain the framework adapts alongside shifting regulations and market conditions.
Assessing GRC Maturity Level
GRC maturity levels measure how effectively an organization manages governance, risk, and compliance.
Assessing these levels involves evaluating processes, tools, and stakeholder engagement.
Benchmarking against industry standards helps identify gaps, such as lack of automation or fragmented data management.
Integrated GRC software, powered by AI, simplifies assessments by automating workflows and analyzing vast datasets.
This reduces manual errors and provides actionable insights, enabling organizations to continuously refine their GRC capabilities and stay ahead of compliance risks.
87% of executives consider reputational risk a top concern for their business, highlighting the importance of effective GRC strategies.
GRC Capability Model Overview
OCEG created the GRC Capability Model as a standardized compass for effective GRC.
This comprehensive framework enables organizations to evaluate and improve their Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) practices, ensuring compliance risk management approaches are robust.
By providing a consistent framework to organize, manage, and measure these key elements, the model fosters effective risk management processes that help organizations achieve their business goals.
The model’s top-level concept is “Principled Performance,” which aids organizations in attaining their objectives while promoting strong, ethical, and prudent governance practices.
This focus on corporate governance is essential for maintaining trust management within the organization, furthering the generation and preservation of organizational value.
The most recent version, the GRC Capability Model 3.5, clarifies these ideas and equips organizations with a centralized tool to address GRC requirements.
This allows them to sidestep pitfalls associated with disconnected systems and varying data structures, ultimately enhancing their risk management practices.
Learn and Understand
Educating your workforce is the most important first step in establishing a strong GRC strategy.
Given that employees are the front line of any organization’s compliance and risk management efforts, educating employees is key.
Training initiatives that are specifically designed to cover the fundamental governance, risk, and compliance concepts go a long way in developing a well-versed GRC-focused workforce.
For instance, periodic workshops or e-learning modules on topics like ethical AI or data protection regulations can empower employees to make informed decisions.
More than just providing training, knowledge sharing helps to develop a culture of compliance and accountability.
Sharing case studies of successful GRC practices within the organization can highlight the importance of aligning individual actions with broader objectives.
Continuous learning opportunities, such as certifications in data privacy or cybersecurity, ensure your team remains updated on evolving standards, further strengthening your GRC foundation.
Align Objectives
Aligning GRC initiatives with your business objectives ensures relevance and effectiveness. Stakeholder involvement is crucial here.
Engaging leaders from diverse departments fosters shared ownership of GRC goals.
For example, aligning risk assessments with strategic growth initiatives can help mitigate potential disruptions.
Routine reviews of these objectives ensure that they remain relevant to and in line with your ever-changing business landscape.
When precise ideas flow from team to team, everyone knows what they need to do to help meet these objectives, reducing cracks in execution.
A regular alignment process goes beyond compliance and really improves their overall operational efficiency and decision making.
Execute and Perform
A structured approach is key to successfully adopting GRC initiatives.
Establishing specific performance indicators, like times to address compliance violations or how well the agency is mitigating top risks, provides a way to track advancement.
Accountability is essential. Accessing accountability at all levels—through role specificity and assigning responsibilities—ensures everyone’s job gets done.
These feedback loops deliver improved insights and help you fine-tune your GRC processes.
We do post-incident reviews to find missing gaps in our processes.
They push for needed improvements and strengthen a culture of proactive governance and risk management.

Essential Elements of GRC Governance
A mature, comprehensive Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) framework is the bedrock of organizational integrity and productivity.
It weaves together governance policies, compliance standards, and risk management into a singular, focused strategy that keeps organizations aligned with business objectives.
By overcoming uncertainty and encouraging accountability, a robust GRC program empowers organizations to accomplish their goals and operate with integrity.
Here, we explore the core GRC governance essentials that are foundational for strong GRC governance.
1. Define Clear Objectives
Setting holistic and clear objectives governs the success of any GRC – or any initiative, for that matter.
Objectives should meet the SMART criteria—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
This process makes it so that goals are both measurable and meaningful, creating a clear outline of priorities.
For example, take an organization that needs to improve its compliance monitoring efforts.
Or, they could set a goal to decrease the number of audit nonconformities by 20% in a year.
Well-defined goals help to inform decisions and prioritize resources.
Teams can prioritize tasks effectively, ensuring alignment with organizational priorities and stakeholder expectations.
Just as important as these approvals are regular reviews of these objectives.
As landscapes change, goals need to be updated to continue to be a measure of success, a natural evolution with changing market dynamics, regulatory environments, or company strategy.
2. Evaluate Current Processes
This first step of evaluating what processes are currently in place is essential to pinpointing areas of inefficiency or gap.
For example, a clunky compliance monitoring regime can result in non-deadlines or mis-filings on regulatory reports.
Every voice is crucial in this evaluation, with stakeholders providing critical context as to what is working or not working in practice.
Strategic continuous improvement initiatives should naturally flow out through these evaluations.
Organizations may need to reengineer processes, implement automation, or leverage more sophisticated tools to fill gaps found.
This is integral to making sure processes continue to adapt to new challenges and opportunities as they arise.
3. Secure Leadership Commitment
Leadership commitment is pivotal in driving GRC efforts. Senior leaders set the tone, fostering a culture of compliance and accountability.
Securing buy-in often involves connecting GRC initiatives to business value—for example, demonstrating how improved risk assessment can enhance operational resilience and safeguard reputations.
Strong leadership backing encourages frequent updates and open dialogue between senior management and their GRC teams.
Making this connection keeps everyone aligned and underscores the importance of their efforts.
Citigroup has faced ongoing challenges in addressing regulatory issues due to inadequately trained employees in risk, compliance, and data roles, underscoring the importance of skilled personnel in GRC functions.
Overcoming GRC Implementation Hurdles
Understanding and overcoming these hurdles is critically important for organizations seeking to implement Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC).
By addressing these concerns proactively, you’ll set the stage for a successful adoption.
By focusing on change management, data integrity, ethical practices, and transparent communication, businesses can create a robust foundation for their GRC initiatives.
Managing Organizational Change
Organizational change management is the bedrock of successful GRC implementation.
If you don’t plan for it, resistance to change can be a major hurdle.
When you clearly communicate the purpose, benefits, and anticipated impact of GRC initiatives to all stakeholders, you foster understanding and alignment right from the start.
Building trust through communication is essential.
Clear and consistent messaging go a long way in understanding what’s uncertain and what is not.
For example, demonstrating how GRC will make compliance easier and risk more visible will show staff members how it directly benefits their daily work.
Allowing employees to be part of the change process improves engagement and buy-in to new processes and workflows.
Cross-departmental participation ensures diverse perspectives are accounted for, allowing more complete risk identification and mitigation efforts.
Offering comprehensive resources like training sessions, workshops, and specialized support channels prepares teams to pivot and implement changes seamlessly.
These precautions, along with reasonable timelines, avoid a rushed implementation and help win the long-term success of the initiative.
Ensuring Data Integrity
Data integrity is the cornerstone of successful GRC implementation because informed decisions must be based on precise, trustworthy information.
Creating data governance standards promotes uniformity and minimizes mistakes or oversights.
Conducting normalcy audits on a quarterly basis is an effective way to control data quality and catch discrepancies before they cause an issue.
Effective use of technology increases the potential of data through efficient collection, storage, and analysis capabilities.
Solutions that harness the power of real-time analytics and automated validation processes greatly reduce the potential for manual error while providing more actionable insights.
Implementing audit trails provides accountability and transparency, which is vital for compliance within regulated industries such as healthcare and finance.
Fostering an Ethical Environment
Ethical culture underpins GRC by ensuring that organizational behavior is in tune with compliance objectives.
Annual ethics training, along with well-defined policies, cultivates accountability and strengthens the culture of ethics required at all levels.
Cultural leadership is critical because when leaders model ethical decision-making, it creates a precedent throughout the organization.
When organizations create an environment for thoughtful conversations about ethical challenges, they build trust and transparency—key ingredients for sustained compliance.
Promoting Transparent Communication
Consistent and transparent communication connects all stakeholders and helps avoid misalignment with GRC initiatives.
Frequent updates, like monthly status reports, ensure stakeholders have clear visibility into both the achievements and hurdles encountered on the journey.
Creating clear pathways and innovative feedback mechanisms, such as anonymous surveys, foster a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.
Continuous, open dialogue creates a shared sense of purpose and direction, empowering the organization to proactively adjust to developing regulations and risks.
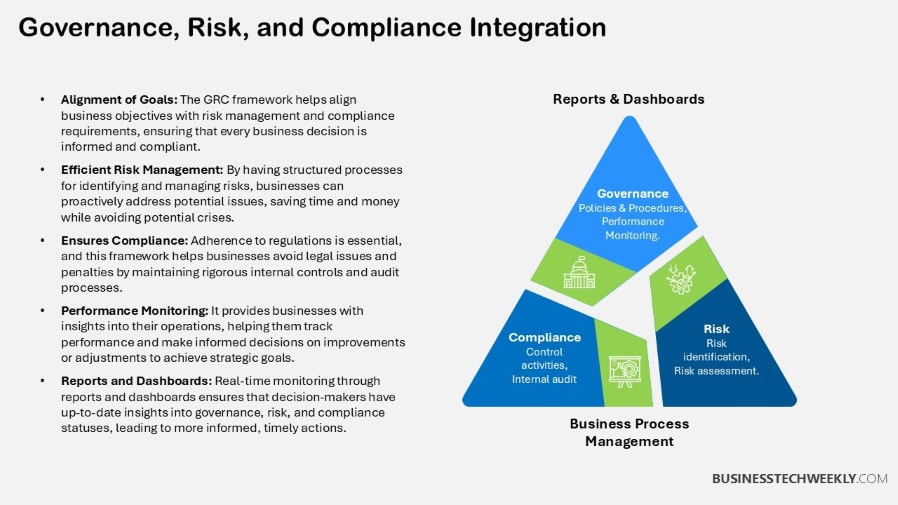
Technology’s Role in GRC
Technology has changed the Governance, Risk Management and Compliance (GRC) landscape.
Today, businesses have the tools to manage all of these essential functions in a more integrated and productive manner.
By leveraging unified platforms, technology enables organizations to consolidate core GRC processes, reducing complexity and aligning operations with their strategic objectives.
This transformation is redefining operational efficiency and more importantly, enabling smarter decision-making with advanced analytics and real-time visibility.
Selecting GRC Software
Choosing the right GRC software is a pivotal step in modernizing your compliance processes.
It’s essential to start by identifying organizational needs, such as risk assessment requirements, reporting capabilities, and industry-specific compliance standards.
Key features to look for include automation capabilities, data visualization tools, and robust reporting functions.
User-friendliness and scalability are equally critical, ensuring the solution adapts as your organization grows.
Engaging key stakeholders, from IT teams to compliance officers, ensures the software aligns with both technical and operational expectations.
While the process may require time and resources, a well-chosen solution simplifies operations and eliminates inefficiencies from manual processes.
Managing User Access
Managing and monitoring access to GRC systems is crucial in protecting PII and other sensitive information.
Implementing role-based access controls (RBAC) allows you to assign permissions based on job responsibilities, reducing the risk of unauthorized activities.
By periodically reviewing user rights, organizations can ensure that they are implementing accurate policies and reducing the risk for potential policy violations.
Training employees on secure access practices, such as using strong passwords and recognizing phishing attempts, reinforces a culture of security.
Together, these measures protect your entire GRC ecosystem from being exposed to vulnerabilities.
Leveraging Security Information
Integrating security information into GRC processes strengthens your risk management framework.
By analyzing data from intrusion detection systems and vulnerability assessments, you can identify risks proactively.
This information supports compliance efforts by ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements.
Continuous monitoring and analysis provide actionable insights, enabling you to refine controls and address emerging threats effectively.
Automating Audit Processes
Automation greatly changes the audit process since it’s easier to collect the data needed for reporting.
Technologies that normalize and correlate control performance data make it possible to report with confidence.
Using automated systems mitigates the risk of human error, speeds up the preparation process, and improves the usefulness and reliability of findings.
Such insights naturally feed into GRC decision-making, generating ongoing improvement and operational resilience.
AI and Automation in GRC
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are revolutionizing GRC by enabling predictive risk assessments and real-time compliance tracking.
For instance, AI-powered tools analyze vast datasets to uncover patterns and anomalies, offering actionable insights.
Automation accelerates routine tasks, such as policy updates or incident reporting, freeing resources for strategic priorities.
Staying informed about emerging technologies ensures your GRC strategy remains innovative and adaptive.
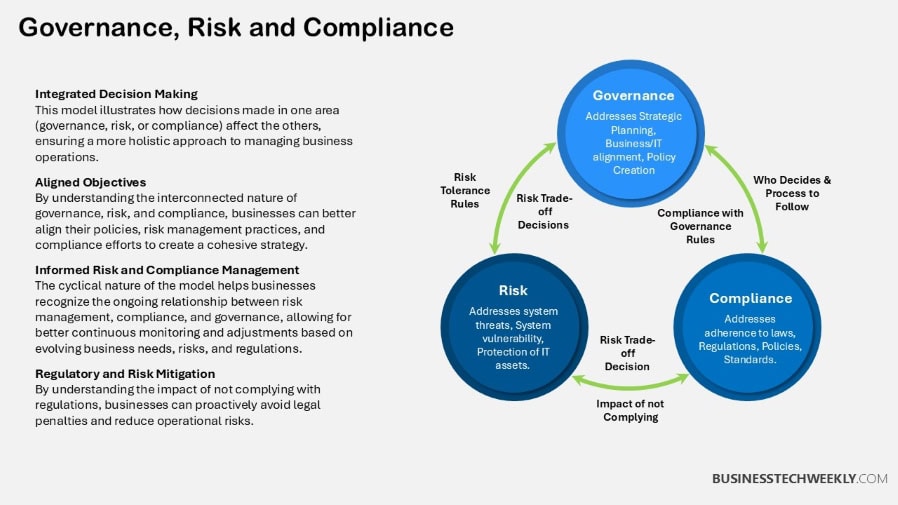
Measuring GRC Success
Measuring success for Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) initiatives is not just about collecting data – it’s about developing a system.
Define realistic metrics and targets. This enables organizations to measure their progress, improve resource allocation, and remain focused on their strategic goals.
By successfully leveraging this measurable data, businesses are held accountable, stakeholders are provided greater confidence, and opportunities for continuous improvement can be identified.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as crucial baseline measurements to assess progress on GRC compliance and performance.
Essential KPIs might include policy adherence rates, incident response times, and audit completion rates.
These metrics provide concrete measures of the completeness and effectiveness of governance frameworks and compliance requirements while supporting a strong risk management strategy.
For instance, measuring the number of required compliance audits completed within a specified time period emphasizes operational efficiency.
KPIs not only guide leadership’s strategic decisions but also enhance risk management practices by helping decision-makers understand where to allocate resources effectively.
If data reveals recurring compliance violations in a specific department, additional training or resources can be directed toward that area, ensuring compliance risk management is prioritized.
To ensure your KPIs yield valuable insights, they should align with your organizational goals.
A healthcare organization, for example, might focus on patient data protection measures to maintain compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
Regularly revisiting KPIs ensures they remain relevant, allowing them to adapt to changes in a company’s objectives or the evolving business environment.
Risk Reduction Metrics
Establishing and monitoring risk reduction metrics is critical in measuring the success of risk management controls across a GRC platform.
Primary metrics are the frequency of risk events and time to remediate known risk.
They measure, directly or indirectly, the decrease in financial losses resulting from these incidents.
An automated security solution that aggregates and correlates all security data can simplify this process significantly, providing one-click visibility into where organizations may be exposed.
Integrating these metrics into overall GRC evaluations allows organizations to identify patterns or gaps in their risk management processes.
For example, a retail company noticing repeated payment fraud instances can refine its cybersecurity measures.
Continuous improvement based on these metrics fosters resilience against emerging threats while reducing operational costs tied to incident investigations.
Compliance Adherence Rates
Compliance adherence rates are among the most important indicators of GRC success, showing the extent to which organizations comply with mandatory regulatory and optional internal policies.
By focusing on tracking compliance throughout each department, you create a sense of ownership and accountability.
For example, measuring the percentage of employees who complete mandatory training informs you where further reinforcement is necessary.
Consistent evaluations identify areas of weakness, making it possible to take action before threats arise.
Key Points to Consider
GRC provides an effective framework for organizing and prioritizing how you manage risks, address compliance requirements, and inform the strategic decisions your business makes today.
It brings together your objectives, obligations, and enabling tools into a coherent, comprehensive framework that preserves the delicate balance.
- Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) helps develop a unified structure of these disciplines. It helps in simplifying workflows, reducing risks, and ensuring compliance with laws and regulations. Given its collaborative nature, its cost is minimal and there’s no duplication of efforts.
- Governance provides a foundation for accountability and transparency, and that is what strengthens public trust. It creates a structured set of rules and procedures that shape decision-making while serving larger corporate objectives. We know that effective governance builds trust, which is essential for long-term success.
- Effective risk management, also known as governance risk management and compliance (GRC), is key to recognizing, managing, and countering risks that jeopardize organizational stability. Financial health and operational resilience are best protected by proactive and adaptive risk management strategies.
- Compliance has a different mission—protecting organizations from noncompliance with legal, regulatory, and internal policy requirements. Robust compliance measures prevent costly fines and damage to reputation while helping to establish an organizational commitment to integrity and ethical behavior.
- Effective integration between governance, risk management, and compliance fuels operational efficiency and effectiveness while supporting sustainable growth by aligning with organizational strategic objectives. Streamlining GRC under one umbrella provides sharper cybersecurity, increased accountability, and improved data-driven decision making on the enterprise level.
- Technology is a key enabler of GRC, automating workflows, improving data management and analytics, and streamlining compliance monitoring and reporting. By leveraging tools such as artificial intelligence and automation, organizations can achieve efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability that’s even more critical in today’s ever-changing regulatory landscape.

