Cybersecurity Compliance: An Executive Overview to Establishing a Cybersecurity Compliance Plan

With cyberattacks increasing in frequency and complexity, governments and agencies have introduced more stringent compliance requirements for cybersecurity. These regulations and conditions can vary depending on the location and industry, making it challenging for businesses to maintain cybersecurity compliance.
Data breaches and cyber threats are not just problems for the IT department of an organization. Such incidents can have severe effects across the company. It is vital that every employee manages cyber risks and stays compliant with the ever-evolving requirements for privacy and security.
On this page:
What is Cybersecurity Compliance?
Cybersecurity compliance is a broad term covering the implementation of risk-based controls to protect the security, availability, and integrity of stored, transferred, or processed data.
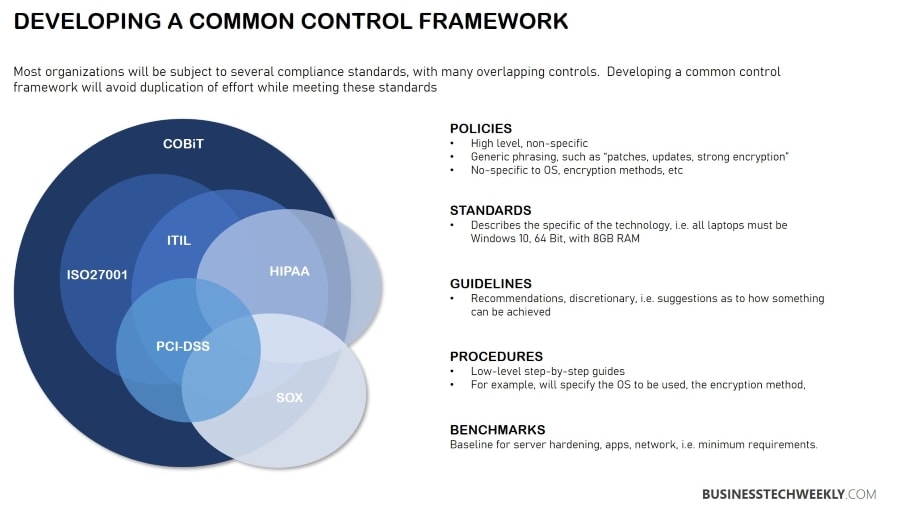
This type of compliance is generally not based on a specific standard or regulation. Instead, the requirements vary by sector and industry. Based on the business, different security standards can overlap, making it confusing and time-consuming at times.
Organizations will find that they are required to adhere to several different standards, regulations and requirements. For example, businesses operating in the healthcare industry should meet the HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability) compliance requirements. However, if the company also uses a POS device to accept payments, it must comply with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards – PCI DSS.
Moreover, the cybersecurity compliance environment undergoes a shift as requirements adopt a risk-based approach. Creating a comprehensive cybersecurity compliance program involves continuous risk management to identify and address all threats on time.
Benefits of Cybersecurity Compliance
Organizations subject to cybersecurity regulations imposed by the location or industry are required to comply with the law.
Companies that don’t meet the compliance face fines and penalties if they encounter a breach. Strict adherence to compliance requirements minimizes the risks of data breach and the costs associated with the response and recovery for such incidents and losses like business interruption, reputation damage, and reduced sales.
With a solid cybersecurity compliance program in place, companies can protect their reputation, earn consumer trust and build loyalty by ensuring customer data’s safety and security.
Moreover, having consistent systems for storage, processing, and managing sensitive information provides the business with several benefits, including improved operational efficiency.
Achieving Cybersecurity Compliance
Apart from protecting sensitive business data as required by law, meeting the requirements of cybersecurity compliance proves to be advantageous for organizations in many other ways.
By implementing proper security measures to protect sensitive employee and customer data, a company can improve its security posture. Thereby protecting intellectual property like product specs, software code, trade secrets, and other information, giving it a competitive edge in the market.
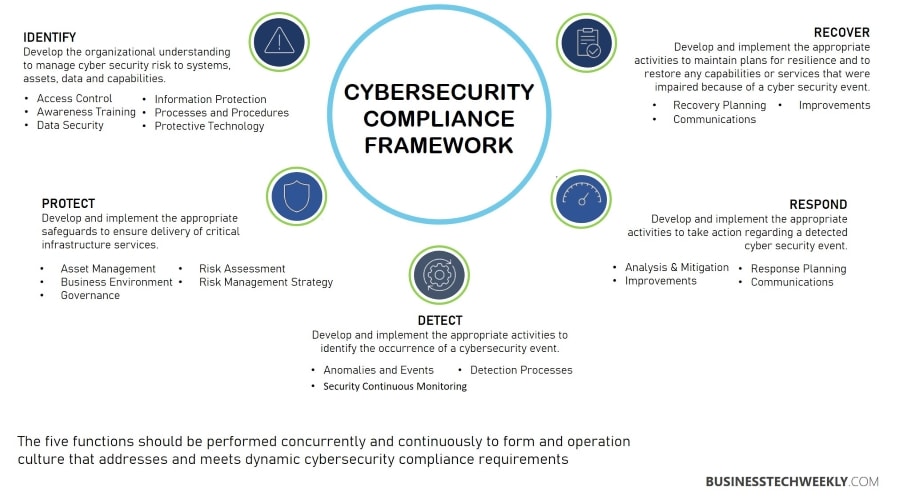
Let us look at some essential steps involved in building a robust cybersecurity compliance program.
Appoint a Cybersecurity Compliance Team
A compliance team is essential for every business, regardless of the size. A majority of the companies may be too small to hire external consultants to manage compliance. Nonetheless, it is a good idea to appoint a team of employees with the right knowledge of information security.
Assigning this task to an employee makes sure you receive regular updates about the status of your cybersecurity process and compliance efforts. It also makes it straightforward for other employees whom they should approach in case of a suspected incident.
Identify Data Assets and Requirements
it is necessary to identify which legislation and regulations you need to comply with. Every state in the country imposes laws concerning data breach notification that requires that businesses notify customers when their information is at risk. Requirements vary by state, and some others apply whether or not your business is located in a state.
Secondly, you must identify what type of data you store and process and the states, regions, and countries you operate in. Several regulations put additional controls on specific types of data. Personally Identifiable Information (PII) includes information that identifies individuals. Examples are:
- Address
- Date of birth
- Social security number
- First and last name
PHI (Protected Health Information) consists of information used to identify an individual and their medical details like:
- Prescription details
- Medical history
- Insurance records
- Admission information
- Medical appointments
Financial data contains information related to credit cards, payment methods, and others that could compromise an individual’s identity and finances.
For example, if stolen, a credit card number can be used to make an unauthorized purchase. Some of the examples of financial data include:
- Bank account number
- Social security numbers
- Credit ratings
- Debit card pin
Some other examples of sensitive data controlled under regulations include:
- Usernames, passwords, email addresses
- IP addresses
- Race, religion
- Voice prints, fingerprints, face recognition data

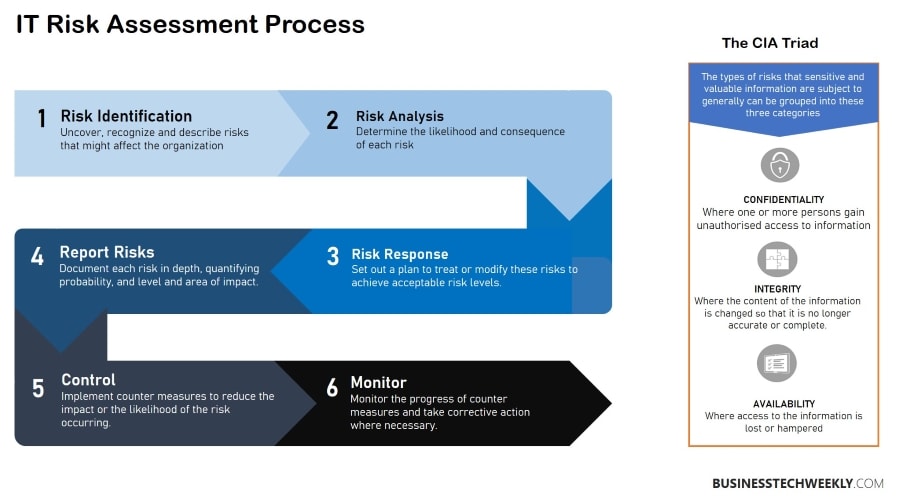
Conduct Risk Assessment
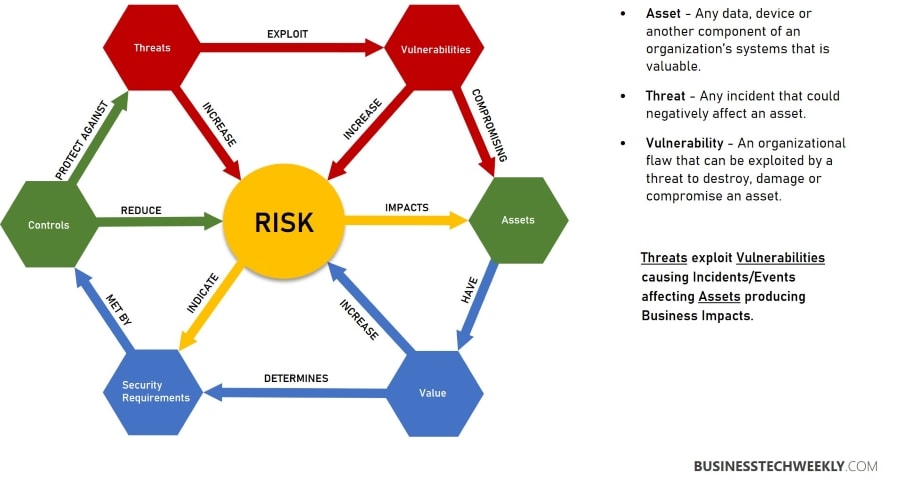
More and more cybersecurity regulations and standards focus on a risk-based approach which is why organizations, small and big, should adopt a risk and vulnerability assessment process. Risk analysis helps the business identify the most critical security flaws and the effectiveness of existing controls.
- Identify – Risk assessment starts with the identification of different data assets and information systems and networks.
- Assess – Next, review the risk level of different data types. This should involve determining where critical information is stored, collected, and transmitted and rating the risks accordingly.
- Analyze – Once assessed; you need to analyze the risk. The general formula used by organizations is: Risk = (chances of breach x impact) / cost
- Set Risk Tolerance – Once you analyze the risk, you can determine whether you should accept, refuse, transfer or mitigate the risk.
Implement Controls
The next step should be to implement controls based on your regulations and risk tolerance. Some of the best examples of technical controls include:
- Encryption
- Firewalls
- Log aggregation
- Anti-virus
- Vendor risk management
- Insurance
- Employee training
Create Policies
Policies are the foundation for internal and external compliance audits as they document all the controls and activities.
Technology alone cannot guarantee data security; non-technical process controls should be in place to protect internal and external risks. Here are some examples of such controls:
- Appointing a cybersecurity team
- Documenting policies and procedures
- Employee cybersecurity training
- Audit and accountability processes
- Assessing risk and vulnerability
Monitor and Review
Compliance requirements focus on how threats evolve. Cybercriminals always look for newer ways to compromise data security.
They may often use a combination of multiple software, which is challenging to identify and mitigate. This is why businesses should consider continuous monitoring, reviewing, and testing of their cybersecurity compliance controls.
Regular tests help ensure you always stay compliant and can successfully detect new threats as they emerge. It is good to evaluate compliance regularly as new requirements are introduced, and existing ones are modified.
Cybersecurity Compliance Best Practices
Cybersecurity compliance is not an easy task. Businesses face problems adhering to the standards and requirements concerning cybersecurity, as the landscape of cyber threats keeps evolving.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution to compliance management. Still, organizations can follow a few best practices to build a comprehensive compliance management program.
Encourage Communication on Cybersecurity Topics
Your company should have cybersecurity teams with big-picture awareness of the topic to encourage conversations. Even when an employee requires occasionally working on a computer, they should prioritize network security. Leaders should explain how valuable cybersecurity and compliance are for them. If they are focused on these goals, employees automatically value the importance of security compliance.
By making the topic a part of the conversation, organizations can foster a work culture of cybersecurity. Employees can better relate their roles with compliance and understand the significance of maintaining standards for the business. Let the people ask questions freely and share their suggestions and ideas about this topic.
Hire Cybersecurity Compliance Professionals
Enterprises with dedicated IT departments may have the resources to hire cybersecurity staff. Smaller businesses may not have that luxury. However, that does not mean they can’t hire a consultant to take care of different types of compliance the business is concerned with. Every business has to adhere to these standards, regardless of the size.
Schedule Regular Audits
Audits are one of the best proactive measures to prevent future risks. Keeping a regular check on your work and staying on top of problems means you can find vulnerabilities and weak points before attackers. When you identify flaws during internal audits, you can control the result, solve the issue, and improve the organization’s overall security posture.
Whether you find problems, it is a good idea to track your operation and cybersecurity requirements. Taking note of flaws and bugs is better than leaving it to third parties. The teams or consultants can quickly fix the issue and prevent cybercriminals from using it to damage the company’s capital and reputation.
Educate Staff on the benefits of Cybersecurity Compliance
Whether your cybersecurity compliance relies on an in-house team or a third-party consultant, make sure you have a robust plan in place and keep all the departments informed about the status. When you assign the task to a consultant, they improve the overall cybersecurity posture of the business.
Final Thoughts
The world gets more digital every day, and cybersecurity is not left unaffected. The increasing shift towards internet-based processes means that businesses should consider cybersecurity standards that ensure the safe and secure delivery of services to customers.
With the right set of tools, policies, and best practices, organizations across industries can guarantee compliance with changing cybersecurity standards and requirements.

